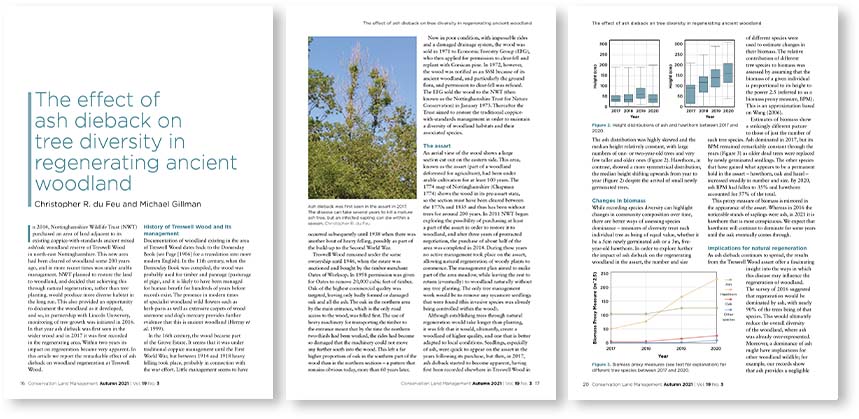
COP26, the 26th annual summit of the United Nations Climate Change Conference, has come to a close. This historic event ran from 31st October to 12th November and aimed to secure global net zero emission targets and keep the 1.5°C target within reach. It also discussed the need to adapt to protect communities and natural habitats, mobilising finance and working together to deliver key commitments. For more information on the lead up to this event, what net zero means and the 1.5°C agreement, read our blog: What is COP26 and Why is it Important? We also looked back on the first week of COP26 in our blog: Climate Challenges: COP26 First Week Update. In this article, we discuss an overview of the major outcomes of this event and how they might affect our efforts to combat climate change.

Key outcomes
A number of key pledges were launched and signed during COP26, including:
- 90% of the world’s economy now striving for net zero emissions, with many aiming for 2050.
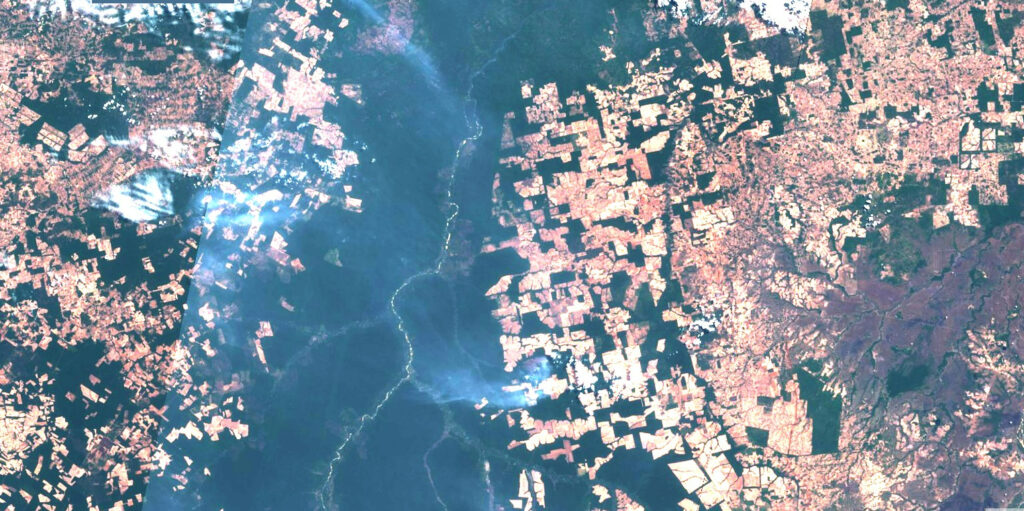
- The Glasgow Leader’s Declaration on Forest and Land Use intends to halt and reverse deforestation and land degradation by 2030, while also delivering sustainable development and promoting an inclusive rural transformation. This pledge has been signed by over 100 world leaders, covering around 85% of the world’s forests.
- More than 100 world leaders have signed the Global Methane Pledge, a U.S. and EU-led commitment to reduce methane emissions by 30% over the next decade from 2020 levels.
- The Breakthrough Agenda, a global initiative launched by the UK, aims to make clean technologies and sustainable solutions the most economical and appealing option for each emitting sector by 2030, with leaders committing to review progress annually, starting in 2022.
- The Coal Pledge, signed by more than 40 countries, aims for nations to move away from coal power by the 2030s for major economies and 2040s for developing countries.
- A $10.5 billion fund for emerging economies to switch to renewable energies will be supplied by the Global Alliance Group, a group of philanthropic foundations and international development banks. They intend to raise $100 billion in public and private capital.
- Around 450 financial organisations, with a combined market capitalisation of $130 trillion, have agreed to shift their investments away from financing fossil fuel-burning industries and toward “clean” technology.
- China and the U.S. have announced an agreement to work together to cut emissions and help the world stay within 1.5°C by cooperating on key areas, such as cutting emissions from transport, energy and industry.

Are they effective?
Many critics and climate experts are concerned that these pledges will not be enough to keep average global temperatures below 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. There are calls for global leaders to do more to meet this goal, as exceeding it will see a worsening in the negative impacts of climate change, potentially putting millions of lives and livelihoods at risk. With countries such as Russia, China, India and Australia refusing to sign the methane pledge, and others, such as the U.S. and China, not signing the coal pledge, it is unclear how successful these agreements will be at tackling climate change. Despite signing the deforestation pledge, Indonesia has stated that it will not halt its developmental growth, which involves cutting forests for new roads and the cultivation of food crops. According to a spokesperson for UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson, this pledge does not forbid the cutting down of forests, but rather seeks to end net deforestation – forest loss must be “replaced sustainably”.
Replacing primary forest with new growth has a variety of negative environmental consequences. Primary, undisturbed, ancient forests are often highly complex ecosystems that support a variety of species, including many specialist species, and have an irreplaceable value. New-growth or secondary forest are less able to support the same level of biodiversity, as they may have significant differences in forest structure and species composition. Abiotic factors can vary during development, reducing the area’s suitability for the previous ecosystem. After a major disturbance, it can take decades for an area to develop into a climax community, such as a forest, through ecological succession. During many of these stages, many of the species that previously inhabited the primary forest will be unable to survive, and the community will most likely be made up of more disturbance-tolerant, generalist species that are often of lower conservation concern.
Once the stable climax habitat has developed, even if the new habitat is similar, the community structure may differ dramatically from the original. Certain plant or wildlife species may have been unable to re-establish due to the presence of new species or a reduction in resources, potentially leading to localised extinctions. It is unknown how long it takes for a secondary forest to develop the levels of biodiversity found in primary forests, but it could be several hundred years. Therefore, this form of “sustainable” deforestation might still result in extinctions and reduced biodiversity. These new-growth regions may be far less ecologically valuable than primary forest and, during much of the successional period, store significantly less carbon.
A deforestation policy that focuses on net deforestation rather than halting or severely limiting all deforestation, could potentially help to reduce world carbon emissions by stabilising, or even increasing global forest cover, but this does not address the whole picture. This policy allows for the continued negative ecological impacts of deforestation on biodiversity and vulnerable species, which could ultimately lead to countless extinctions.

Glasgow Climate Pact
Only effective implementation of pledges and tangible action, much of which has not been seen following previous promises of past summits, can ensure the success of COP26. The Glasgow Climate Pact is the agreement reached at COP26 and the first deal ever to explicitly plan to reduce coal. This document initially aimed to clarify and build on the Paris Agreement, proposing that countries agree to accelerate the phasing out of fossil fuels and for developed countries to double their climate finance commitments for funding adaptation. However, many demonstrators throughout the two-week event have called for bolder commitments and stricter accountability to combat climate change, followed by appropriate and effective action.
The first draft of the document was criticised for a variety of reasons, including a lack of financial aid for developing nations and the need for clearer commitments to force countries to increase their emissions cuts. The second draft retained the core demand to return to the negotiating table next year to improve countries’ national emission reduction plans, but included even softer language. COP26 President Alok Sharma stated he was “deeply sorry”, as this final deal shifted from requiring countries to “phase out” coal to “phase down”, a change that has disappointed some. Many now look to the meeting next year that may see further pledges to cut emissions to reach the 1.5°C goal, as an analysis showed that the world is on track for a 2.4°C rise, despite these new pledges.

References and useful resources
A news report on the countries that are now aiming for net zero: https://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2021-11-01-80-world-economy-now-aiming-net-zero-not-all-pledges-are-equal
The COP26 website information on the Glasgow Leader’s declaration on forests and land use: https://ukcop26.org/glasgow-leaders-declaration-on-forests-and-land-use/
A news report on the COP26 deforestation pledge: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-59088498
The UK Government’s Press release on the new Breakthrough Agenda: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/world-leaders-join-uks-glasgow-breakthroughs-to-speed-up-affordable-clean-tech-worldwide
The New York Times report of the Global Energy Alliance: https://www.nytimes.com/2021/11/03/world/europe/global-energy-alliance-fund-cop26.html
The Guardian news report on the Coal Pledge and its criticisms: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2021/nov/03/more-than-40-countries-agree-to-phase-out-coal-fired-power
Indonesia believes the pledge is unfair: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/nov/05/indonesia-says-cop26-zero-deforestation-pledge-it-signed unfairhttps://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/
Stages of Ecological Succession: https://sciencing.com/stages-ecological-succession-8324279.html
Barlow, J. et al. 2007. Quantifying the biodiversity value of tropical primary, secondary, and plantation forests. PNAS 104(47): 18555-18560. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0703333104
A news report on China and the US’ plan to work together on cutting emissions: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2021/nov/10/china-and-the-us-announce-plan-to-work-together-on-cutting-emissions
A news report detailing the criticism of the first Cop26 draft: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2021/nov/10/cop26-draft-calls-for-tougher-emissions-pledges-by-next-year
The draft document, published on 12 November 2021: https://unfccc.int/documents/310987
A news report on the Glasgow Climate Pact: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-59277788
A new report on Climate Action Tracker’s analysis of the potential 2.4°C in global average temperatures: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2021/nov/09/cop26-sets-course-for-disastrous-heating-of-more-than-24c-says-key-report