 **** A long overdue recognition of the female wolf
**** A long overdue recognition of the female wolf
The wolves reintroduced to Yellowstone National Park in 1995 are some of the best-studied mammals on the planet. Biological technician and park ranger Rick McIntyre has spent over two decades scrutinising their daily lives, venturing into the park every single day. Where his previous books focused on three notable alpha males, it is ultimately the females that call the shots and make the decisions with lasting consequences. This book is a long overdue recognition of the female wolf and continues this multigenerational saga.
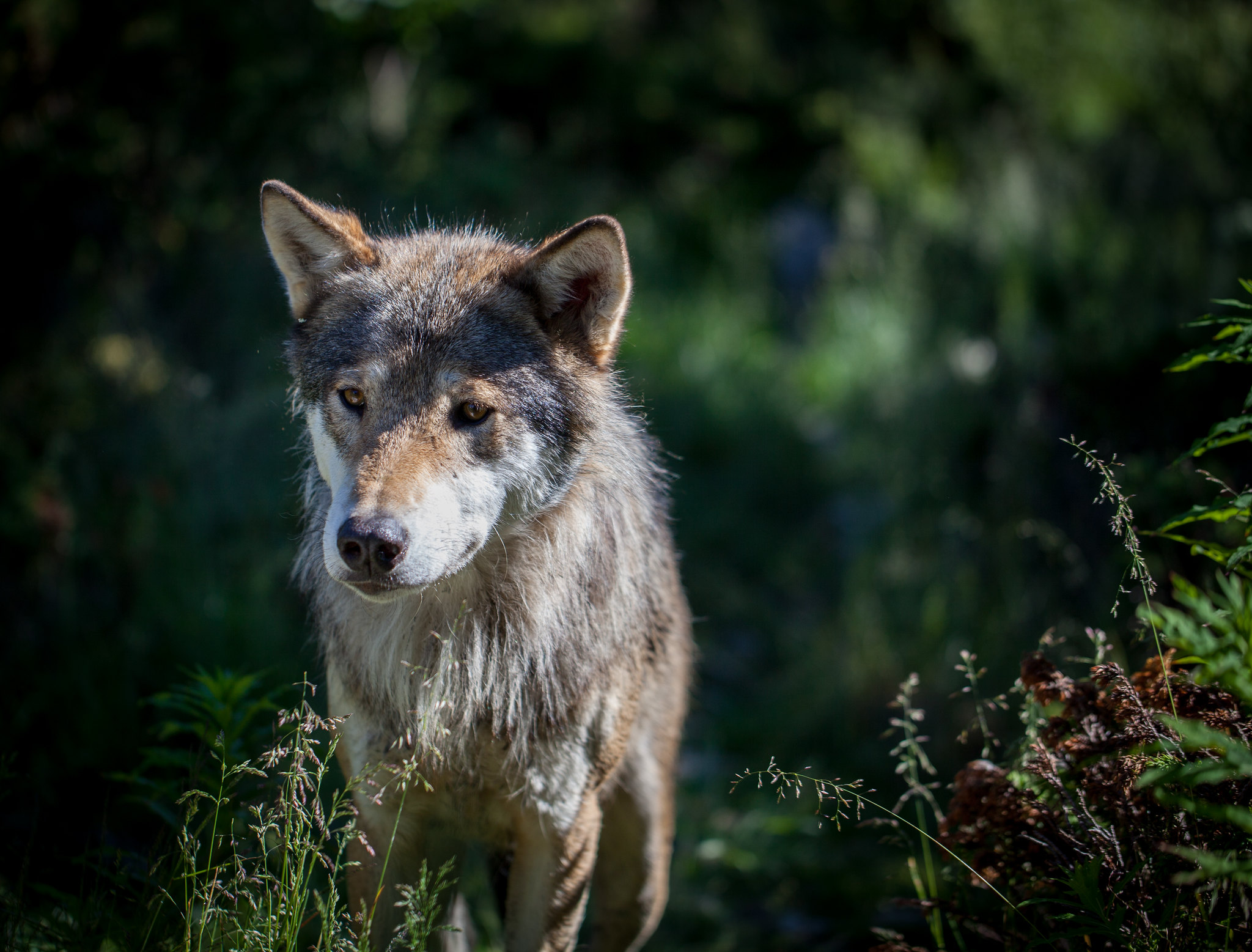
If wolf 21, the subject of the second book, was the most famous male wolf in Yellowstone, then his granddaughter 06 (named after her year of birth, 2006) can safely be called the most famous female wolf. This fourth book picks up where the third book ended, covering the period 2009–2015. It tells 06’s life story, her untimely death, and the fate of one of her daughters. To refreshen your mind, some prefatory sections give a brief list of notable matriarchs through the years and a short history of the Druid Peak pack, which were the ancestors of 06.
The fact that wolves have unique characters is again confirmed here: 06 is a gorgeous wolf that has many suitors but, until age four, she rejects them all and is a rare example of a lone female wolf. Lone wolves, quite rare to begin with, are usually males in search of a new pack with unrelated females. In 2010 she forms the Lamar Canyon pack with two brothers younger than her: 754 and 755. Three successful years follow in which she has a litter of pups every year. Through a combination of fearlessness and wise choices, all pups survive their first year. A particular challenge is the nearby Mollie’s pack, led by an aggressive female, that starts making incursions into 06’s territory. There is a long-running feud between the Mollie’s and the very successful Druid Peak pack and its descendants, which can be traced back to 1996 when Druids killed several wolves of Mollie’s pack.

This book has the task of both continuing the story but also looking back. Several chapters end with boxes that briefly tell the story of other notable female wolves past and present. If you have read all or some of the previous trilogy, you know that the writing might not win prizes for its style. Instead, McIntyre distils thousands of days spent in the field and as many pages of notes into a deeply informed, unembellished eyewitness account of the daily lives of these wolves. He always clearly indicates where he reconstructs likely events not observed first-hand or imagines the inner lives of the wolves. As before, The Alpha Female Wolf is divided into parts that each cover a year, usually subdivided into several chapters. This time there are unfortunately no family trees included, which I would have found helpful, though the cast of characters remains manageable.
My impression is that this book contains more references to scientific research than the previous ones. There are observations on chronic wasting disease, contagious to elk, and how wolves are likely limiting its spread by selectively killing sick elk. McIntyre asks a wolf geneticist just how different the introduced wolves from Canada are from the original wolves that lived in this area, and gives some deeper insights into the genetic history of US wolf populations. And he speaks to two researchers studying wolf howling and how each individual produces unique harmonic overtones by which the wolves might recognize each other, to which McIntyre contributes some informal observations later in the book. There are also numerous interesting behavioural and natural history observations. Food features in particular, with chance observations of wolves feeding on eggs of ground-nesting birds, fruit from a rosebush, and the occasional beaver. McIntyre observes hunting sequences that show the wolves using the local terrain to their advantage.
McIntyre is on form in the first two-thirds of the book, detailing how 06’s fierceness and intelligence help her not only to survive but to thrive. She carefully chooses her partners to form a strong, cooperative team, while her choice of denning site under a natural rockfall provides superior protection from a raid by the Mollie’s pack. At various points in the book, McIntyre highlights how the actions and choices of 06 and others show the important role of alpha females in shaping pack life and pack dynamics in the park. Inspired by the many military veterans that visit Yellowstone, he draws a human parallel, describing the alpha female as a commanding officer while the alpha male is an executive officer carrying out her agenda.
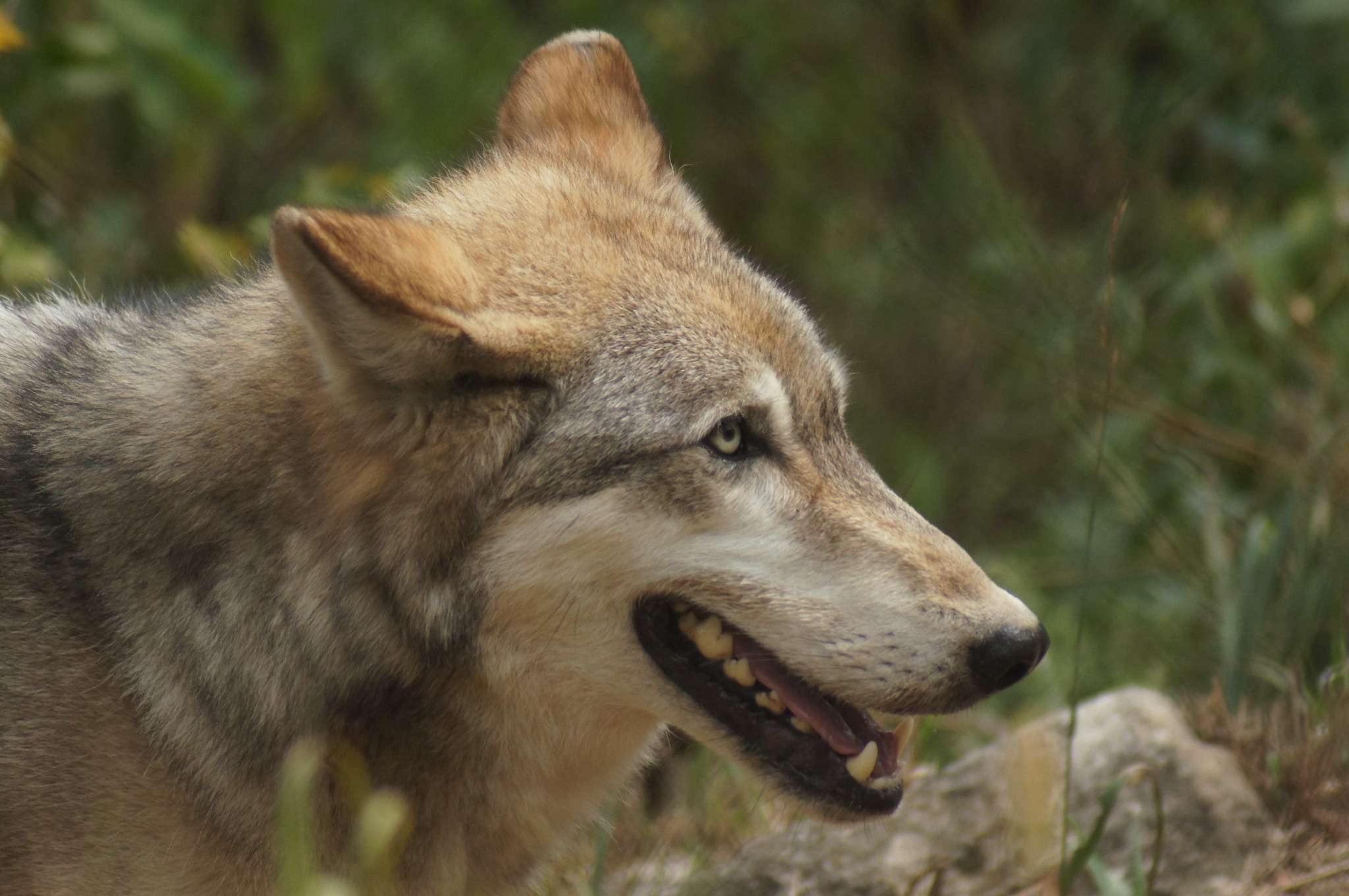

How cruel, then, is the sudden death of first 754 and then 06 when they venture just outside park boundaries and are shot, legally, by hunters. I have to admit that I found this twist of fate really upsetting to read. Both McIntyre and the book never really recover from the blow. While the first three years (2010–2012) take up two-thirds of the book, the next three years (2013–2015) are covered in the remaining one-third. McIntyre commits himself to documenting the fall-out of these killings, which sees 755 go through several failed attempts at establishing a new family, and follows the fate of one of 06’s daughters, 926. Although there are happy endings of a sort, the lives of both these survivors are shot through with hardship and loss. Where the threat of hunting was only theoretical in the previous book, here it becomes reality with the removal of wolves from the endangered species list. Remarkably, even though the events have an emotional impact on both him and other wolf biologists and spotters, McIntyre continues to refrain from voicing his opinion or discussing in any depth the reasons for, and problems with, the hunting of wolves. He hints at the why of this when talking to a group of schoolchildren: “being a National Park Service employee in uniform, I could not voice a political opinion about wolf-hunting regulations outside the park” (p. 233). There is much here that remains unsaid, and Nate Blakeslee’s book The Wolf offers an outsider’s perspective on the whole situation that is well worth reading.
Ecologists know how important long-term research is, but also both how hard and rare it is. McIntyre’s decades-long commitment to observing the Yellowstone wolves, and then turning these into books for the general public, is commendable. The Alpha Female Wolf succeeds in both celebrating 06’s remarkably successful life and in indicating the important role of the female of this species. In a conversation with McIntyre last year, he mentioned one more book is planned that will cover events up to 2021. There are yet more stories to be told about these iconic animals and I am looking forward to immersing myself one more time in their lives.














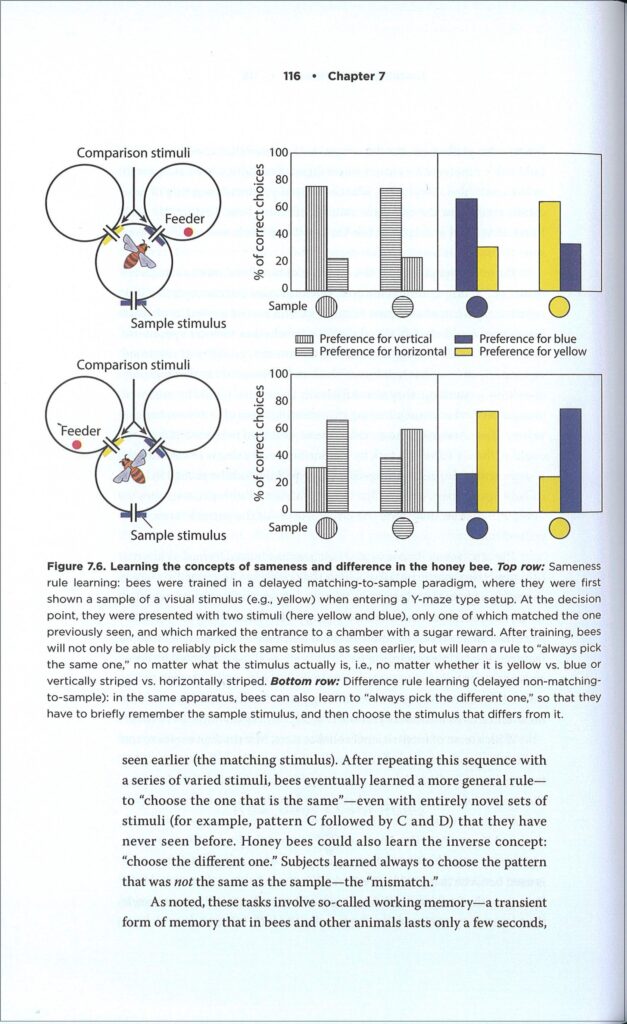 Justifiably, the book opens with sensory biology. Before we understand what is in the mind of any organism, Chittka argues, we first need to understand the gateways, the sense organs, through which information from the outside world is filtered. These are shaped by both evolutionary history and daily life (i.e. what information matters on a day-to-day basis and what can be safely ignored). Chapter 2 deals with the historical research that showed that bees do have colour vision and furthermore can perceive ultraviolet (UV) light. Chapter 3 bundles together research on numerous other senses, including ones familiar (smell, taste, and hearing) and unfamiliar to us (perception of polarised light, Earth’s magnetic field, and electric fields). The antennae of bees, in particular, are marvels; Chittka likens them to a biological Swiss army knife, packing numerous different sense organs into two small appendages. Tightly connected to sensory biology is how this incoming information is processed in the brain, though Chittka postpones discussing neurobiology to chapter 9. He describes the discovery and function of different brain areas and highlights the work of Frederick Kenyon who would inspire the better-remembered Santiago Ramón y Cajal. Thanks to them, we now understand that brains consist of numerous specialised nerve cells. Though the bee brain is small, Chittka argues that size is a poor predictor of cognitive skills; it is the wiring of neurons that matters. Rather than be surprised that small-brained insects such as bees can do so many clever things, Chittka instead tickles the reader with the opposite question: “Why does any animal need as large a brain as a bee’s?” (p. 153).
Justifiably, the book opens with sensory biology. Before we understand what is in the mind of any organism, Chittka argues, we first need to understand the gateways, the sense organs, through which information from the outside world is filtered. These are shaped by both evolutionary history and daily life (i.e. what information matters on a day-to-day basis and what can be safely ignored). Chapter 2 deals with the historical research that showed that bees do have colour vision and furthermore can perceive ultraviolet (UV) light. Chapter 3 bundles together research on numerous other senses, including ones familiar (smell, taste, and hearing) and unfamiliar to us (perception of polarised light, Earth’s magnetic field, and electric fields). The antennae of bees, in particular, are marvels; Chittka likens them to a biological Swiss army knife, packing numerous different sense organs into two small appendages. Tightly connected to sensory biology is how this incoming information is processed in the brain, though Chittka postpones discussing neurobiology to chapter 9. He describes the discovery and function of different brain areas and highlights the work of Frederick Kenyon who would inspire the better-remembered Santiago Ramón y Cajal. Thanks to them, we now understand that brains consist of numerous specialised nerve cells. Though the bee brain is small, Chittka argues that size is a poor predictor of cognitive skills; it is the wiring of neurons that matters. Rather than be surprised that small-brained insects such as bees can do so many clever things, Chittka instead tickles the reader with the opposite question: “Why does any animal need as large a brain as a bee’s?” (p. 153). What clever things do bees do, you ask? That is the subject of the preceding five chapters where Chittka surveys a large body of behavioural research. Honey bees are famous for their waggle dance by which they communicate the location of flowers but also, this was news to me, the location of potential nest sites when the swarm relocates. But Chittka discusses more, much more: how bees navigate space using landmarks, show a rudimentary form of counting, solve the travelling salesman problem, learn to extract nectar from complex flowers, learn when to exploit certain flowers (and when to ignore them), and learn new tricks by observing other bees. But what about instinct, something most behaviours were traditionally ascribed to? He has some insightful comments on this: “even the most elemental behavior routines need to be refined by learning: instinct provides little more than a rough template” (p. 50). What really made me fall off my chair is that bees have long been outsmarting researchers in choice experiments. Many behavioural experiments take the form of choice tests, where bees need to pick between two locations or objects that differ in e.g. colour or shape with one option containing a sugary solution as a reward. Bumblebees would simply be lazy and check out both options in random order. Until, that is, protocols were modified by adding a bitter-tasting solution to the wrong choice as a penalty.
What clever things do bees do, you ask? That is the subject of the preceding five chapters where Chittka surveys a large body of behavioural research. Honey bees are famous for their waggle dance by which they communicate the location of flowers but also, this was news to me, the location of potential nest sites when the swarm relocates. But Chittka discusses more, much more: how bees navigate space using landmarks, show a rudimentary form of counting, solve the travelling salesman problem, learn to extract nectar from complex flowers, learn when to exploit certain flowers (and when to ignore them), and learn new tricks by observing other bees. But what about instinct, something most behaviours were traditionally ascribed to? He has some insightful comments on this: “even the most elemental behavior routines need to be refined by learning: instinct provides little more than a rough template” (p. 50). What really made me fall off my chair is that bees have long been outsmarting researchers in choice experiments. Many behavioural experiments take the form of choice tests, where bees need to pick between two locations or objects that differ in e.g. colour or shape with one option containing a sugary solution as a reward. Bumblebees would simply be lazy and check out both options in random order. Until, that is, protocols were modified by adding a bitter-tasting solution to the wrong choice as a penalty.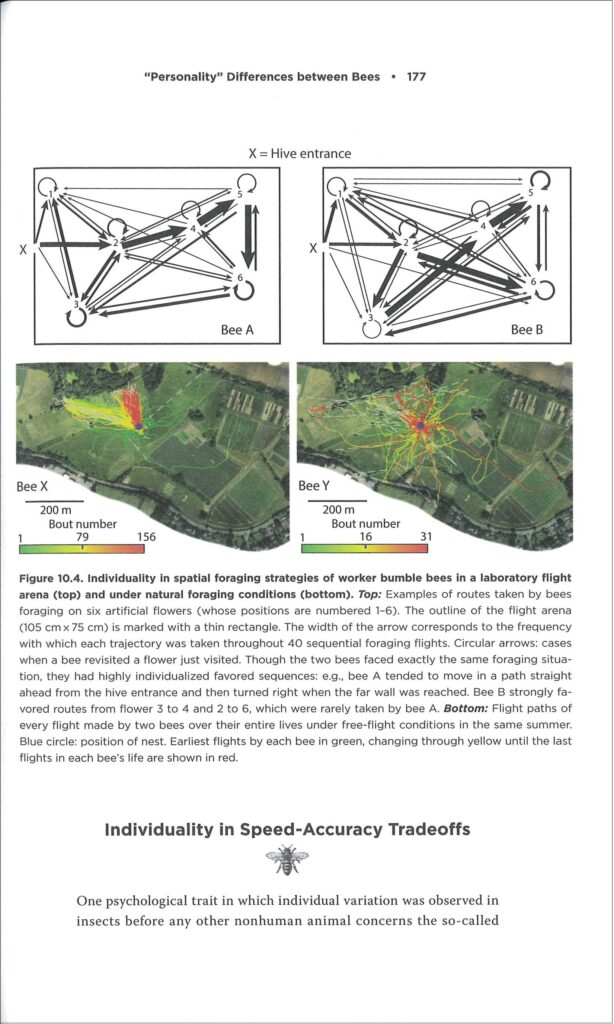 As mentioned above, this book is focused. If you enjoy reading about the facts and the study system with minimal (autobiographical) diversions, Chittka has got you covered. The only digression he allows himself is to include biographical details of older generations of scientists. This includes inspiring tales such as Karl von Frisch who described the honey bee waggle dance and later barely escaped being dismissed from his post by the Nazis. And look out for repeat appearances of Charles Turner, a now largely forgotten African American scientist who published pioneering work despite having been denied a professorship based on his ethnicity. But there are also tragic stories such as Kenyon’s, who snapped under pressure of not securing a permanent job and was incarcerated in a lunatic asylum where he died more than 40 years later, alone and forgotten. Chittka includes occasional quotations from historical literature to show that “many seemingly contemporary ideas about the minds of bees had already been expressed, in some form, over a century ago” (p. 15).
As mentioned above, this book is focused. If you enjoy reading about the facts and the study system with minimal (autobiographical) diversions, Chittka has got you covered. The only digression he allows himself is to include biographical details of older generations of scientists. This includes inspiring tales such as Karl von Frisch who described the honey bee waggle dance and later barely escaped being dismissed from his post by the Nazis. And look out for repeat appearances of Charles Turner, a now largely forgotten African American scientist who published pioneering work despite having been denied a professorship based on his ethnicity. But there are also tragic stories such as Kenyon’s, who snapped under pressure of not securing a permanent job and was incarcerated in a lunatic asylum where he died more than 40 years later, alone and forgotten. Chittka includes occasional quotations from historical literature to show that “many seemingly contemporary ideas about the minds of bees had already been expressed, in some form, over a century ago” (p. 15).
































