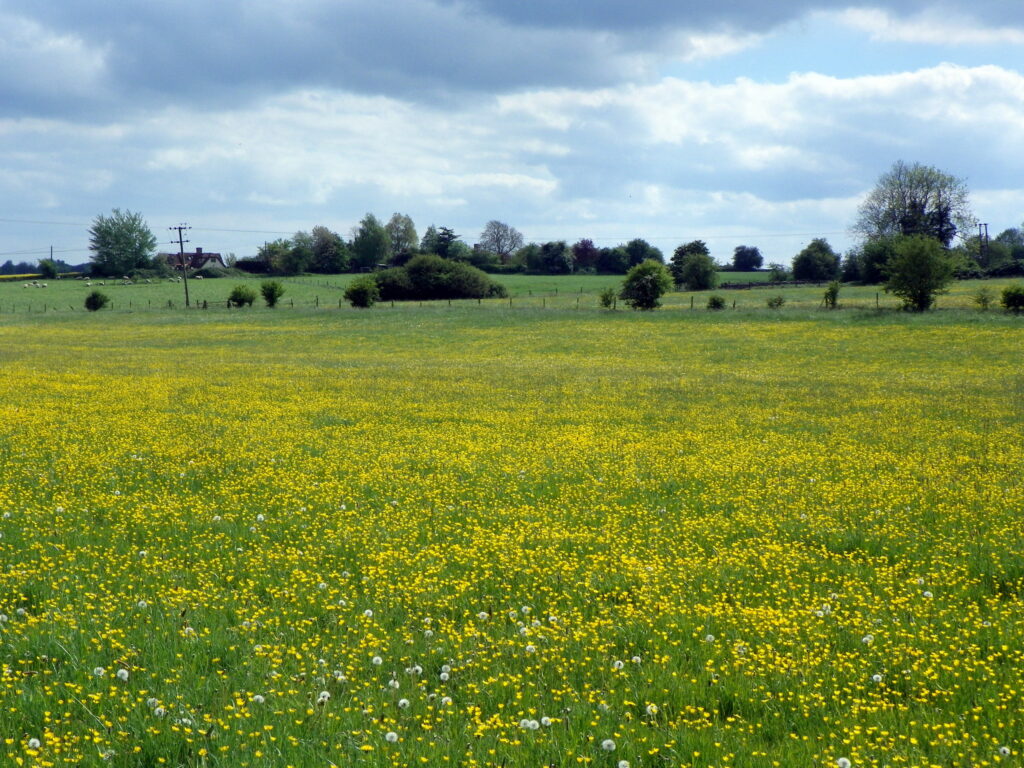
Grassland habitats are areas of vegetation dominated by grasses. Similarly to heathland, grassland can be divided into lowland and upland (above 200m). The type of sediment can also be used to classify grassland habitats, such as calcareous (lime-rich soils), acidic (sands, gravels and siliceous rocks) and neutral (clay and loam soils). They are often maintained by human intervention, through mowing, fertilising, drainage, burning or chemical treatments, as well as livestock grazing. They can also be maintained by natural processes such as grazing or browsing, or due to exposed conditions at the coast or at high altitudes where shrub and tree growth is limited.
Grassland can also be separated into unimproved, semi-improved and improved. This refers to the amount of agricultural interference in the habitat. Improved grasslands have undergone high modification or intensive agriculture, and thus typically have fewer species with a limited variety of grasses and flowering plants. (white clover, perennial ryegrass and other agricultural species usually cover more than 50% of improved grasslands). These habitats are covered more in-depth in another blog: The NHBS Introduction to Habitats: Farmland.
Semi-improved grassland is a transition category between improved and unimproved grasslands that have undergone some modification through the use of, for example, fertilisers, herbicides and grazing. These habitats have a reduced range of plant species compared to unimproved grassland but a wider diversity than improved grassland.
Unimproved grassland, also termed species-rich, has not been artificially fertilised, ploughed or reseeded. Grassland habitats are considered to be species-rich if they have more than fifteen plant species per square metre, a wildflower and sedge cover of more than 30% (excluding creeping buttercup, white clover and invasive weed species), and less than 10% cover of white clover and perennial ryegrass. Species-rich grassland habitats not only support a large number of flora species but also many fauna species such as invertebrates and birds. They improve and maintain the health of soils, protect against soil erosion, sequester carbon and provide food for browsing and grazing species such as deer and livestock.
Other examples of grassland habitats include lowland meadows, upland hay meadows, montane grasslands, purple moor-grass and rush pasture, marshy grassland, wet grassland and calaminarian grassland.
What species can you find here?
Flora
The number and type of flora species found in grasslands depends on the type and health of the habitat. Unimproved, species-rich habitats can support a huge variety of grasses, wildflowers and other vegetation. They all provide food and shelter for the many different fauna species that can be found in grasslands.
Crested dog’s-tail (Cynosurus cristatus)
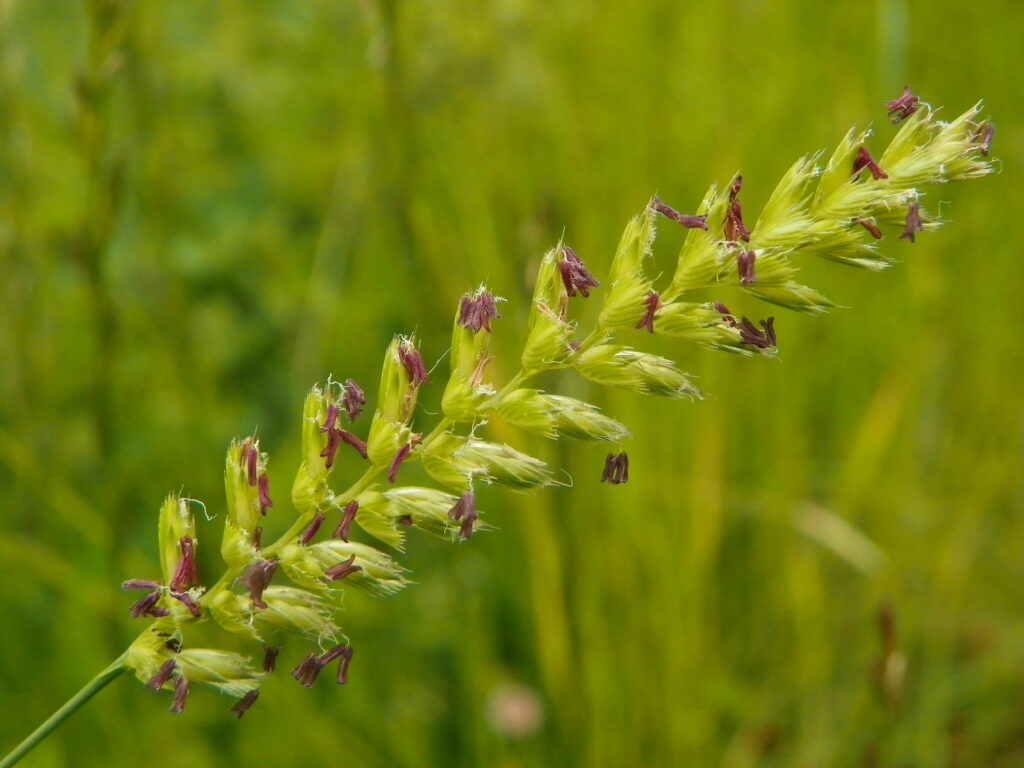

Grassland is dominated by grass cover and the species of grasses present can depend on factors such as soil type, altitude, level of agricultural improvement and maintenance routine. Crested dog’s-tail is found in many grassland habitats. It is a wiry, tufted grass that grows between 15–60 cm tall and is a traditional grazing grass. It is a common species that prefers lowland grassland and is the foodplant of many caterpillar species, such as the large skipper (Ochlodes sylvanus).
Quaking-grass (Briza media)
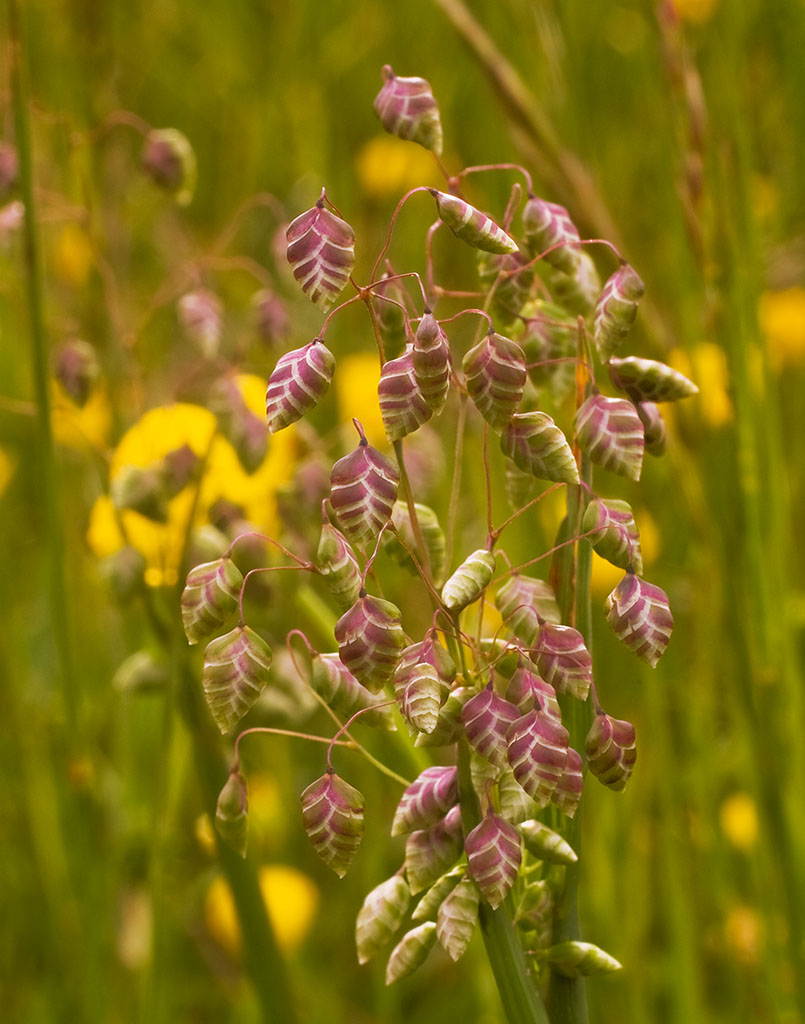

Another grass species is quaking-grass, with purple and green heart-shaped flower heads on delicate stems that appear to ‘quake’ or quiver in the breeze. Resembling miniature hops, this plant is also called totter grass, dithery dock, jiggle-joggles, earthquakes and toddling grass. The seeds of this species are a source of food for many bird species, such as yellowhammers and house sparrows.
Grasses are important foraging plants and their leaves and grain are eaten by a wide variety of species, such as small mammals, livestock, deer and many invertebrates. They also provide shelter and nesting materials, often used as the base or weaving material for many bird nests. Grasses can also help to stabilise the soil.
Cowslip (Primula veris)
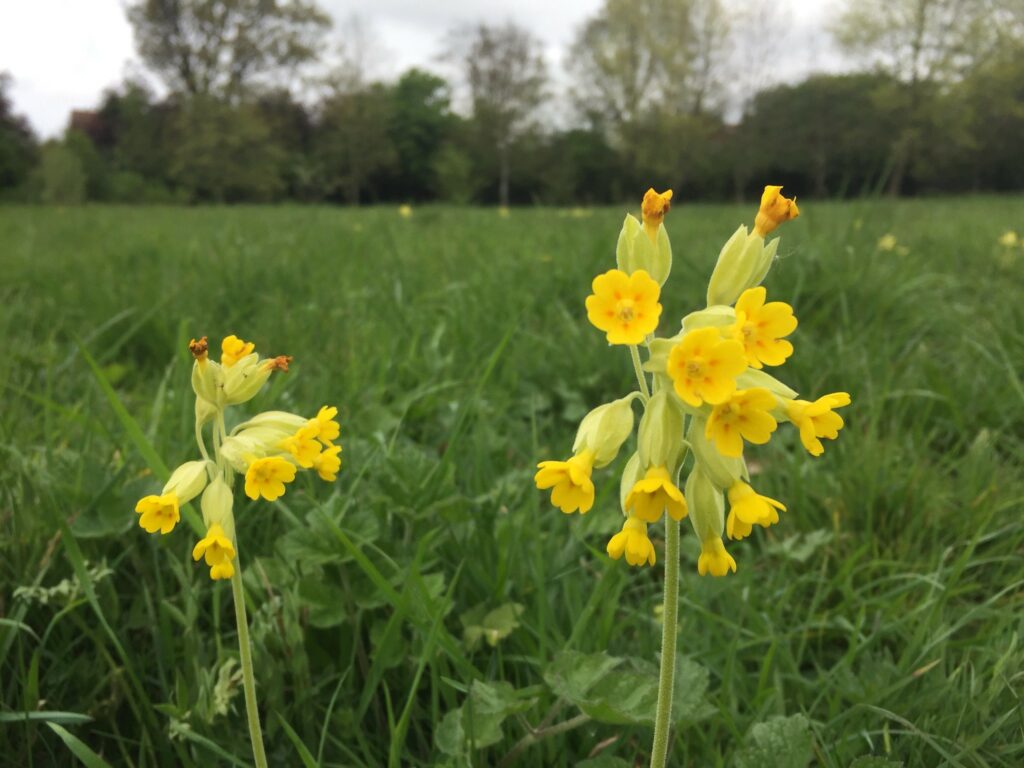

There are thousands of wildflower species in grassland habitats, providing an important nectar and pollen source for many invertebrate species. Cowslip favours dry, calcareous grassland, but is also found in woodland, hedgerows and road verges. It flowers from April to May and its yellow, bell-shaped flowers are encased in a long, green tube-shaped calyx and grow in clusters. The flowers all face one side of the plant and have five petals, each with a small indent on the top edge. Cowslip is particularly important as it is an early food source for many pollinators.
Eyebright (Euphrasia sp.)
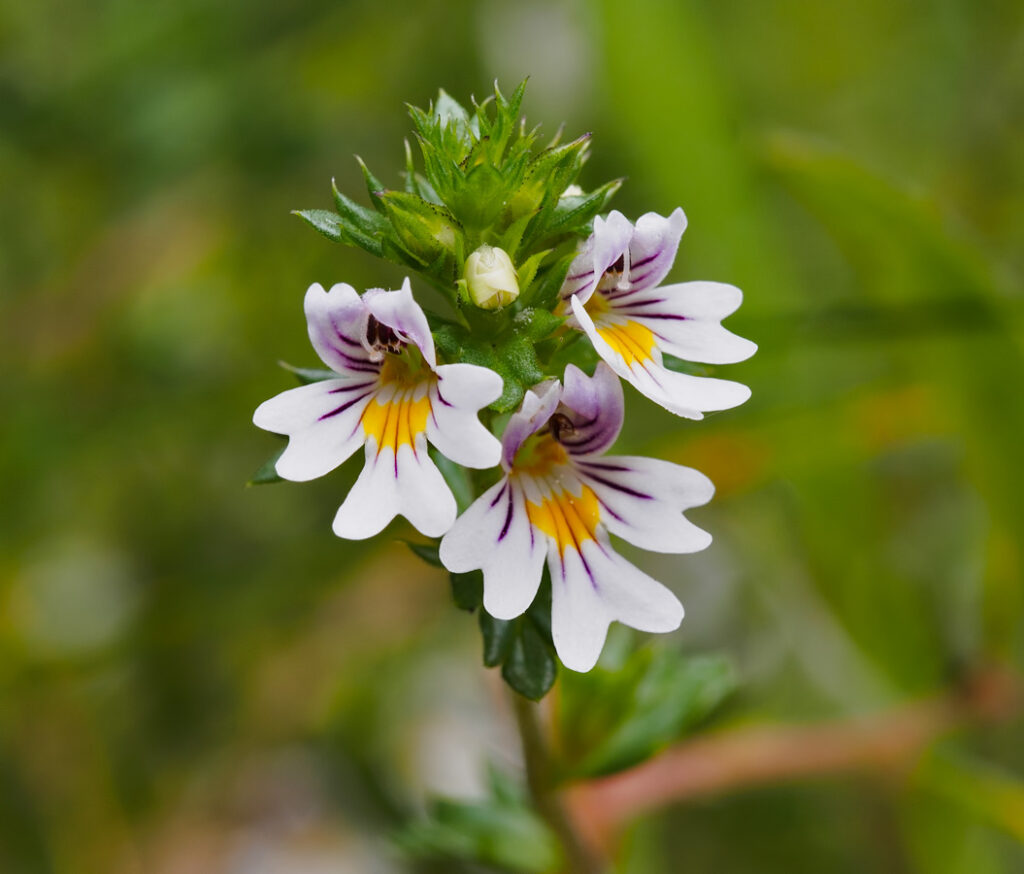

Another example of a wildflower species found in grassland habitats is eyebright. There are multiple eyebright species, including many hybrids, and identification in the field is often difficult. They’re semi-parasitic, feeding on the nutrients of the roots of nearby grasses. This can help control the spread of more aggressive grass species, allowing other wildflowers to grow.
For more examples of wildflowers, check out our guide to UK wild flower identification.
Fungi
Fungi form an important part of grassland habitats, playing a vital role by breaking down organic matter in the soil and facilitating the cycling of nutrients. They also food for many different species, including insects, mammals, gastropods like slugs and snails, nematodes, bacteria and even other fungi.
Scarlet waxcap (Hygrocybe coccinea)
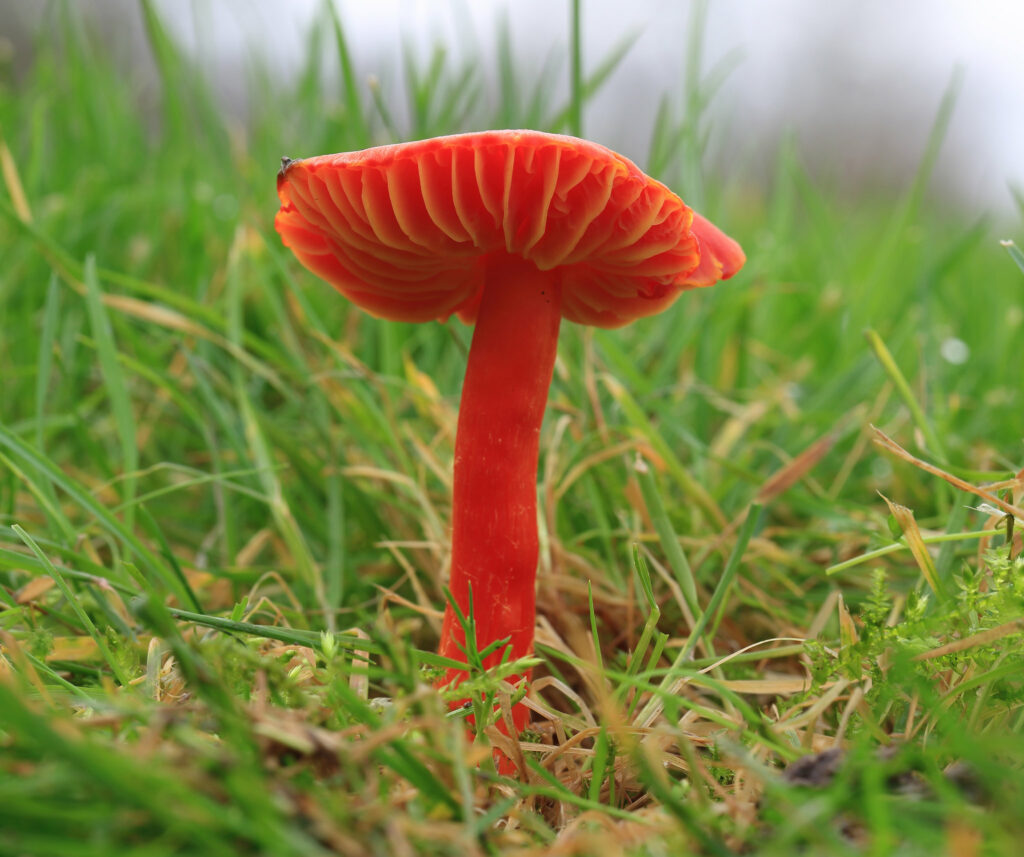

Waxcaps are associated with unimproved grasslands that have a short sward and are nutrient-poor, moss-rich and long-established, and occur in both upland and lowland areas. Due to changes in agricultural practices, these habitats have been declining in Europe, and conservation efforts have been made to protect them. These waxcap grasslands are also home to other fungi species including agarics, clavarioid fungi and earthtongues.
Sometimes called the scarlet hood or righteous red waxy cap, the scarlet waxcap can be found across the Northern Hemisphere. They’re found in fields, open woodland, lawns and roadside but they prefer unimproved grassland, where no fertiliser, chemical treatment or ploughing has occurred.
White Spindles/Fairy Fingers (Clavaria fragilis)
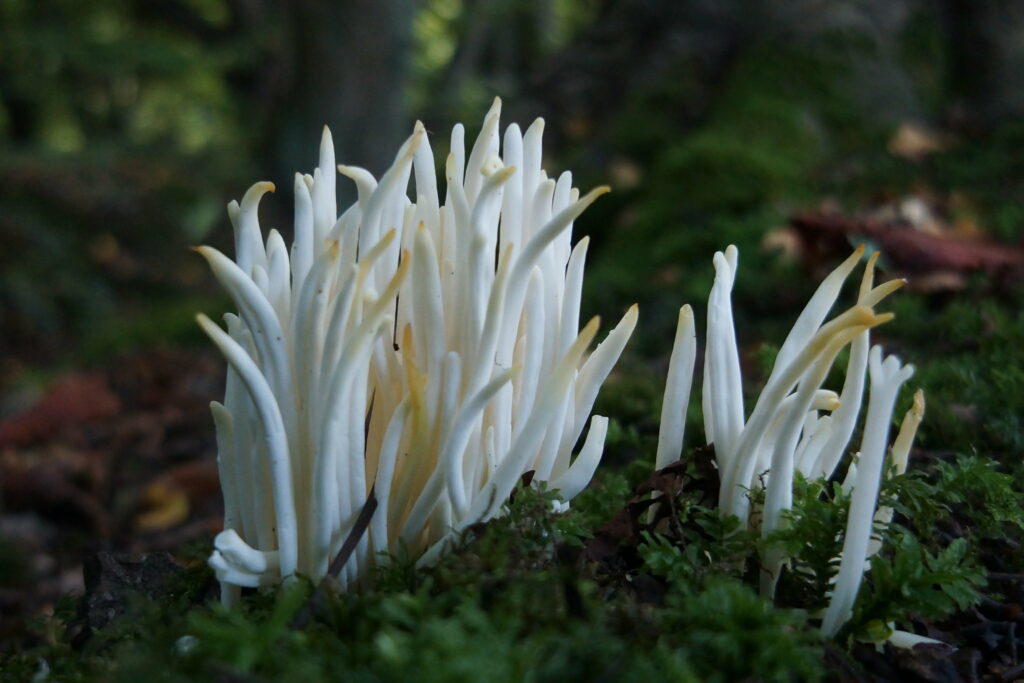

This species is an upright fungus consisting of tubular, unbranched basidiocarps (the fruiting body). They are white with browning at the tips and are very fragile, with smooth, soft and somewhat brittle flesh. They also occur in waxcap grassland and other old, unimproved grasslands.
Shaggy Inkcap (Coprinus comatus)
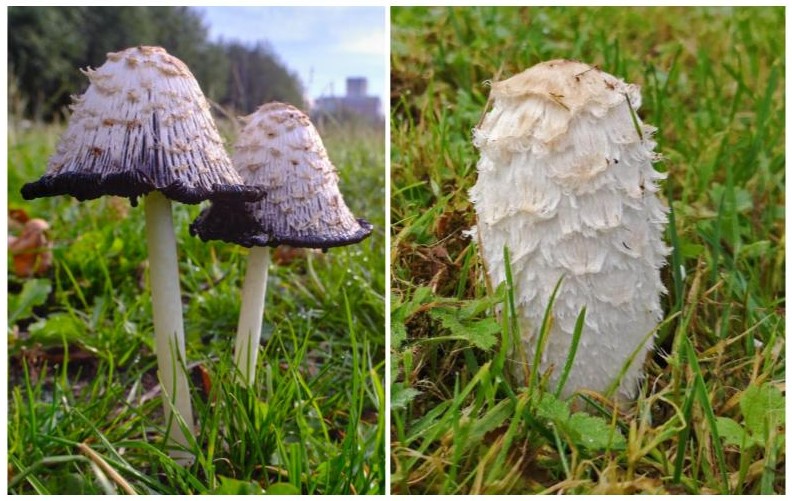

This fungus, also known as lawyer’s wig, is very common in parklands, grasslands and lawns, with a tall, shaggy cap that begins white before turning browner and grey with age. The cap opens to a bell shape as the gills turn from white to pink and then black, dissolving from the base of the cap until it’s almost completely gone. This dissolving fruitbody breaks down into a black fluid that is full of fungal spores, aiding dispersal. This fluid was historically used as an ink substitute.
Fauna
Diverse grasslands can provide habitats for a wide variety of wildlife. There is a lot of cross over between grassland and farmland species, due to much agricultural land being improved grassland habitats. Grassland is home to several species of birds, such as ground-nesting species and birds of prey. They also support small mammals, reptiles and many grazing and browsing species, such as deer, rabbits and wild horses. They are also important habitats for a huge number of invertebrates, with wildflower-rich habitats supporting many pollinator species.
Common field grasshopper (Chorthippus brunneus)
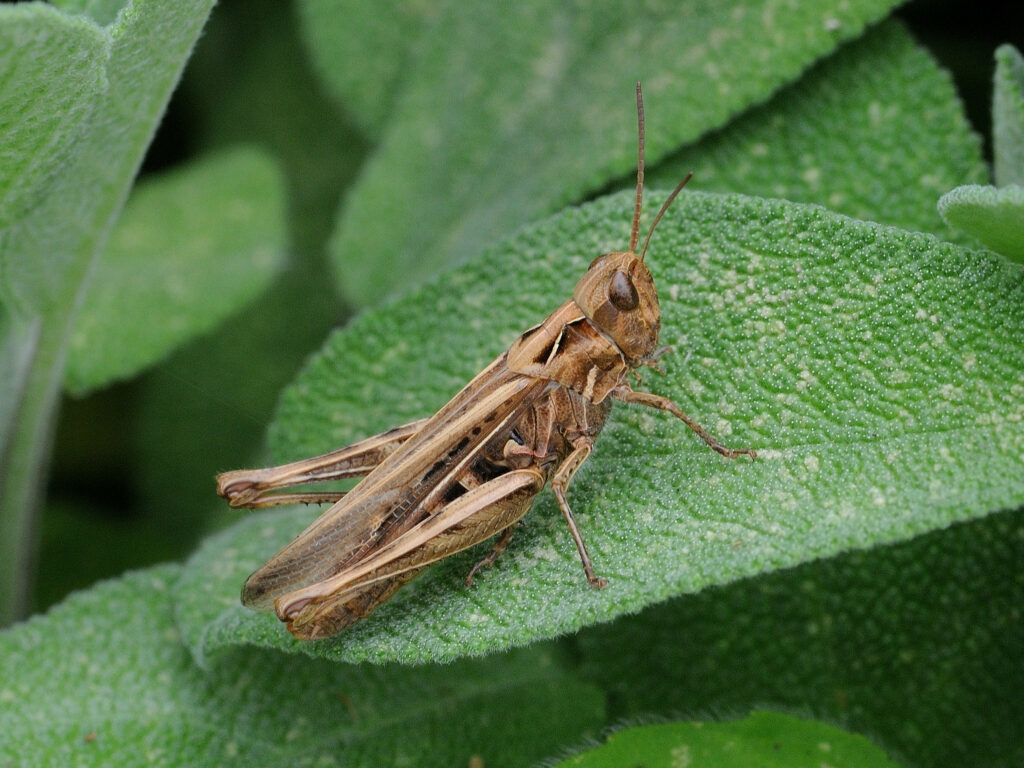

This common and widespread species feeds on grasses and other plants. They prefer dry habitats and are found in grassland, heathland and agricultural areas, but tend to occur in higher densities in ungrazed areas. Many invertebrate species play important roles in grassland habitats, allowing air penetration and nutrient cycling in the soils and the breakdown of dead organic material. They are also prey for species such as birds, reptiles and some small mammals.
Marbled white (Melanargia galathea)
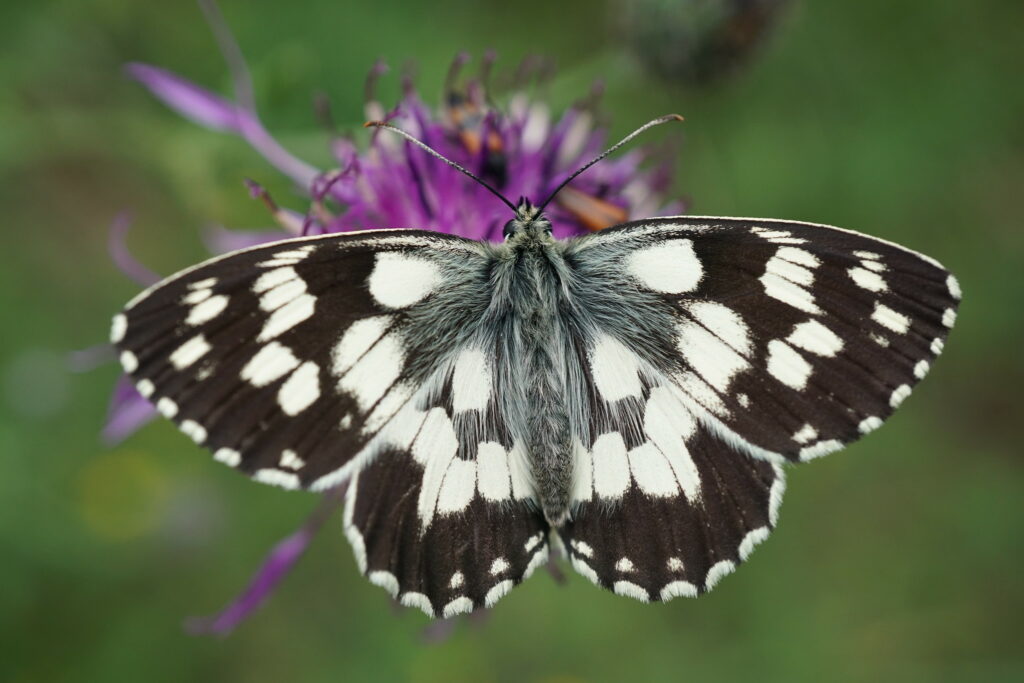
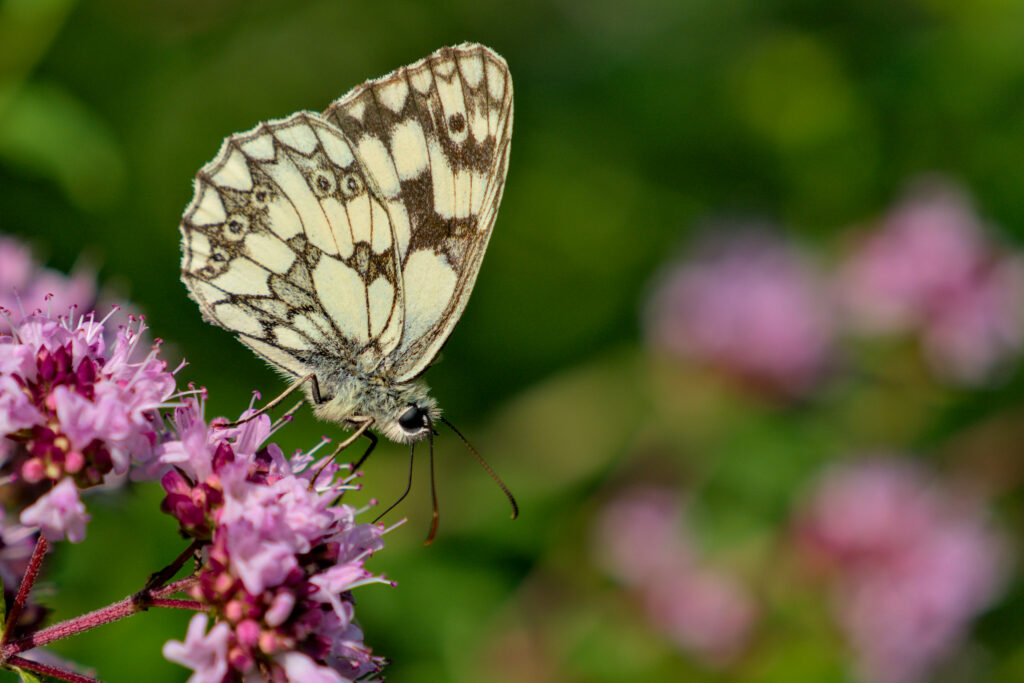


Butterflies are another group of invertebrates that are common in grassland habitats, particularly species-rich grasslands, due to the presence of many food plants and shelter provided by scattered scrub. Although some species can be found in multiple different grassland types, the habitat can sometimes be characterised by the presence of different butterfly and moth assemblages.
The marbled white is found in unimproved grassland with tall sward, as well as gardens, road verges and railway embankments, and is widespread in southern Britain. Its range has been expanding northwards and eastwards. Its caterpillars rely on red fescue (Festuca rubra) as a foodplant, as well as sheep’s fescue (F. ovina), Yorkshire-fog (Holcus lanatus) and tor-grass (Brachypodium pinnatum).
Bloody-nosed Beetle (Timarcha tenebricosa)
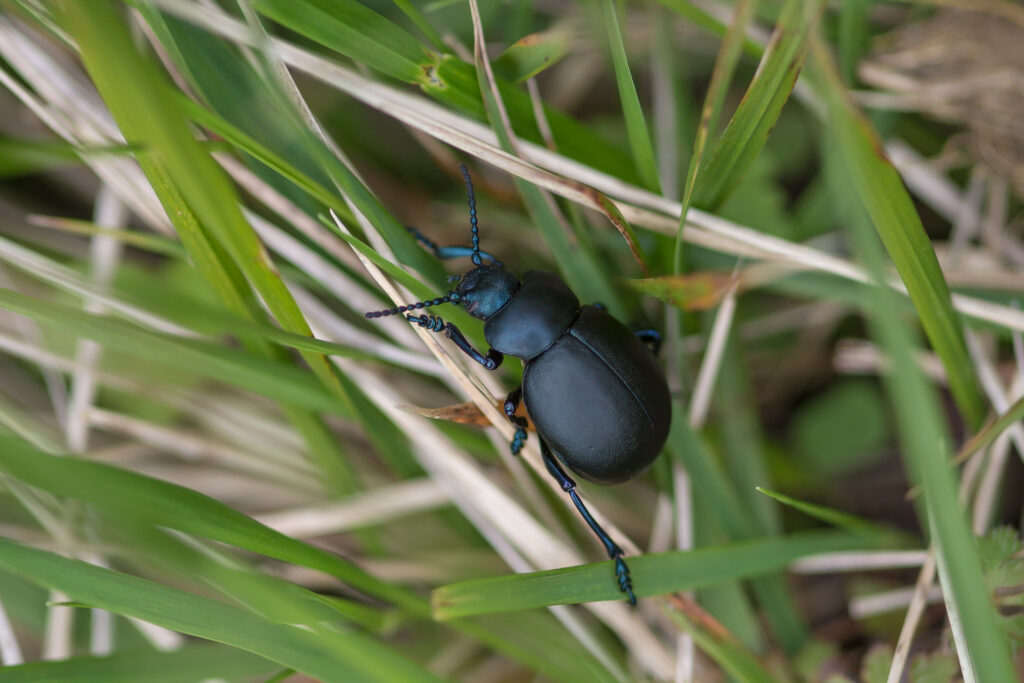

Beetles often make up a large percentage of invertebrate assemblages in grassland habitats. They play many important roles in grassland ecosystems, as plant feeders, prey, predators, parasites and scavengers, recycling nutrients from organic matter both into the soil and through the food chain. Bloody nosed beetles are black, flightless beetles that are often found in grasslands and coastal areas, particularly in the south and central UK. Their common name comes from their peculiar defence mechanism. They secrete foul-tasting, bright red hemolymph (a fluid analogous to blood) from their mouth when threatened.
Skylark (Alauda arvensis)
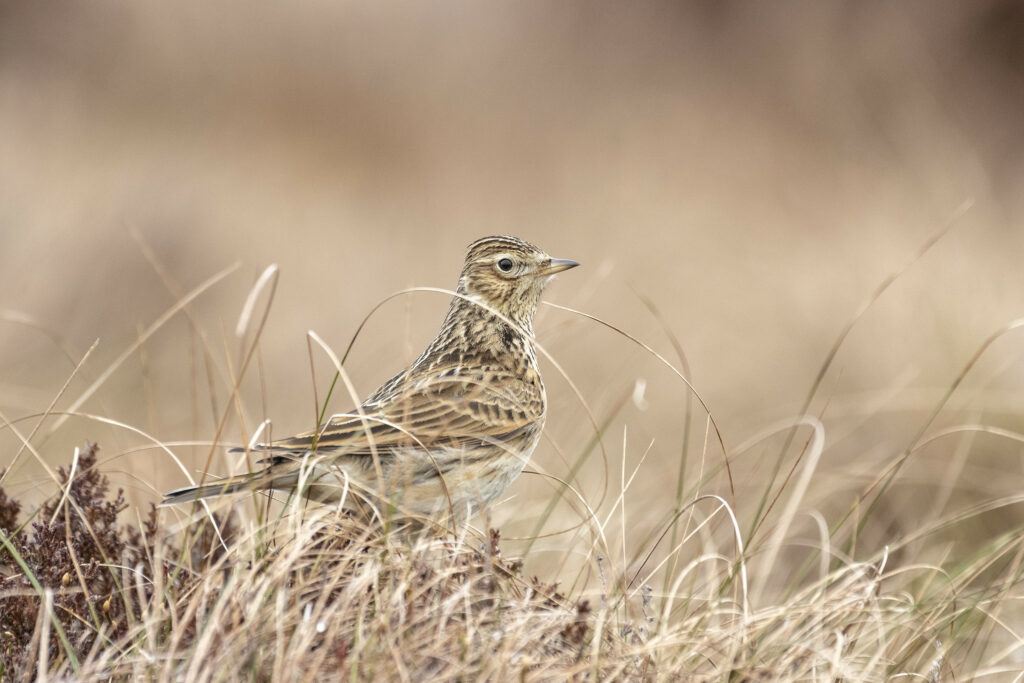

Many birds nest in grassland habitats, such as vulnerable wading birds (lapwing and curlew) and the skylark. A small bird, the skylark has a streaky brown plumage with a small crest. It is listed on the Birds of Conservation Concern 4 (BoCC 4) red list due to its recent population declines. These declines have been associated with agricultural intensification and the resultant reduction of grassland availability and suitability of farmland habitats for breeding and foraging. Birds such as the skylark use grassland as foraging grounds, feeding on seeds and insects. They are prey for other species such as birds of prey and foxes.
Kestrel (Falco tinnunculus)
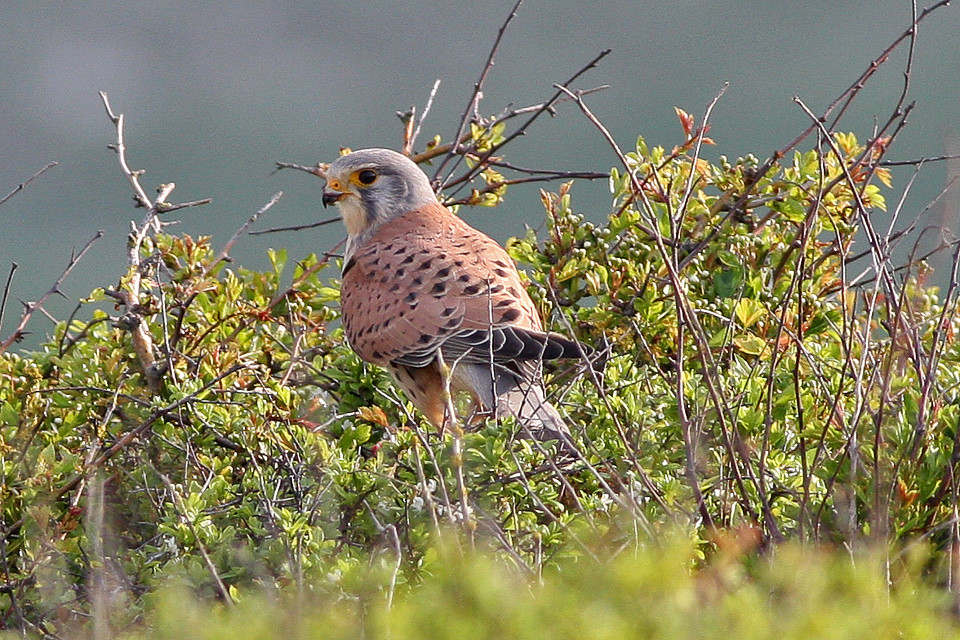

Several predator species utilise grassland habitats, namely foxes, weasels, stoats and some birds of prey. A number of birds of prey use grasslands to hunt for small mammals and other prey species. Kestrels predate almost exclusively on small mammals, such as voles, shrews and mice. They also occasionally prey on birds, particularly fledglings during the early weeks of summer, as well as bats, lizards and some invertebrates.
Roe Deer (Capreolus capreolus)
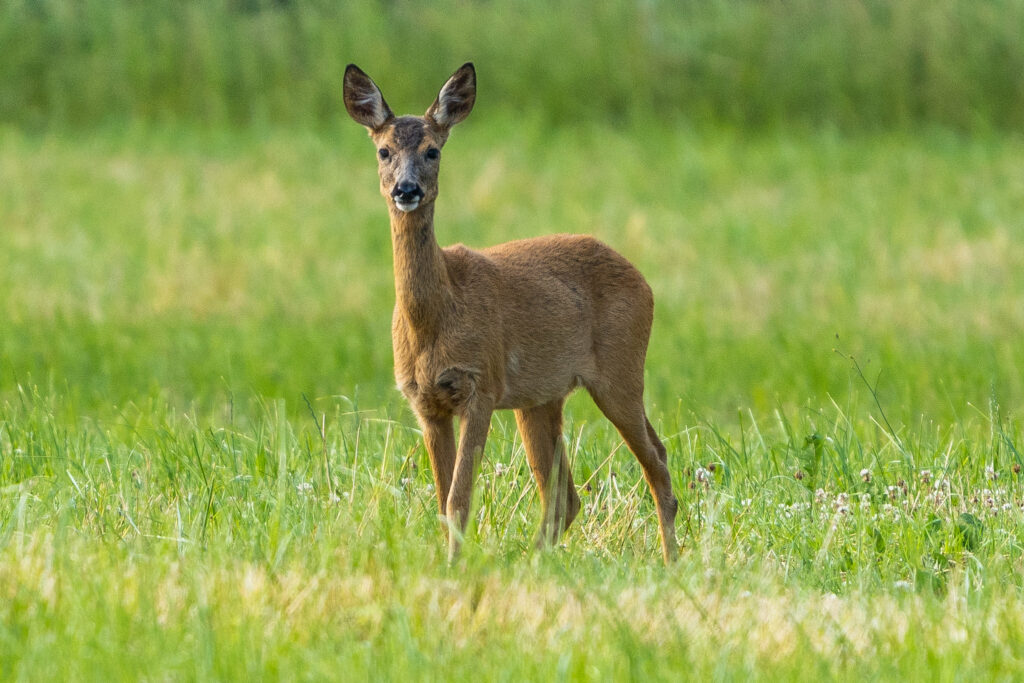

The UK has six deer species, although only two are native: red and roe deer. Fallow deer are thought to have been introduced by the Normans and the three other species, Reeves’ muntjac, Chinese water deer and sika, were introduced in the 19th and early 20th centuries. For more information on these species, check out our guide to UK deer identification.
Roe deer are small deer, with a reddish-brown colour during summer and a paler or black colouration in winter. They have a large white rump that becomes less obvious during the winter. Many grassland habitats are maintained by grazing and browsing, where species such as deer feed on the shoots of trees and scrub species that would otherwise encroach on the habitat. In many countries, deer populations are controlled by predators such as wolves, to help reduce the extent of their impact on grasslands. Other habitats are then able to develop, allowing the expansion of woodland, shrubland and heathland. The UK does not have any large predators anymore, however, therefore deer populations are managed through culling to prevent overgrazing.
For more information on other species that may occur in grassland habitats, including reptiles, moths, bumblebees and other mammal and bird species that may occur in grassland habitats, check out some of our other guides to UK species identification.
Threats
Species-rich grasslands are highly threatened habitats, as most grassland in the UK is improved or semi-improved. The main threats to grassland habitats are agricultural improvement and development. Ploughing, re-sowing, intensive grazing or mowing and heavy use of fertilisers can fundamentally change soil type and quality. This, along with clearing for development, reduces the quality and area of habitat, which would impact the number and range of flora and fauna they can support. Heavy recreational use can also impact grasslands, particularly fragile vegetation.
Another threat is encroachment from scrub and trees because of abandonment, incorrect or lax maintenance or intentional efforts to increase woodland cover. Woodland is often prioritised over grassland (that is not used for agriculture), as it is seen as more environmentally important, particularly in relation to carbon sequestration. The consequent fragmentation of grasslands is a threat in itself, as habitat patches that are too small or isolated may no longer be able to support viable populations of some species.
Areas of significance
Grassland can be found across the UK but there are some areas of significance such as the Culm grasslands and Rhôs pastures (purple moor grass and rush pastures), East Anglian Breckland and areas of the new forest (lowland dry acid grassland) and the Keen of Hamar in Shetland (calaminarian grassland).
Further reading and useful equipment
£3.75
Check out other Field Studies Council Fold-out Guides
 Grassland Fungi: A Field Guide
Grassland Fungi: A Field Guide
£19.99
 Grassland Restoration and Management
Grassland Restoration and Management
£34.99
 Opticron Hand Lens: 23mm 15x Magnification
Opticron Hand Lens: 23mm 15x Magnification
£14.50 £16.50
Check out our guide to hand lenses and our full range.
£59.99 £65.60
£15.50
All prices correct at the time of this article’s publication.