The Field Studies Council has been educating the public on Britain’s natural environment for 70 years, and its publications have played a vital part in making nature more accessible. Three generations of wildlife enthusiasts and conservation professionals have learned about the UK’s plants and animals through Field Studies Council courses and honed their skills with Field Studies Council publications.
The Field Studies Council has published an impressive range of handy fold-out charts, as well as a large series of AIDGAP Guides, which are aimed at non-specialists and are intended to assist with the identification of difficult groups of plants and animals. Their back catalogue also includes a selection of more specialised titles, such as the Royal Entomological Society Handbooks on British Insects, and wildlife distribution atlases produced for the Centre for Ecology and Hydrology’s Biological Records Centre.
We recently had the opportunity to speak with Dr Rebecca Farley-Brown, Head of Publications at the Field Studies Council, about the many courses they run, how they develop their identification guides, their exciting new projects for the New Year and more.
Can you tell us a little bit about yourself and what your role within the Field Studies Council entails?

My role within the Field Studies Council is Head of Publications, based in our warehouse in Telford. I started out in academic research and lecturing before moving to Field Studies Council in 2000. As well as business and product development, I manage the postal sales team that processes orders for our retailers as well as our e-commerce shop. It’s a busy role – every year we mail out over 145,000 guides and aim to publish at least four new ones. We also develop commissioned guides to support citizen science projects.
Developing identification guides is a key part of what we do – for those that take the first step of peering into the garden in search of butterflies and bees on flowerheads, through to guides for enthusiasts, fieldworkers and scientists. I am lucky to have a job which can make a difference, and successful identification is fundamental to survey work and biological recording – if we can’t name it, we can’t protect it.
Founded in 1943, Field Studies Council aims to facilitate an array of opportunities for people to learn about nature, which includes field or outdoor educational classes, residential and day centres, natural history courses and more. How large is your operation and what can be expected from one of your courses?
We have a network of 11 residential field centres and seven day centres across the UK, where we welcome over 100,000 learners from schools, colleges and universities every year. There is no substitute for first-hand experiences in nature, and our charity gives learners a special opportunity to see and explore natural landscapes for themselves. There are wider benefits too – being outdoors is good for mental health and wellbeing.
Our teams provide over 200 natural history courses a year, taking place online or in stunning locations. Whether you’re learning online at a pace that suits you, or in-person gaining practical hands-on experience, all of our courses are led by expert tutors who have a wealth of knowledge, and participants often leave feeling very inspired.

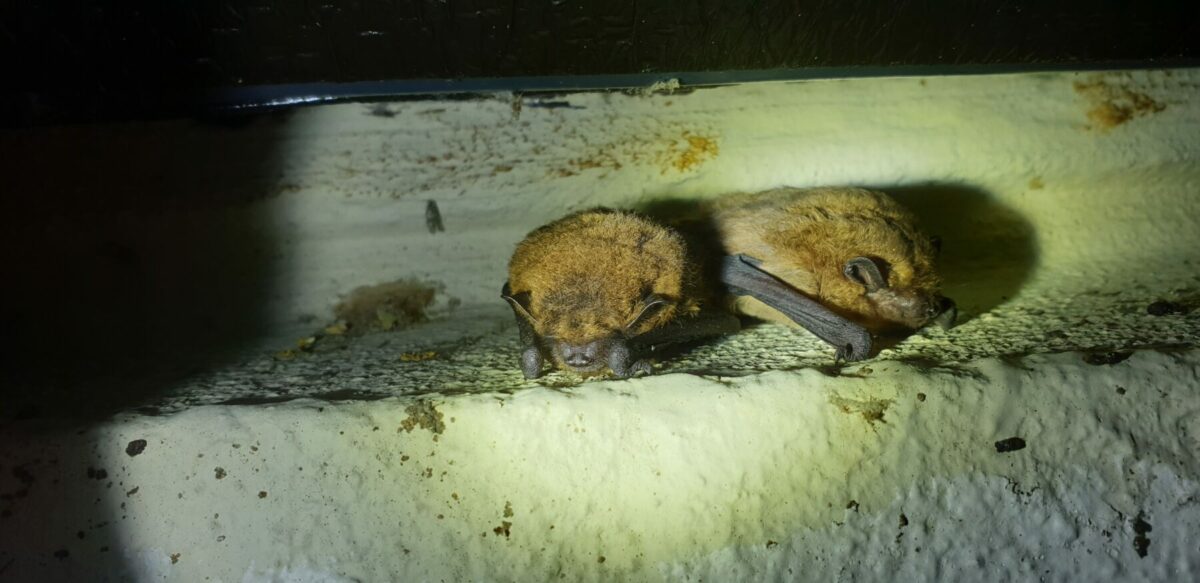
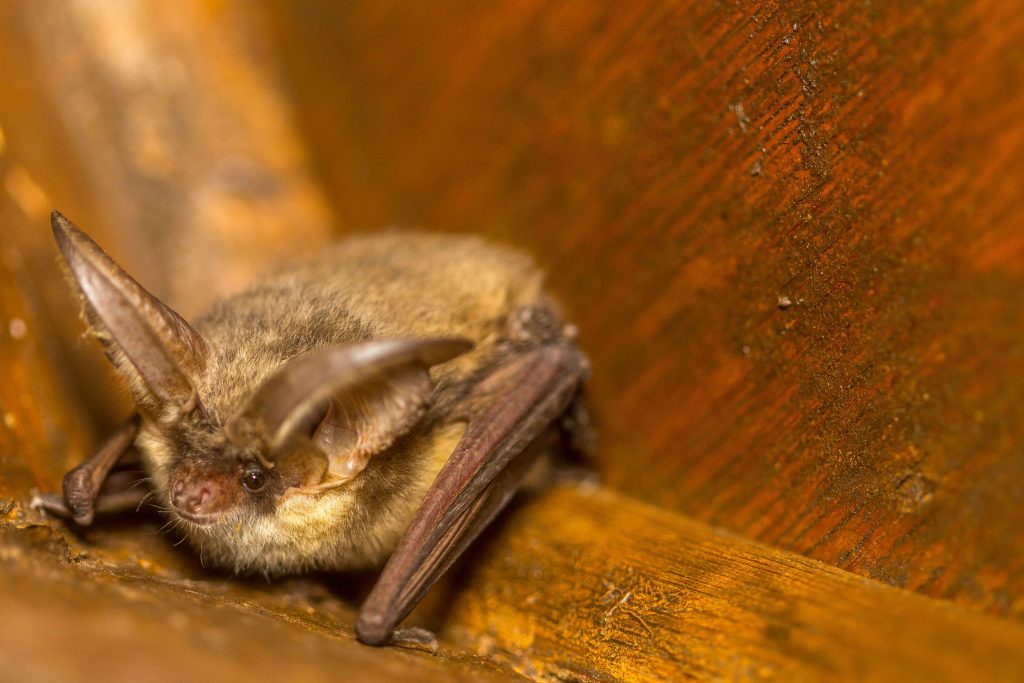
There is always a large demand for professional skills courses from those within the environmental job sector, including topics like habitat surveying, protected species, and understanding Biodiversity Net Gain. Alongside this, we get a lot of enthusiasts and students who are looking to improve identification skills for biological recording and knowledge to further their careers. As an example, our two-and-a-half day ‘Bats: Ecology, Surveying, and Conservation’ course will see you explore areas around our field centre in Shrewsbury. It offers hands-on experience with equipment such as bat detectors, where you will complete a bat survey and analyse the results. Plus, if you’re staying with us overnight, you can have a chilled catch-up with other like-minded people in the evening.
The charity has been creating Field Studies Council identification guides for many years, with a catalogue of over 200 guides to date. These resources cover a vast range of topics from plants and fungi to mammals and insects – can you share with us how you decide which subjects to focus on?
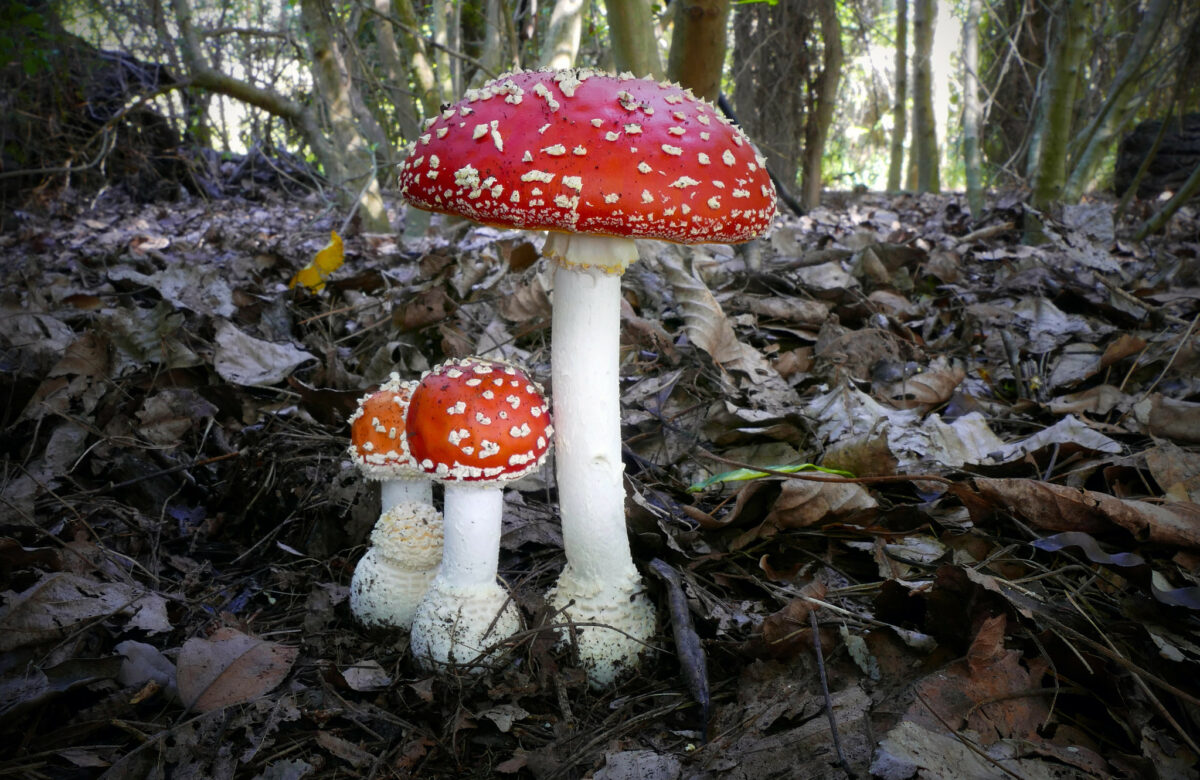
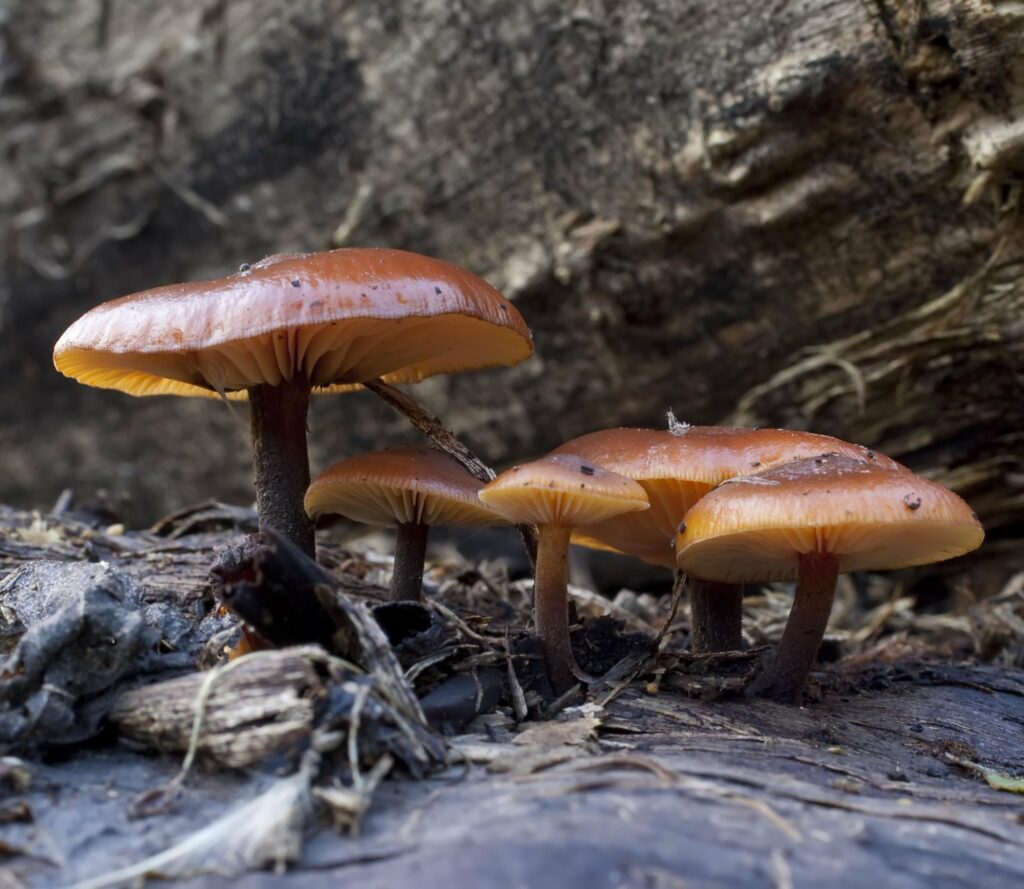
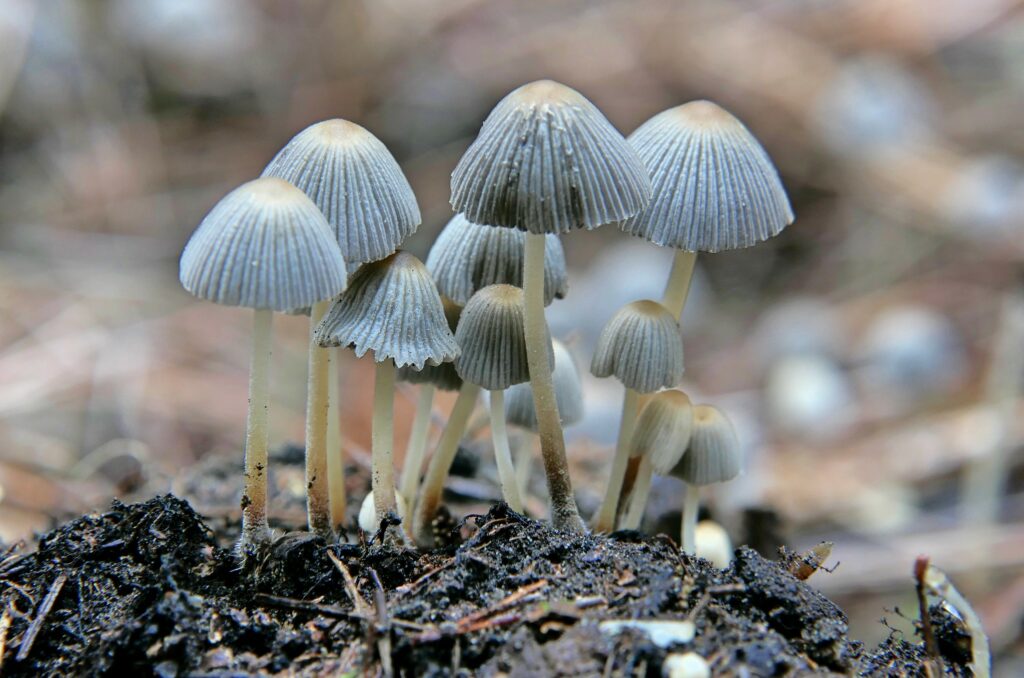
We try to keep an overview of what guides we have, where there are gaps and what needs updating. We had fungi marked as a potential area for a few years, but struggled to find an author until we started working with fungi expert Geoffrey Kibby in 2023, and we now have three WildID guides to distinctive fungi which have been really popular this autumn.
We also think about levels – people need different types of guides depending on their knowledge and experience. Someone starting to look at local wildlife might be happy to know they have found a grasshopper, whereas the enthusiasts and recorders will want to identify it to species level.
That being said, some keys are a challenge to develop and might not make it through to publication. We like to thoroughly test our guides with a range of people, including experts in the subject to make sure they are accurate and useful.
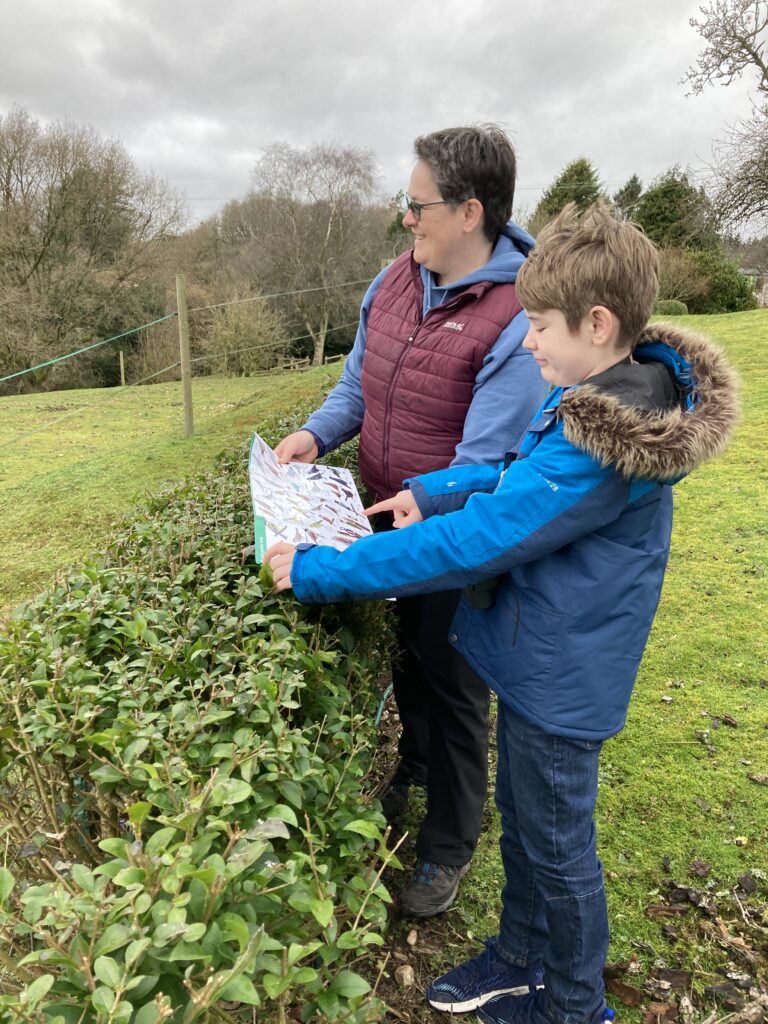

Each guide is beautifully produced and printed, featuring numerous detailed illustrations to aid reliable identification. What process do you go through when selecting an expert illustrator for each guide?
We’re lucky to have good working relationships with several artists, so we have a regular group we tend to use, some of whom are experts in their field too. Sometimes we can reuse existing artwork such as Richard Lewington’s butterflies and dragonflies – the detail on these is exquisite and so accurate, even down to wing venation.
Other times we might need to commission new illustrations, and it is always good to see these develop. Lizzie Harper does many of our plant illustrations, and we recently worked with her on the Waterside Plants WildID guide. Once we have decided on the species and the features that need illustrating, Lizzie will produce sketches that the final artwork will be based on – it’s always an exciting moment when these arrive!
Suddenly you can start to visualise the finished guide. This is the time to check the details. Are any modifications needed? Are there particular features, such as hairs, that need to be brought out in the final painting? All of this is discussed, and then we sit back and wait for the finished artwork to arrive. Lizzie has a lovely blog on her website, which gives an insight into how she develops her artwork.

What are some of the challenges that the charity has faced over the past few years, and what are your hopes for the future of the Field Studies Council going forward?
One of the biggest challenges was COVID-19 – lockdown meant that our field centres were closed, and the majority of staff were placed on furlough. But it was also an opportunity, and sales of the wildlife guides flourished as more people had time to spend outdoors exploring.
During this period, we also developed a couple of online natural history courses. These proved extremely popular, and over time we’ve increased our range to over 44 topics which we run every year. Feedback on these showed that it was a fantastic way for people to learn about nature from their own home, especially with time restrictions or accessibility constraints.
We hope to continue to increase the variety of online training we offer; while improving accessibility, we will also be mirroring these topics in our practical field-based courses to offer progression routes.
With 2025 just around the corner, are there any exciting new projects on the horizon that we can hear about?
We are always working on new guides. Some are still a few years away from completion, but a guide to raptors in flight is nearly finished and an AIDGAP guide to micro ladybirds and another fungi guide are planned for 2025. We also have a sedges guide in development, which will hopefully be progressing to the layout stage next year.
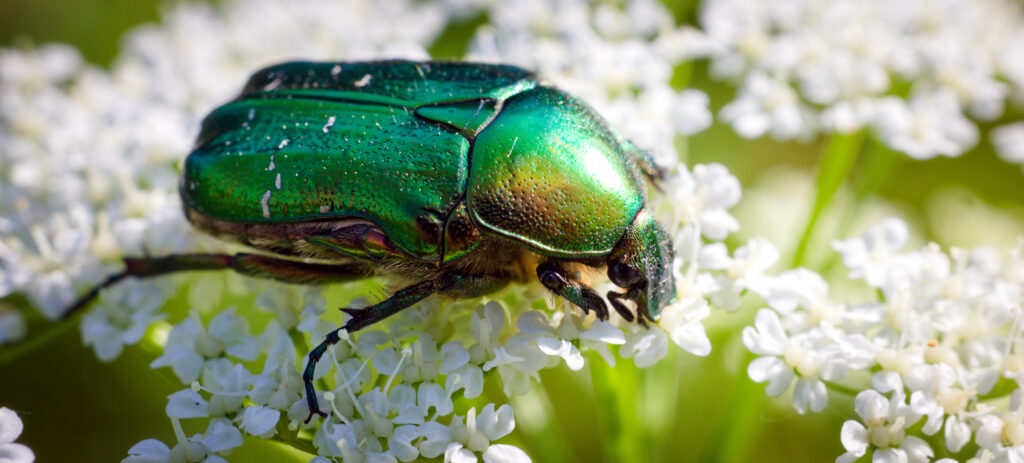
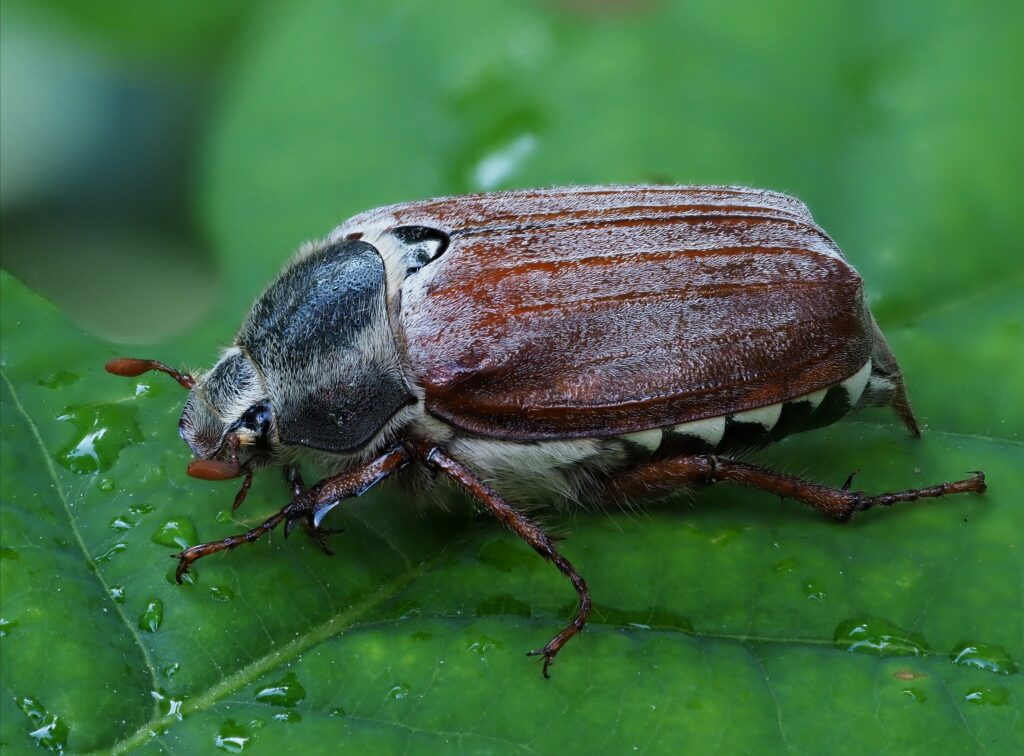
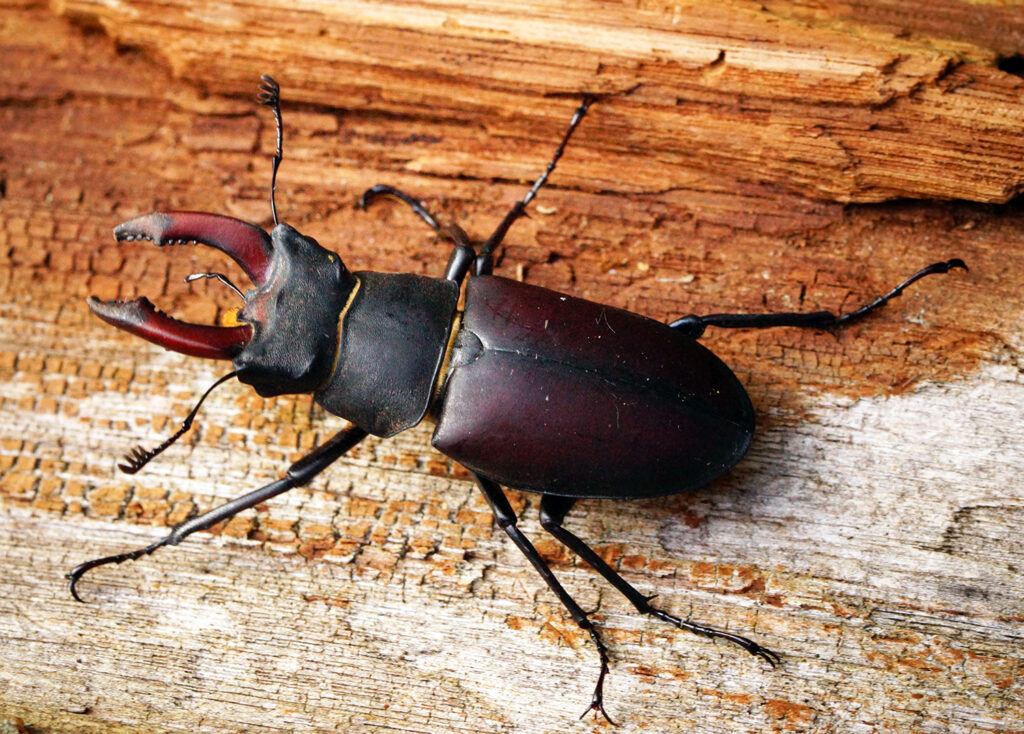
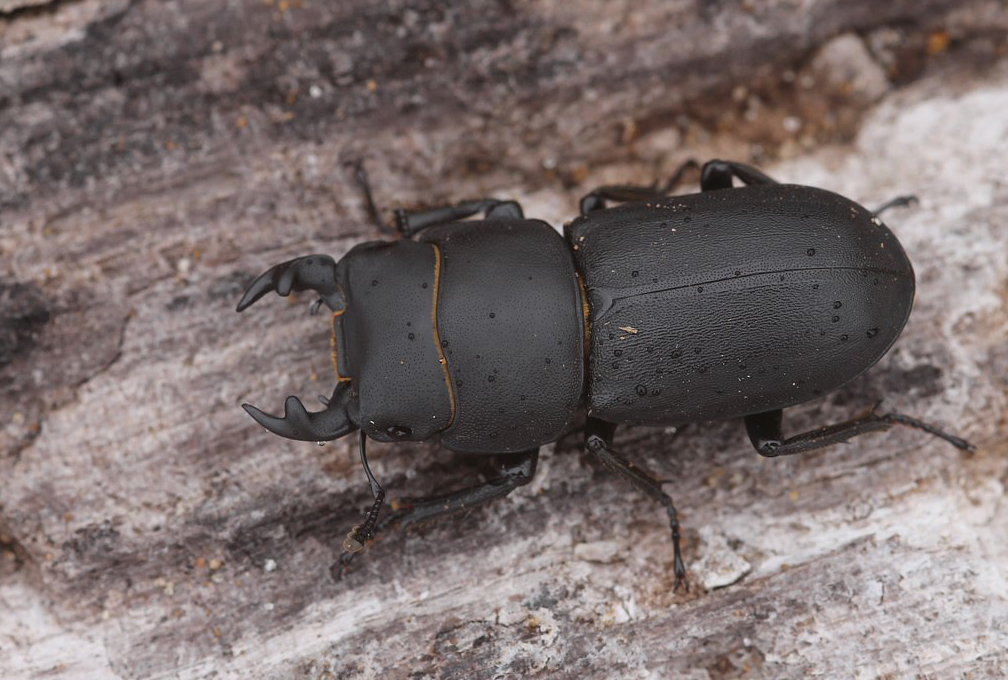
We’re also thinking about beetles, and working on another introductory guide series to common wildlife that we hope to launch in the spring.
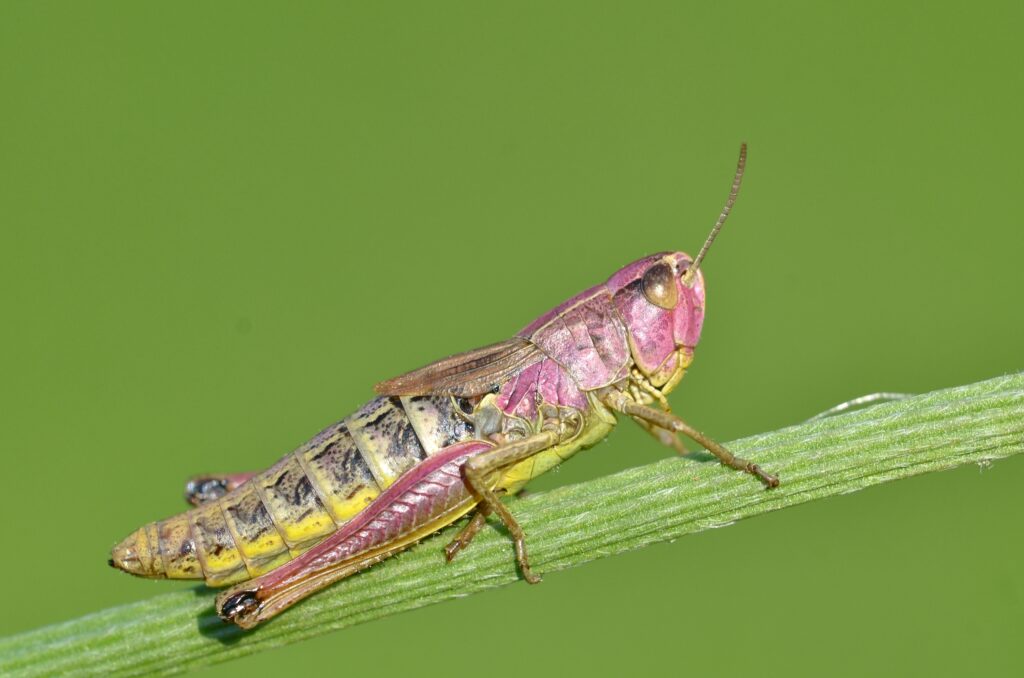
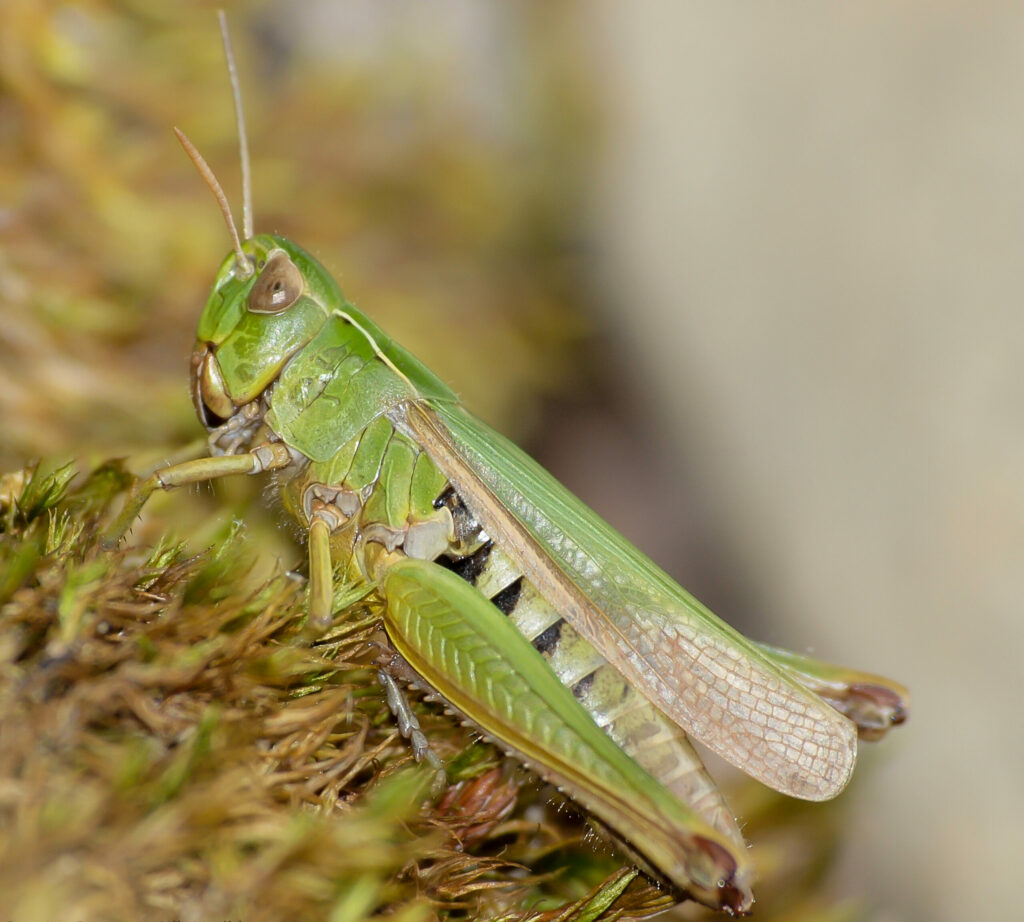
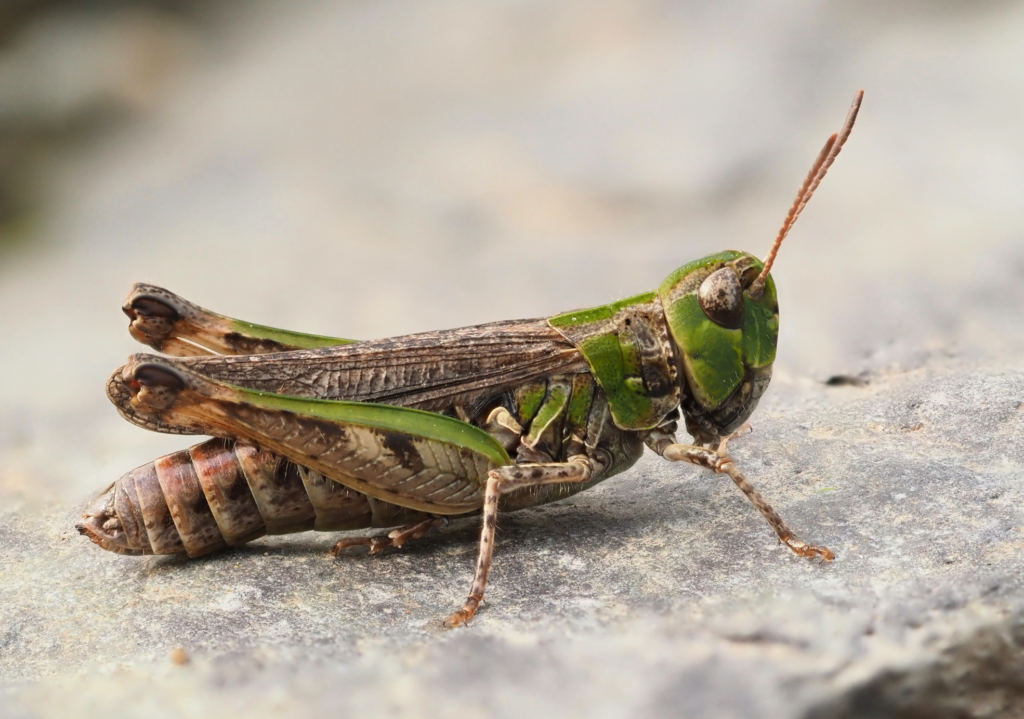
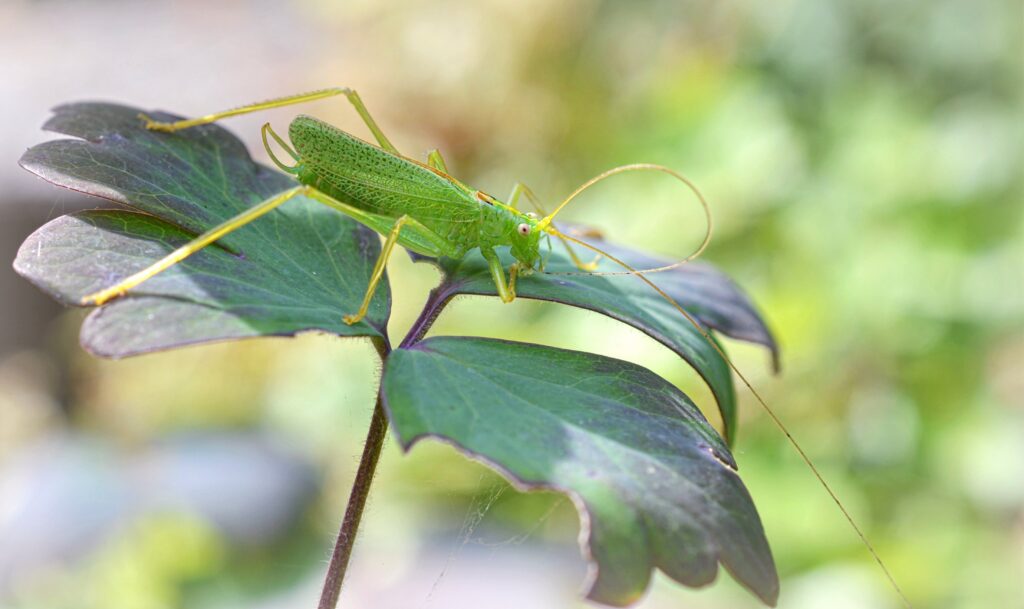
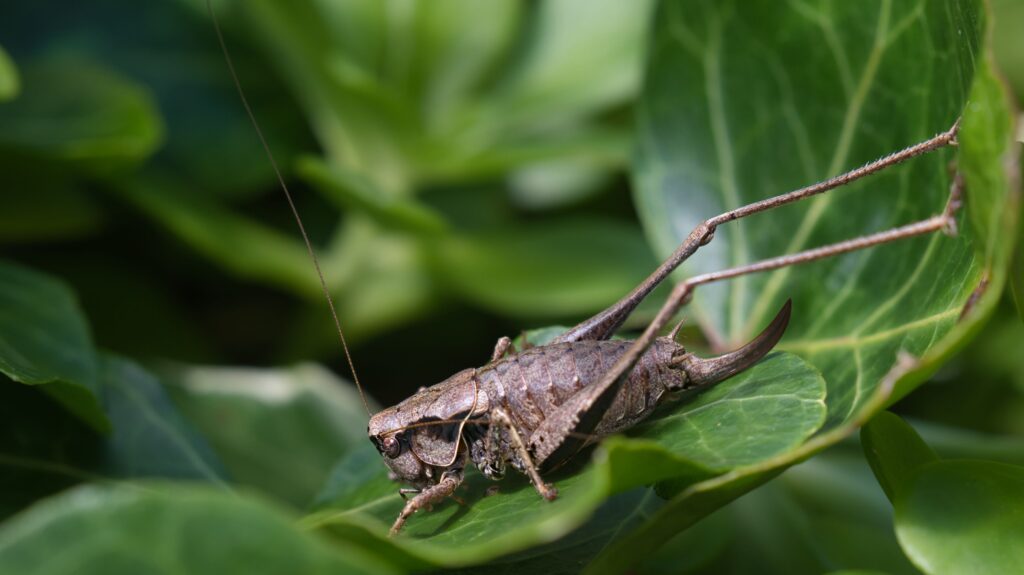
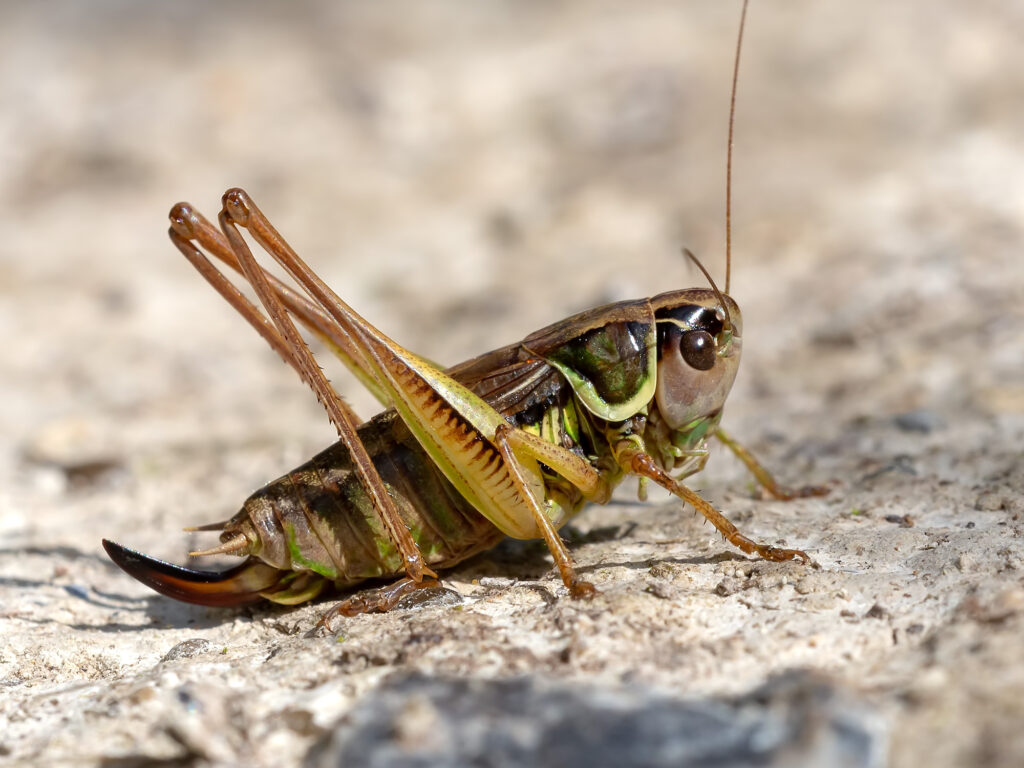
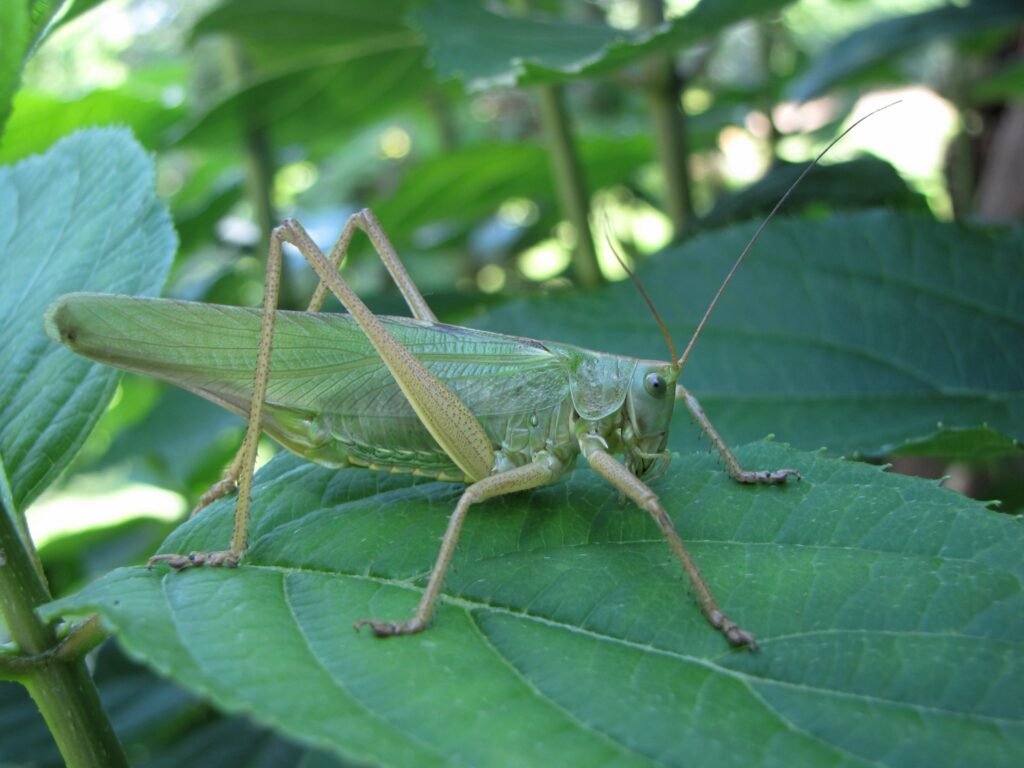
































































 Grasshoppers of Britain and Western Europe
Grasshoppers of Britain and Western Europe Orthoptera and Dermaptera
Orthoptera and Dermaptera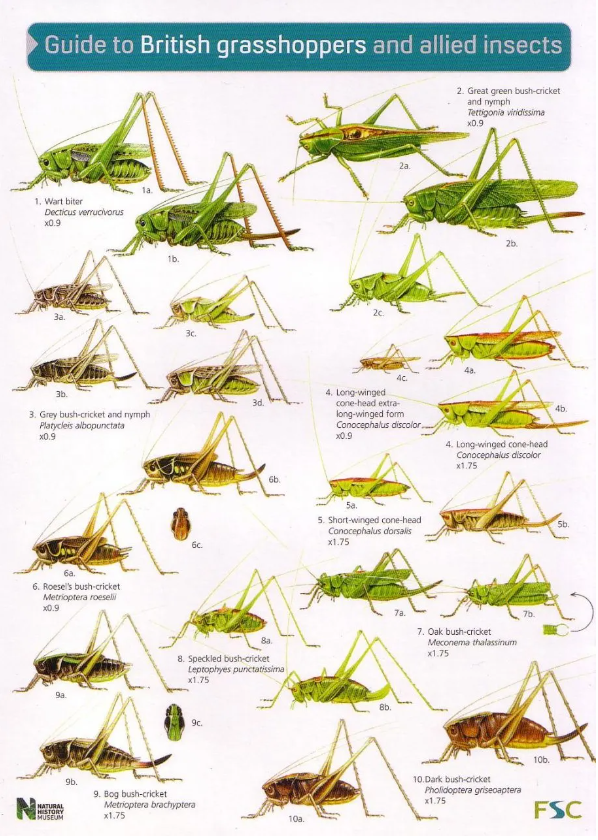



 The Scottish Wildlife Trust is the leading charity seeking to protect and restore the diversity of the Scottish landscape and its species. Based in Edinburgh, this membership-based organisation has a key role in the conservation of over 90,000 species through practical work, campaigning, education and management in over 100 wildlife reserves.
The Scottish Wildlife Trust is the leading charity seeking to protect and restore the diversity of the Scottish landscape and its species. Based in Edinburgh, this membership-based organisation has a key role in the conservation of over 90,000 species through practical work, campaigning, education and management in over 100 wildlife reserves.













