Passionate naturalist, author and illustrator David Wege has led an exciting 30-year career in international bird conservation. Now sharing the joy of tracking through teaching, he aims to encourage others to deepen their connection with the world around us.
For his latest work, he has turned his attention to mammals and has created Mammal Tracks of Europe. After rediscovering his passion for tracking, David hopes to inspire others to engage with the art through his latest work. This book includes the tracks of 72 European mammals, with detailed drawings and portraits of each species.
We recently had the chance to chat with David about how he first became interested in tracking, why he included Homo sapiens in his new mammal tracks field guide, what he’s currently working on and more.
This unique field guide features a broad selection of European mammals. What criteria did you use when choosing which species to include?
I set out with the intention of creating a mammal tracks guide that anyone could take out into the field, anywhere in Europe, and identify the tracks they were looking at. This meant including all of Europe’s larger terrestrial mammals, including the Arctic species from Scandinavia (such as Wolverine, Arctic Fox and Muskox), and the species that have ranges just into the Mediterranean countries (like Crested Porcupine and Egyptian Mongoose). So, all larger European mammals that you are likely to find tracks of are featured. Even the domesticated species that, as trackers, we often find the tracks of– such as cats, dogs, cows, sheep and Alpacas! The small mammals (such as the mice, voles and shrews) are not covered quite as well, but all species for which we have track photos are included. The end result, is a book with the tracks and trails of an incredible 72 European mammal species.
Creating a book that anyone can use meant making it accessible to people right across Europe. So, each species is represented by a small portrait of the animal; is identified by its scientific name; and its common name is given in eight European languages. As well as helping people navigate the book quickly, I think the species portraits make sure that we keep the connection between tracks and the animal that made them.
Tracking is increasing in popularity across Europe and is being used more and more as we rewild areas and reintroduce species in the region. My hope is that this guide will help encourage more people to connect with mammal tracks and engage with the conservation movement, wherever they are.
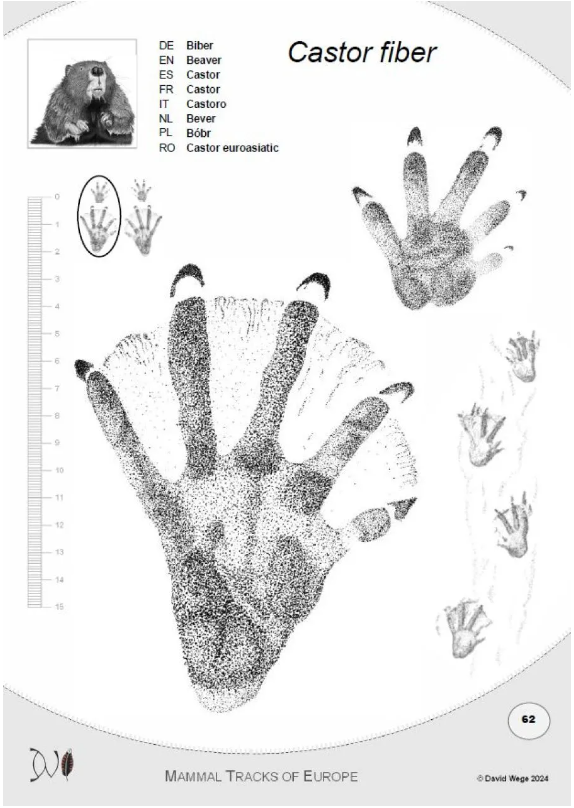
Why did you choose to include Homo sapiens in the field guide, and why were these tracks presented first?
Humans are part of nature. We’re mammals just like every other mammal in the book, so presenting ‘human’ in exactly the same way as our mammalian cousins – as Homo sapiens, a species that also makes tracks – seemed important. Connecting with nature starts with us recognising our place within it, so ‘human’ on Page 1 is a nod to our place as equals among other animal beings. There’s a practical aspect to this too. As a teacher passing on tracking knowledge to others, using our human hands and feet as a reference point for where toe pads, nails, palm pads, heels, carpal pads etc. are, is a great way for people to learn and relate to the track morphology of other mammalian beings. Human hands and feet (and the tracks they create) are a wonderful baseline against which we can start comparing the tracks of other species.
Instead of written descriptions, the field guide uses drawings as a primary aid to identification. What challenges did you face in illustrating the guide?
The guide really does have very little text and relies on drawings to do the talking – to be a graphic reference when you’re out in the field. I wanted to create precise representations of tracks for each species – to let the illustrations communicate all that was needed in a true ‘to be used in the field’ field guide. A noble desire, and easily said, but there really are many challenges. The first of which arises from the fact that no two tracks in the mud, sand, clay or snow are the same, so which one is best to illustrate? To overcome this, I ‘traced’ (electronically, on a tablet) as many track photos as possible to build up (as near as possible) a perfect average. This hopefully compensates for the vagaries of different substrates. Drawing from track photos means that those images need to be good too! They have to be taken from directly above, with not too much shadow, and with a scale or ruler in the photo. When you start drawing from photos it really makes you appreciate which are good (and useful/usable) and which are not. Once I had my ‘good‘ track photos, I started drawing– trying to keep strictly to what I was seeing in the tracks. This has hopefully resulted in illustrations that allow people to pick out the identification features that are most noticeable to them.
Another challenge is that some of the species I’ve illustrated are rare, or from parts of Europe I have not been tracking, so I have had to rely on track photos shared generously by other trackers. It is definitely harder to illustrate a track that you’ve never seen in the field yourself – it’s difficult to get a ‘feel’ for the essence of it, but I think I’ve managed to create good representations of tracks for all the mammals.

Where did your initial interest in animal tracking come from, and how did you begin your journey into this field of study?
I was totally hooked on tracking as a child when my parents gave me a book – Nature Detective by Hugh Faulkus. However, without a tracking mentor, I actively pursued my other passion of birds and birdwatching – a passion that I still have and that led me to a successful career in bird conservation with BirdLife International. Then, about ten years ago, I chanced upon a tracking mentor in John Rhyder (author of Track and Sign, and one of Europe’s foremost trackers), and have been learning from him and teaching with him ever since. We have just finished a book together titled Bird Tracks: a field guide to British species. Tracking just seems like a natural component of being in nature for me. Wandering in nature means intuitively noticing who was there, doing what and when, which birds are calling or singing, what plants are emerging or flowering (and so much more). Reading the tracks is just a part of this awareness, although I’m still learning how to balance an awareness of tracks on the ground with noticing birds up in the trees!
What will be next for you? Are there any plans for more tracking guides?
One of the many wonders of tracking (by which I mean reading and interpreting the tracks and signs that animals leave on the landscape) is that there is always more to learn. Animals constantly surprise and we’re often discovering new behaviours revealed in tracks and signs. I’m still learning but I also have the privilege of teaching the art and science of tracking to others. So, I will be spreading the tracking joy, with my book in hand, to people who can hopefully then use the skill to connect to nature, or apply their tracking skills to help monitor, conserve and restore wildlife. This book was designed as a resource for people across Europe, but I would like to see my track and trail illustrations used for local or national field guides that might then be accessible to a wider audience. Anything to help encourage nature connection through tracking.

Mammal Tracks of Europe: A Field Guide to The Tracks and Trails of European Mammals is available on our online bookstore here.