
Wilder Sensing, founded in 2021, is bringing innovative techniques to conservation, providing additional insights into biodiversity. This promising tech start-up featured on Springwatch this Wednesday (12th June), showcasing the applications of this innovation. We had the opportunity to chat with Geoff Carss, CEO of Wilder Sensing, on the organisation, its role in conservation and the future of technology in the field.
Can you share with us why Wilder Sensing was founded and what the company is involved in?
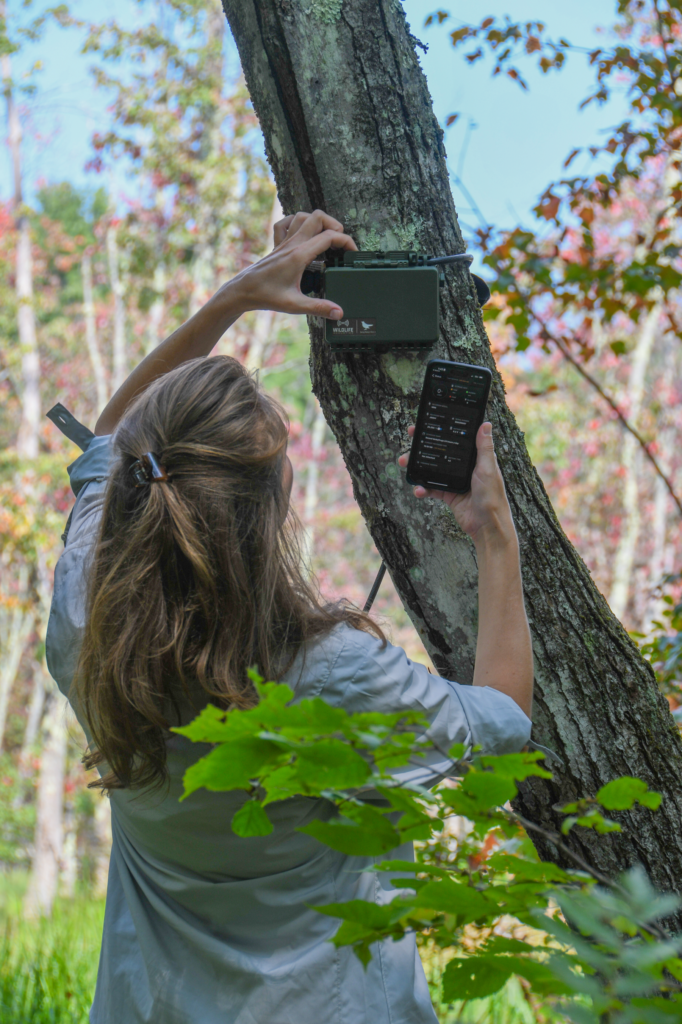
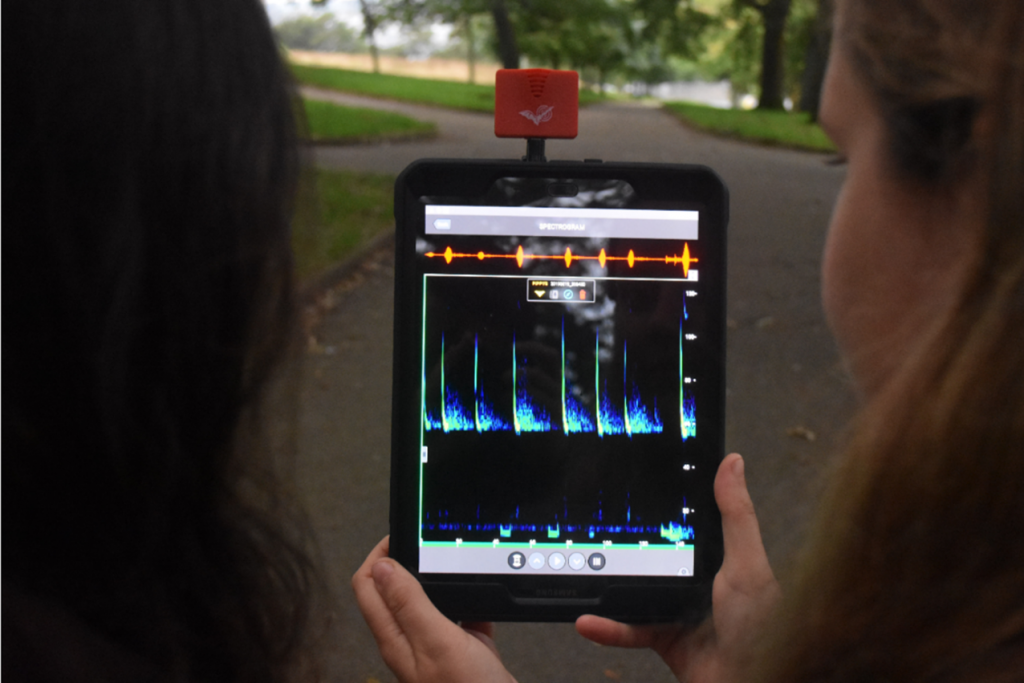
Wilder Sensing was founded to ensure that anyone can collect high-quality, long-term biodiversity data. There are many different ways of doing this, but we focus on sound. By recording 24/7 for weeks, or even months, you can build up a very rich picture of what is present in an environment. The technology we use is low-cost with limited bias, and it is easy to use, even for non-professionals. It’s not perfect, especially because we are focusing on birds at the moment. Not all birds make much noise – some make very subtle noises which we can’t pick up – but for most species it works well.
Can you tell us about the capabilities of Wilder Sensing technology and the insights that it can provide for a given environment?
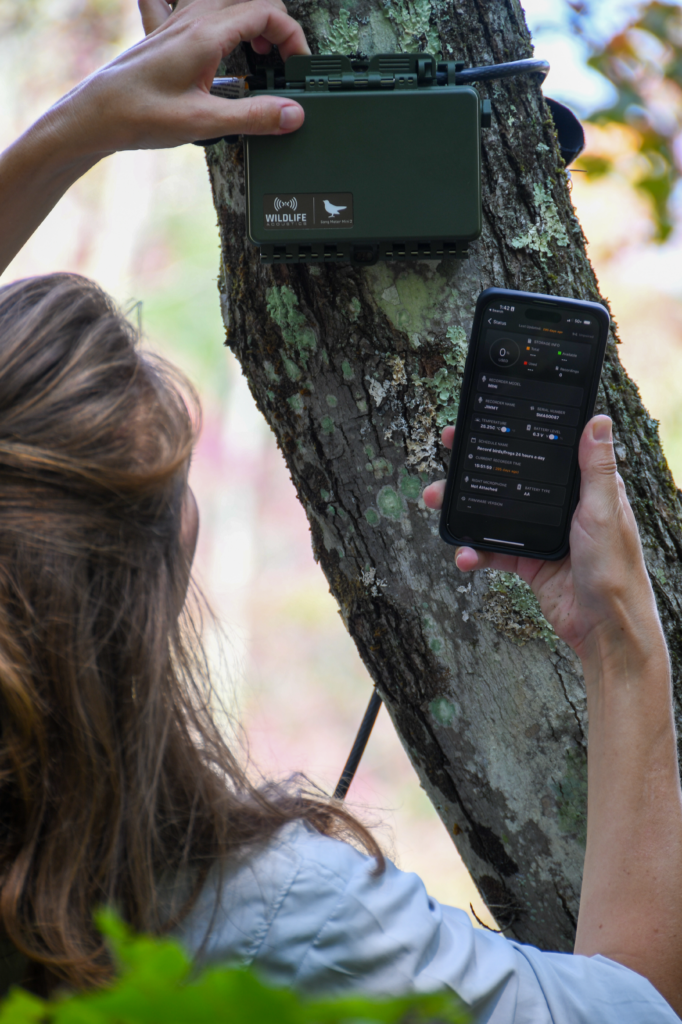
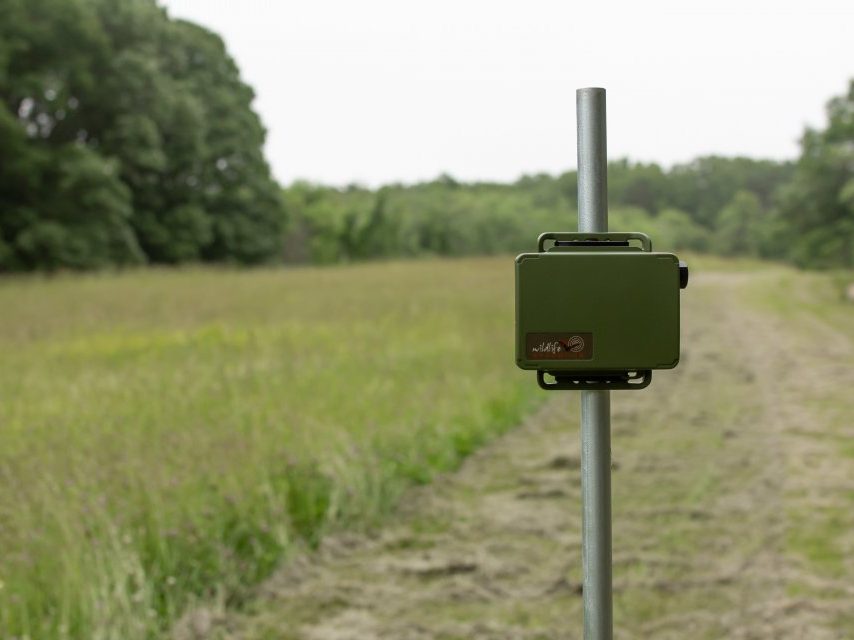
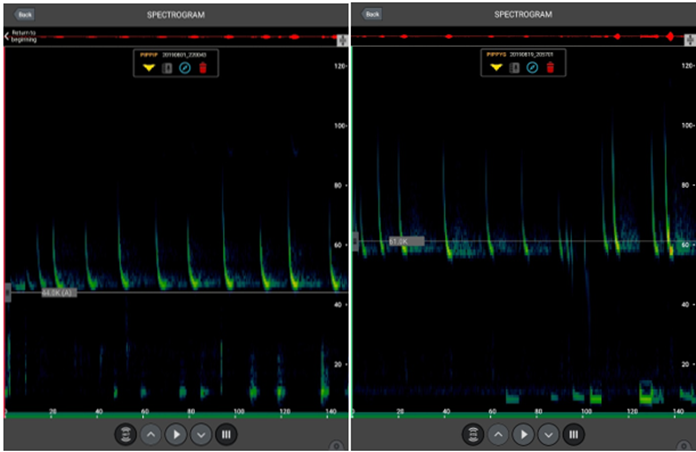
We work with our customers to agree on survey patterns and how many recorders should be deployed on each site. The customer uploads their audio files to our website, and once they have arrived, we automatically process them using machine learning. It takes us around 20 seconds to process an hour-long file, and we can process many in parallel. During this, the technology checks every three seconds to see if a sound has been detected – every sound gets a species match, and a probability is assigned. So, for instance, the technology will be 92% certain that it has detected a Robin. Through this, we can give a species richness assessment, which is a species list at the moment. Our technology is currently unable to tell us how many individuals there are in a given space – there could be one very noisy bird, or ten very quiet ones.
However, bioacoustic surveying technology does not remove the need for ground truthing. It is still important to get the baseline. Ecologists will find species that we don’t pick up. And the converse is true as well. We can find 20-30% more species when combining acoustic and traditional surveys. We are also working on other approaches for the future, like triangulation, which could identify exactly where a sound is coming from.

Over 45,000 records were species-matched in the Peruvian Amazon. Image by Wilder Sensing.Can you tell us about the current projects that you are involved in and the role that bioacoustics played in conservation?
We’re involved with a whole raft of different projects. We are working with environmental consultancies, Wildlife Trusts and NGO’s using acoustic technology for long-term surveying. Wendling Beck in Norfolk is a site that we have been working on for around 18 months. We realised that Skylarks are using one small part of the site, but you don’t see this until you look at the data – when you are just walking around, you don’t make that connection. If you look at some species, you might think that you have a ubiquitous habitat, but when you start looking at the distribution of birds and their calls, you may find that there are many times more calls in one part of the site. If you were to redevelop an area, you would probably lose some species altogether, but going into a development project, knowing that’s a likely ecological consequence, is really important and that is why acoustic technology is so valuable.
What is the future for AI in conservation? Where do you think its applications could take us over the coming years??
I think it has a lot to contribute. To get good, accurate data you need highly skilled ecologists, people that really understand bird sound – it takes years to build those skills. I think the role will change so that ecologists will get more involved in survey design and interpreting the data to understand the consequences of a project. It becomes much more evidence-based and more quantitative. We have some customers who deploy up to 20 recorders, and you can get a quarter of a million acoustic records on each device. With that amount of data, you can start to ask different questions and we can see all kinds of behaviours that we couldn’t see before.
In the South-west, some farmland was purchased to develop into allotments and after digging, they found that Skylarks were nesting on-site. Biodiversity Net Gain (BNG) does not look at species, so a habitat survey would not record Skylarks in the area. If acoustic recorders had been deployed on site, ecologists would know they were present – so well-rounded data will also help developers plan better, mitigating issues from the onset of construction. The BNG survey was designed to be consistent and relatively easy to use, and species surveys could prove to be more difficult because of inconsistencies and methodologies etc. With AI we can move to a new level of understanding. If you just stick the recorder out, it is consistent in how it works and removes bias.

For those interested in bioacoustics, it is worth noting that you will be holding webinars from July. What can we expect from these sessions?
We have three sessions lined up. The first one is on 7th July and is about measuring nature using sound. It’ll dig into both how the technology works and how it compares against other methods, and hopefully we’ll have an open discussion around its strengths and weaknesses. The session is intended for people who are interested in the subject, and we will go through some examples.
This will be followed by two in the autumn, which are more technical and are perhaps more suited to professional ecologists. These sessions will be touching on some of the technology behind Wilder Sensing and some of the ways it should and shouldn’t be used.
What is Wilder Sensing hoping to achieve over the next decade?
I am hoping to move onto other taxa, the obvious ones being insects and bats. We would also like to look at triangulation as well – if we can triangulate how birds and bats are using a landscape, we can use this to help inform better environmental management. I think this data will be used with other environmental data in the future. People doing nature restoration or project planning need to understand the water quality, air quality, the climate etc. to get a better environmental outcome. And even forward-looking companies, we can look at their supply chain as well.

Increasingly the media are reporting on the quietening of British soundscapes, a symptom of the biodiversity and climate crisis we are facing. How do you think Wilder Sensing will adapt to an increasingly quiet environment? Will technology need to adapt to keep up?
Wilder Sensing technology will quantify exactly what is happening in the biodiversity crisis. I have a copy of the iconic Silent Spring by Rachel Carson, which was published 60 years ago, and we haven’t learned from that. I think this type of technology will hold a mirror up to people to show exactly what is going on. I would love to get a good quality recording from 50 years ago, maybe two or three hours of dawn chorus in woodland, and go back to the same time of year in the same place (assuming it still exists) and compare it. Showing exactly that this is the difference in diversity.
To find out more about the innovative work by Wilder Sensing, their blog features some interesting case studies on the applications of their technology and they are also active on LinkedIn. For more information on Wilder Sensing and their product, email info@wildersensing.com.




 What has stayed the same?
What has stayed the same?



















 Kaleidoscope Pro is now available as an
Kaleidoscope Pro is now available as an