The NHBS team are passionate about nature and conservation, and to help them to get involved with local volunteer schemes, NHBS encourages colleagues to apply for up to three paid days each year to volunteer with a conservation project or organisation of their choice. Catherine Mitson, Assistant Editor for British Wildlife and Conservation Land Management, tells us about her time volunteering with Buglife and the bee species she is surveying.
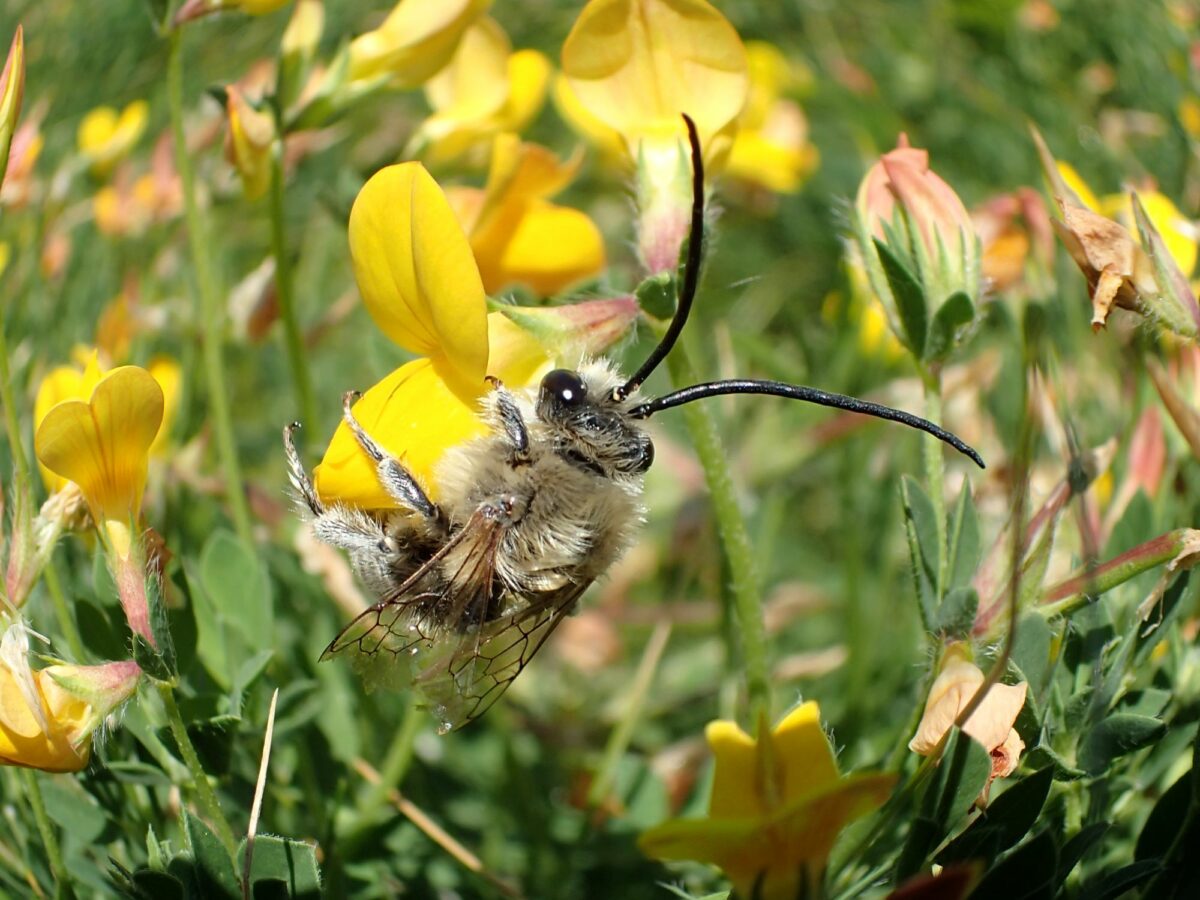
The Long-horned Bee Eucera longicornis truly lives up to its name. The males sport bizarrely long antennae, and this in combination with their large size makes them instantly recognisable. Female Long-horned Bees, however, lack these oversized antennae and are more robust compared to the males, and can sometimes be confused with Anthophora (flower bees) species. Although the Long-horned Bee is a type of solitary bee and each female will dig her own nest hole, they tend to nest in aggregations in a variety of habitats, such as woodland rides and clearings, brownfield sites and coastal meadows. Here, however, we are focused on the south-facing soft cliffs along the South Devon coastline.
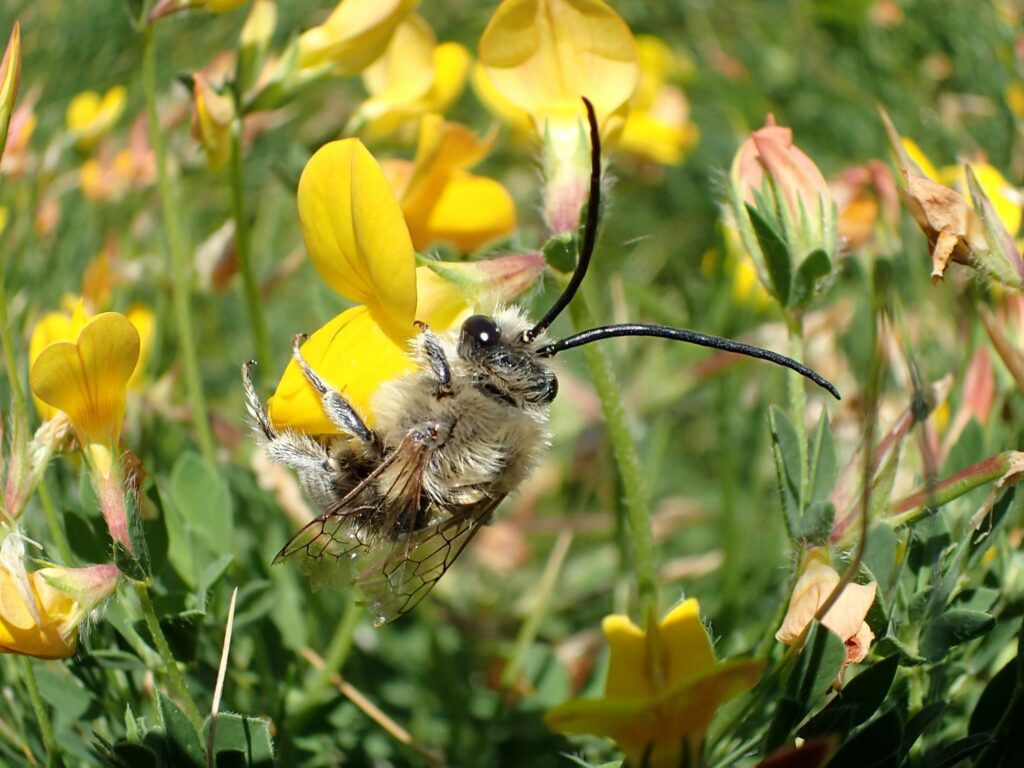

Prawle Point SSSI is a fantastic site for invertebrates, including the Long-horned Bee which can be found nesting in the cliff face or foraging on plants such as clovers, Bird’s-foot-trefoil and Narrow-leaved Everlasting-pea along the cliff top. What makes Prawle Point even more special is that it is the only site in the UK where the Long-horned Bee’s cuckoo, the Six-banded Nomad Bee Nomada sexfasciata, is known to be found. Like the bird, cuckoo bees lay their eggs in the nest of another bee, the host, and once hatched the larvae will eat the food stores that had been gathered by the host for its own larvae.
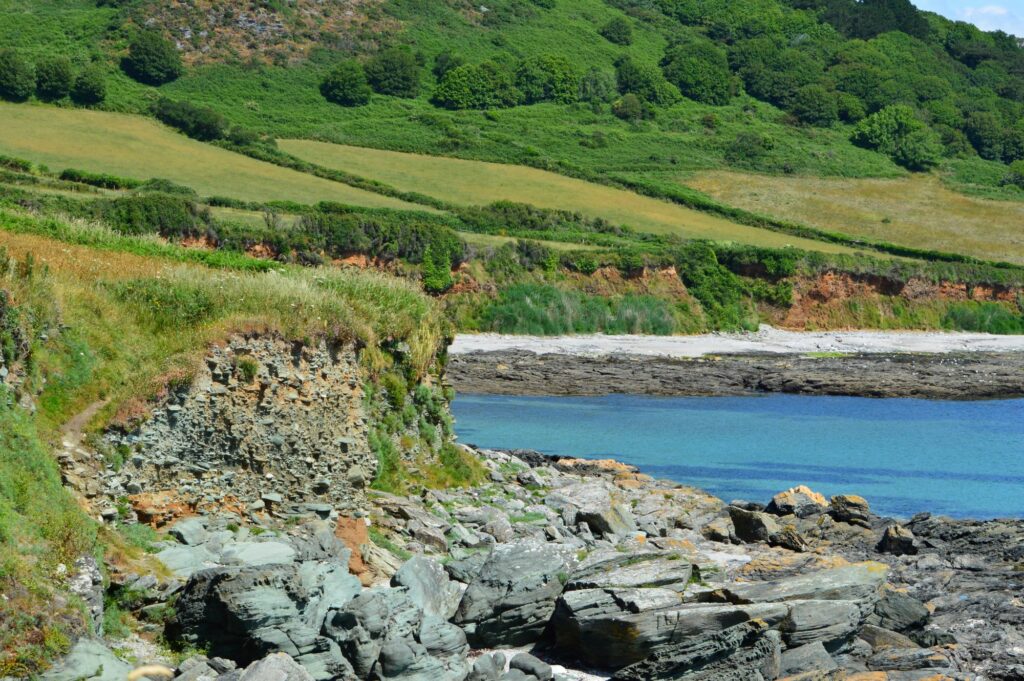

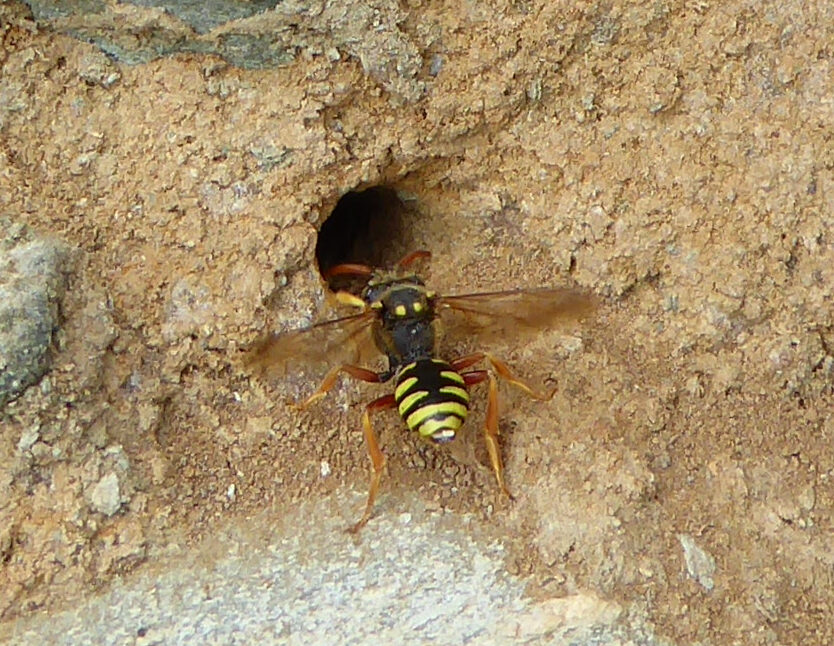
The Six-banded Nomad Bee is arguably the UK’s rarest bee, and relies on a healthy, viable population of its host. Sadly, due to the loss of flower-rich grassland, the Long-horned Bee has declined dramatically; once found in most southern English counties, its range is now restricted to the south coast of England and Wales with a few scattered inland sites. But a new project is hoping to turn the tide for the Long-horned Bee, the Six-banded Nomad Bee and many other rare invertebrates along the South Devon coast.

Life on the Edge
Life on the Edge, funded by the National Lottery Heritage Fund, is an exciting new partnership with South Devon Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, Buglife, National Trust, Torbay Coast and Countryside Trust, and the South West Coast Path Association. Focused on the South Devon coast between Berry Head and Wembury, Life on the Edge is aiming to restore viable populations of some the UK’s rarest invertebrates, including the Six-Banded Nomad Bee, by expanding and reconnecting the vital coastal habitats on which these species depend. There are 30 invertebrate species that this project will support, such as the Moon Spider, Great Green Bush-cricket, Mediterranean Oil Beetle and the Devon Red-legged Robberfly, but of course, by improving and expanding the habitats used by these species, a plethora of wildlife will benefit.

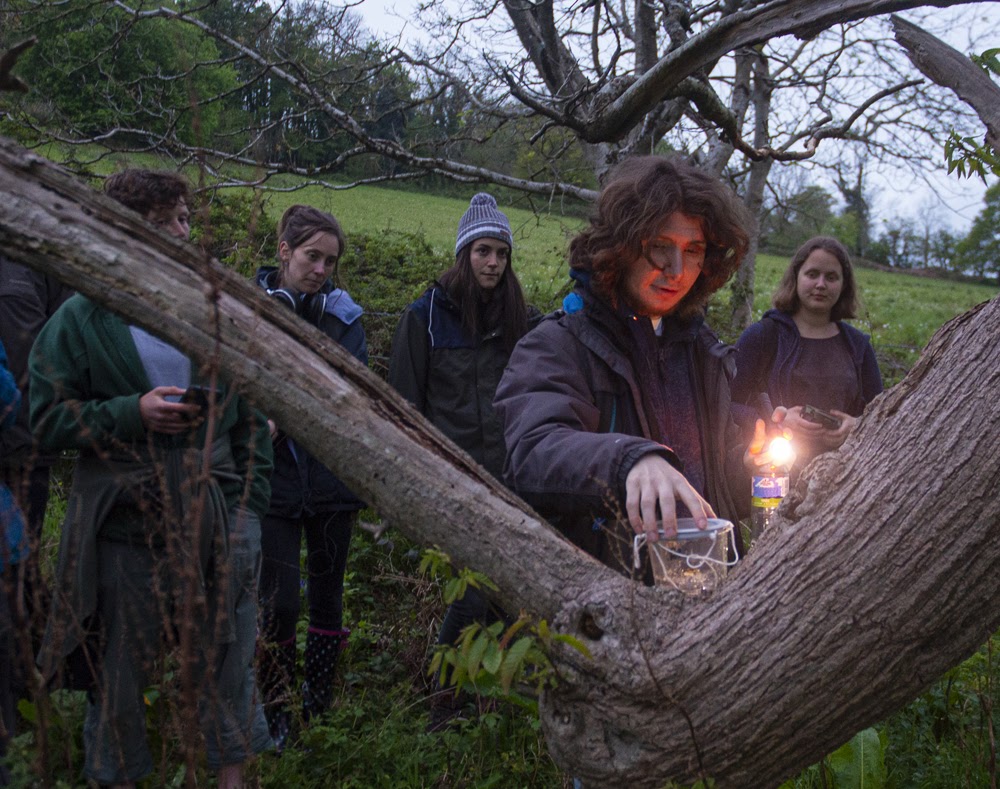
Buglife will be working alongside its project partners to create opportunities for local communities, landowners, parish councils and schools to get involved via volunteer days, habitat management and creation workshops, wildlife gardening and species monitoring. The project is currently in its development phase and is focused on public consultation and species and habitat monitoring – this work will help to secure funding for the next phase of the project.
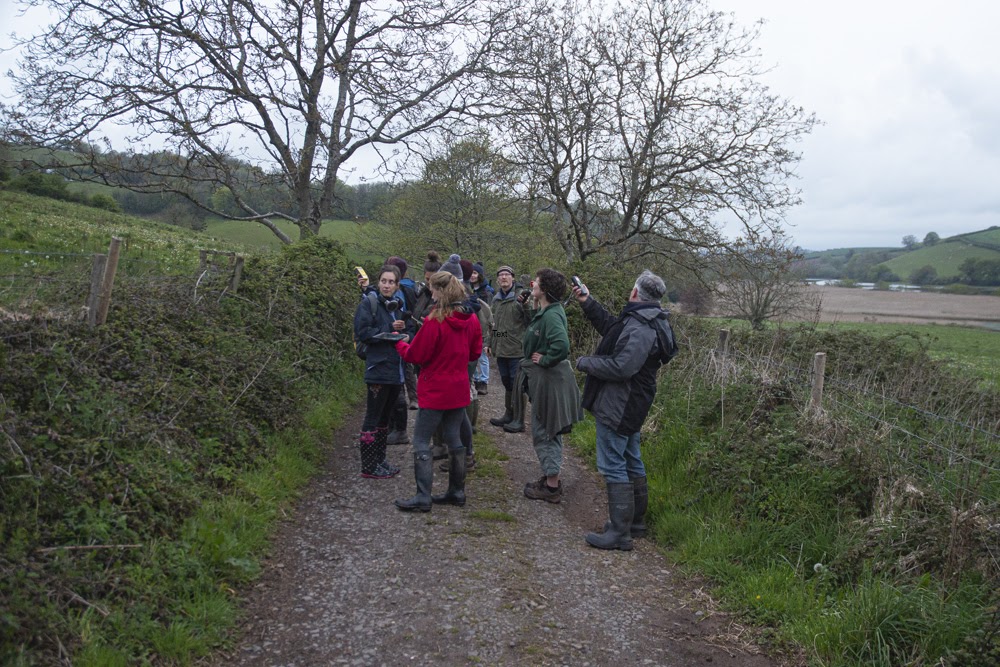
NHBS conservation volunteering day
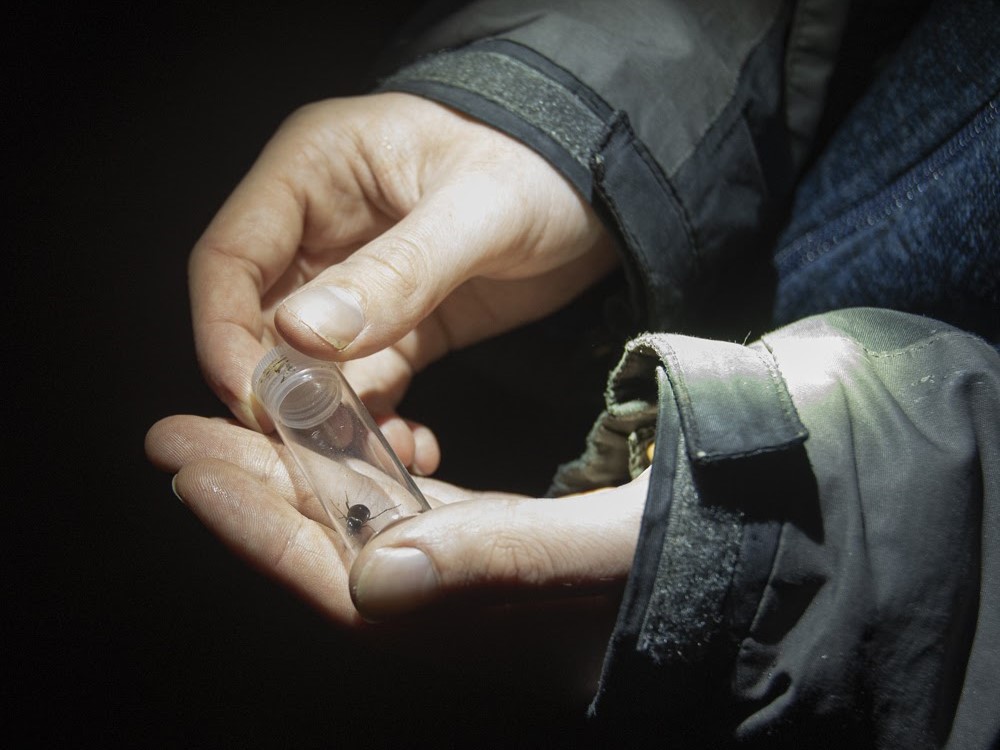
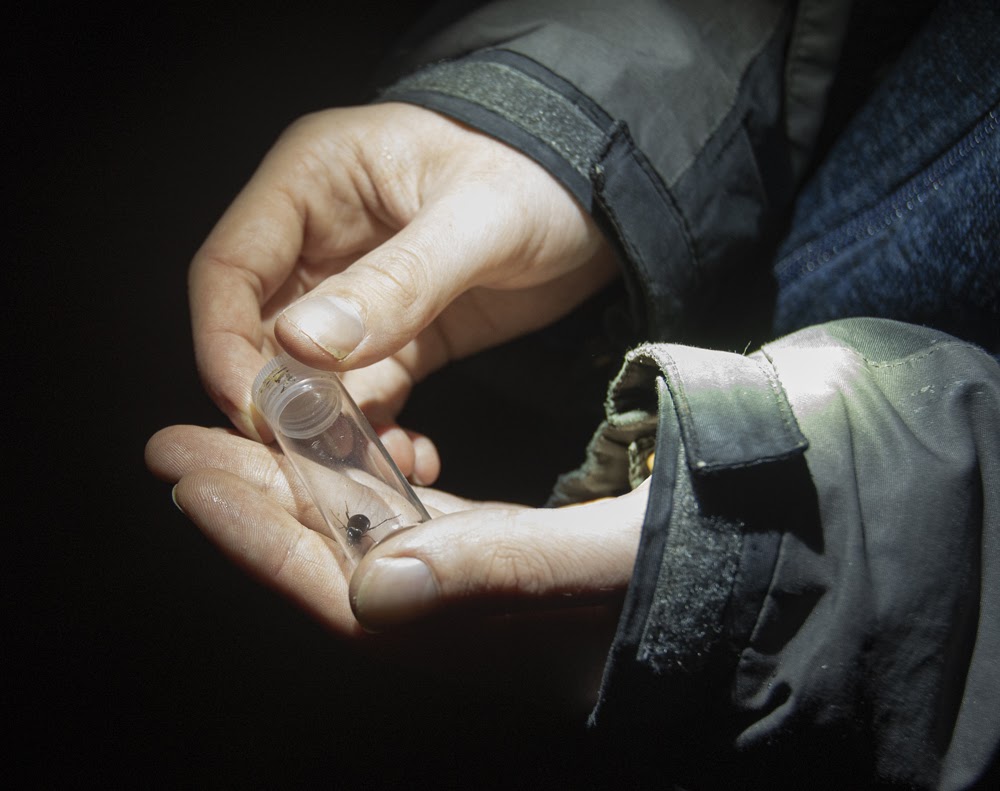
My role as a volunteer is to undertake surveys throughout the flight season of both the Long-horned Bee and its cuckoo between May and July and record the number of individuals seen along this stretch of coast, with a particular focus on known nest aggregation sites and the coastal path between Gara Rock and Mattiscombe Sands. The survey consists of slowly walking along the coastal path, stopping to count Long-horned Bees when I see them. I record the number of males and females, the location/grid reference, and any extra information that may be useful, such as the plants that they are feeding on.
It was wonderful to see so many Long-horned Bees foraging along the cliff top throughout the day. As mentioned above, they tend to favour plants such as Bird’s-foot-trefoil, clovers, Narrow-leaved Everlasting-pea, brambles and Kidney Vetch, and there are sections of the coastal path where these can be found in abundance. Unfortunately, these plentiful patches are in short supply, and Buglife hopes to identify the key areas for habitat enhancement to support the population of Long-horned Bees, which will in turn benefit the Six-banded Nomad Bee.
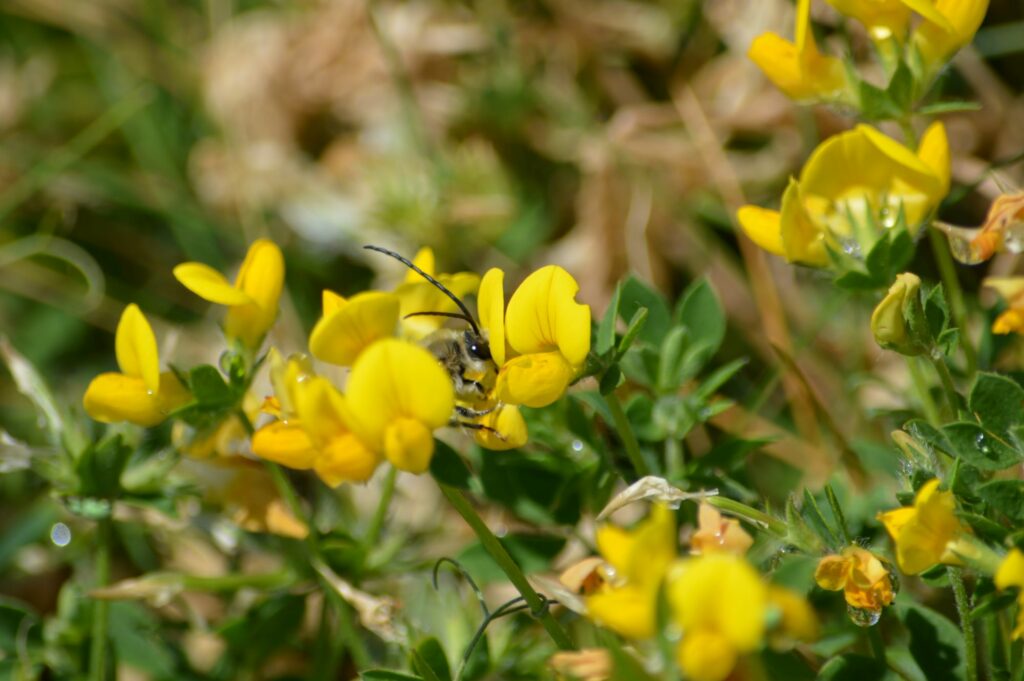

The highlight of the day was watching one nest aggregation in particular, a site that we have become quite familiar with over the years. It is always a bustling hub of activity and is primarily where the Six-banded Nomad Bee has been recorded in the past. Female Long-horned Bees were repeatedly flitting in and out of the nest entrance holes, with the occasional male patrolling the nest entrances in search of a mate. Sadly, I did not see the Six-banded Nomad Bees this time but was pleased to count a total of 75 Long-horned Bee sightings throughout the day.
I have been involved in monitoring this site since 2017 and so it was wonderful to have the support of NHBS to spend some time at Prawle Point to contribute to this year’s records. It is vital that monitoring along this stretch of coastline continues, especially as our records of the Six-banded Nomad Bee are so few. To find out more about Buglife, the conservation projects they are currently involved in and how you can get involved, visit www.buglife.org.uk.
References
Saunders, P. 2018. Conservation of the Long-horned Bee in Cornwall. British Wildlife 29: 321–327.




















































































 Advanced Bug Hunting Kit
Advanced Bug Hunting Kit



















