There are six owl species in the UK, although only four are native (barn, tawny, long-eared and short-eared owl). We also get occasional visitors, such as the snowy owl (Nyctea scandiaca).
Owls are mainly nocturnal and feed on predominantly small mammals such as the field vole (Microtus agrestis), but also some small birds, invertebrates, amphibians and fish. All these species are listed as ‘least concern’ by the IUCN red list but face serious threats in the UK, such as habitat loss, declining prey populations and a decrease in nesting sites, as well as direct deaths such as from car collisions or poisoning. Owls can be used as an indicator species for the health of the food chain: their decline may indicate that other wildlife that also depend on the same habitats are also under threat.
Identification of owl species usually relies on colouration and eye colour, as well as their call. This is particularly important as owls are often active at night and therefore are hard to identify by sight.
There are several types of equipment that can be useful when searching for owls, such as binoculars, night vision monoculars, a headlamp or flashlight and a guide to owl pellet identification. If you wish to encourage owls onto your land, there are a variety of nest boxes available, depending on the species you wish to attract.
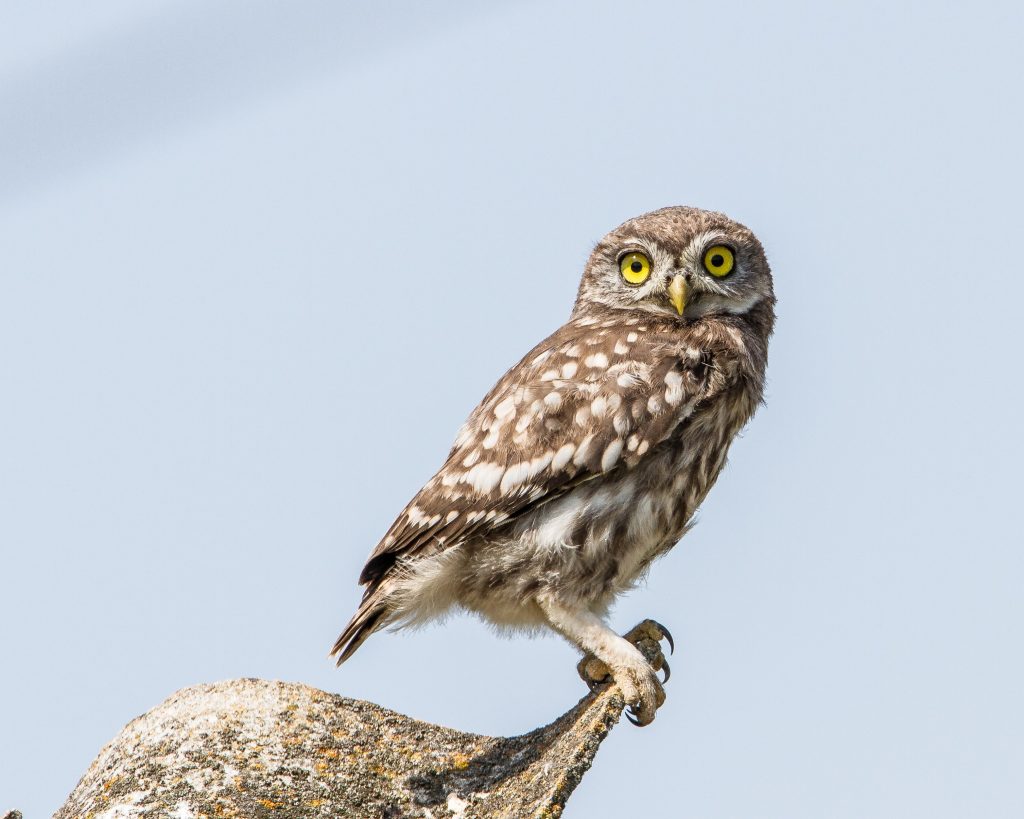
Little Owl (Athene noctua)
Distribution: Widespread throughout England and parts of Wales. Rare in southern Scotland
What to look for: The little owl is a small species, with brown and white feathers in a dappled appearance. It has a short tail and bright yellow eyes. Usually out at night, it is most likely to be seen perched on structures such as trees, telegraph poles and fences.
Did you know? The little owl is non-native in the UK and was introduced in the late 1800s. It is not thought to cause any detrimental impacts on any other species.

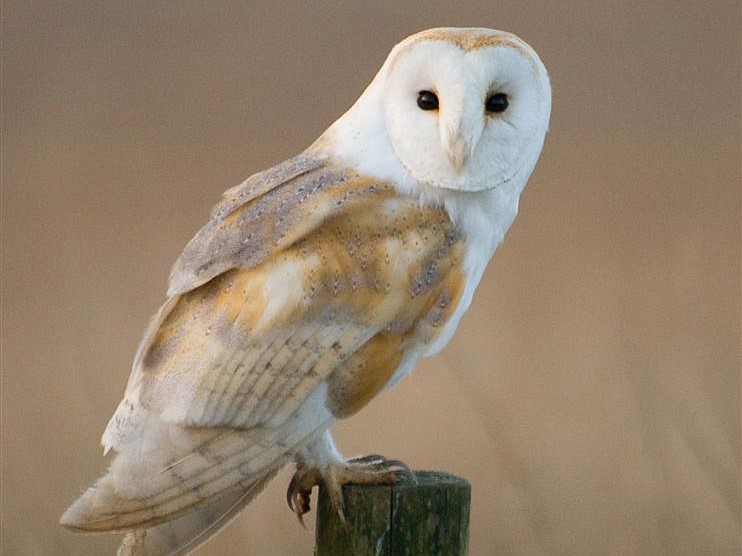
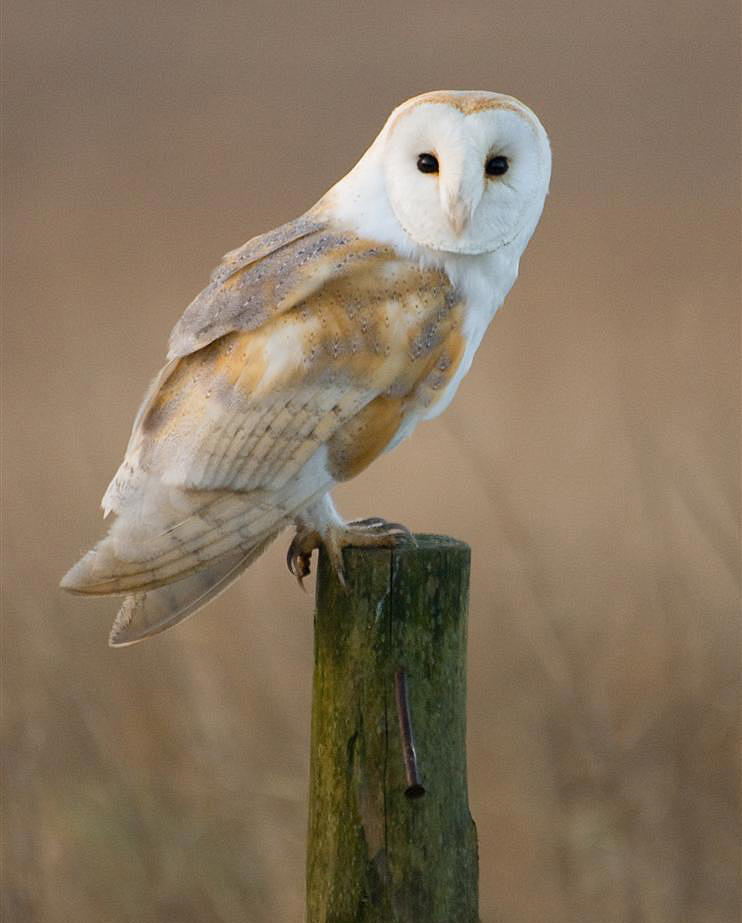
Barn Owl (Tyto alba alba)
Distribution: Widespread across England and Wales, with decreasing density towards north Scotland and scattered distribution in Ireland
What to look for: An iconic species, the barn owl is instantly recognisable. Its silver and golden-brown back and pure white underside and face are distinctive, along with its heart-shaped face and black eyes. Its face shape plays an important function for hunting, as it directs high-frequency sound to their ear openings, such as those produced by mice and voles. This helps the barn owl to perform precision hunting in tall vegetation. Another subspecies, Tyto alba guttata, which has a darker coloured underside, also occurs in the UK.
Did you know? Owing to their large wing size compared to their body mass, and the structure of their feathers, barn owls fly almost completely silently.

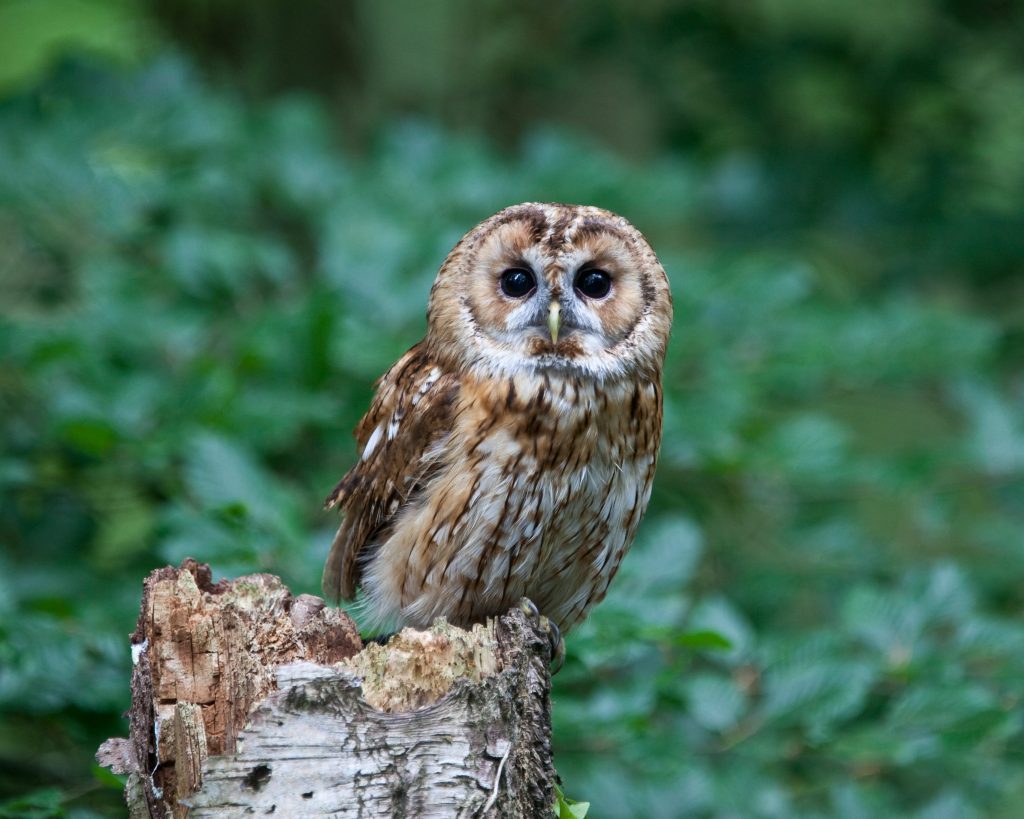
Tawny Owl (Strix aluco)
Distribution: Widely distributed in England, Wales, and parts of Scotland, but not in Northern Ireland
What to look for: The tawny owl has mottled brown feathers with flecks of white and more reddish-brown. Its colouration can vary from brown to grey. This species has a paler underside and a round head, with large black eyes and a dark ring pattern around its face.

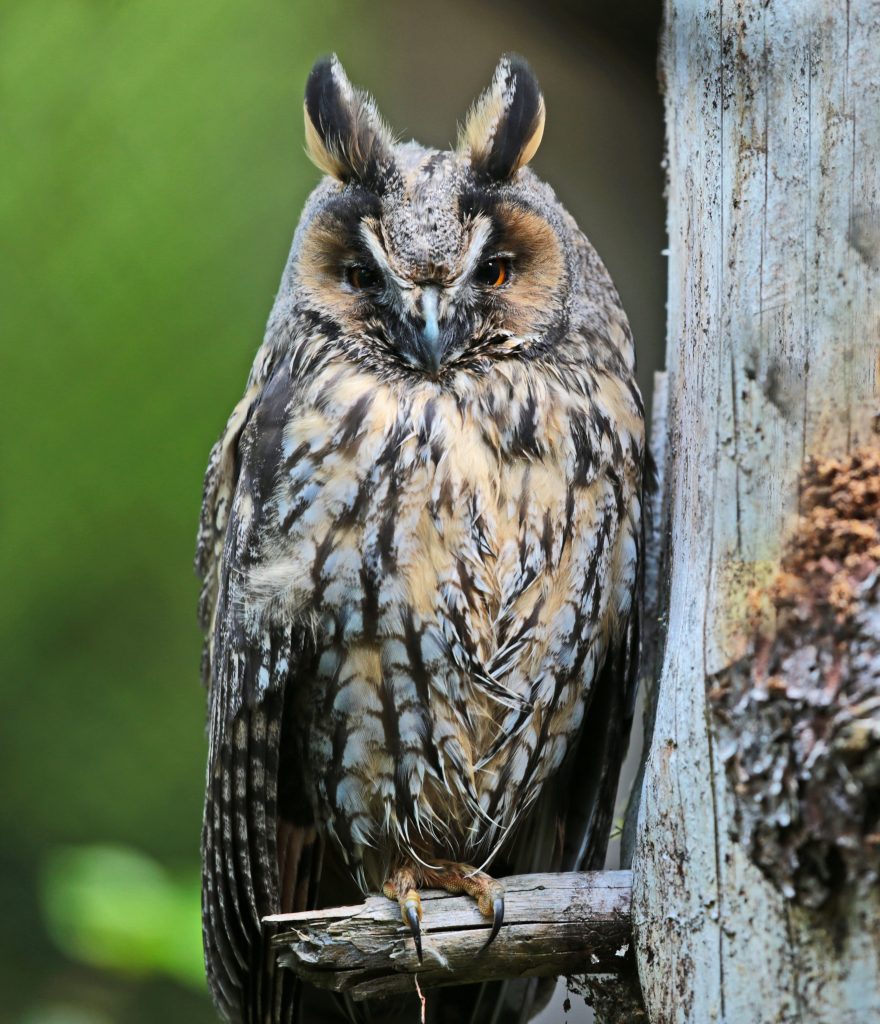
Long-Eared Owl (Asio otus)
Distribution: Widespread across the UK, although fewer individuals in Wales and south west England.
What to look for: This mottled brown species has bright orange-red eyes and long tufts that resemble ears, hence the common name. The long-eared owl is a shy, nocturnal species that can be found in communal roosts in densely covered woodland and forests. The population is boosted in winter due to numbers of migrating individuals from other parts of Europe.

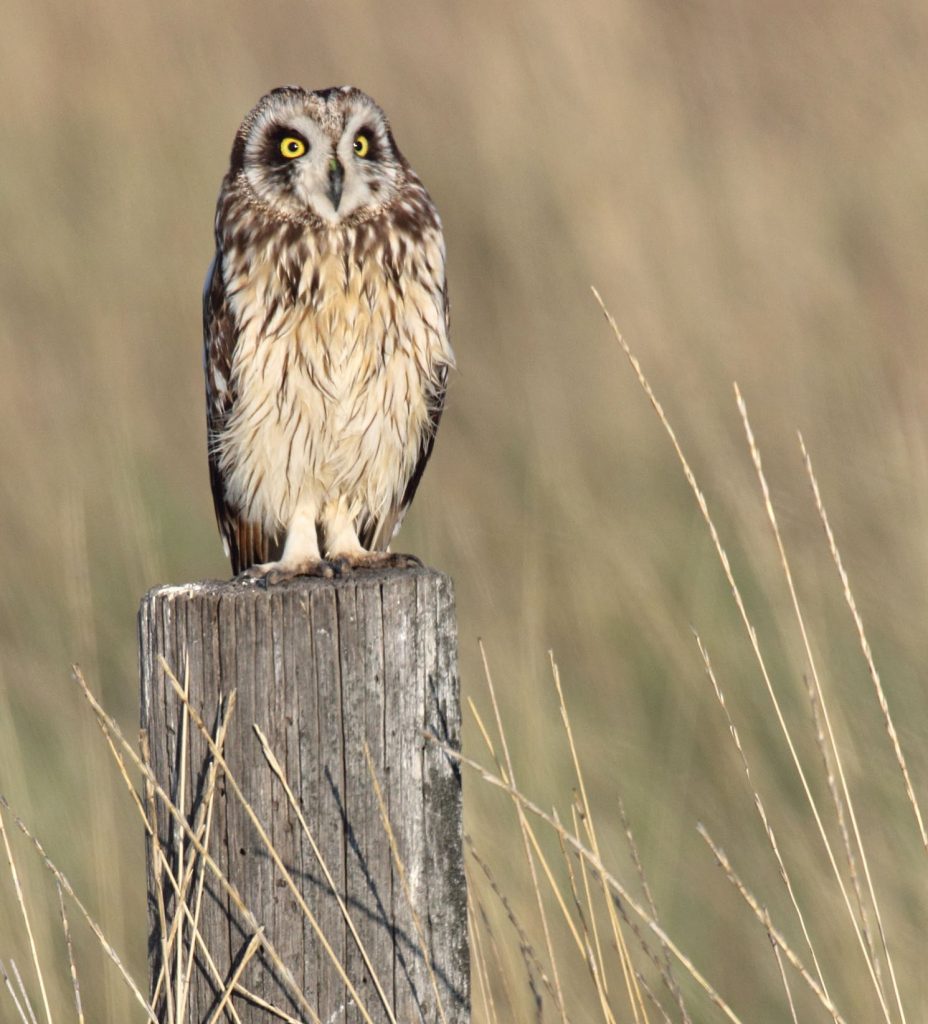
Short-Eared Owl (Asio flammeus)
Distribution: Migratory species, found across Scotland and northern England in summer before moving further south during winter.
What to look for: Often confused with the long-eared owl, this species is slightly slimmer, with a paler colour and yellow eyes rather than the long-eared owl’s orange. It has brown feathers on its back and a pale belly, with darker feathers framing its eyes. They also rarely display their ‘ear’ tufts.

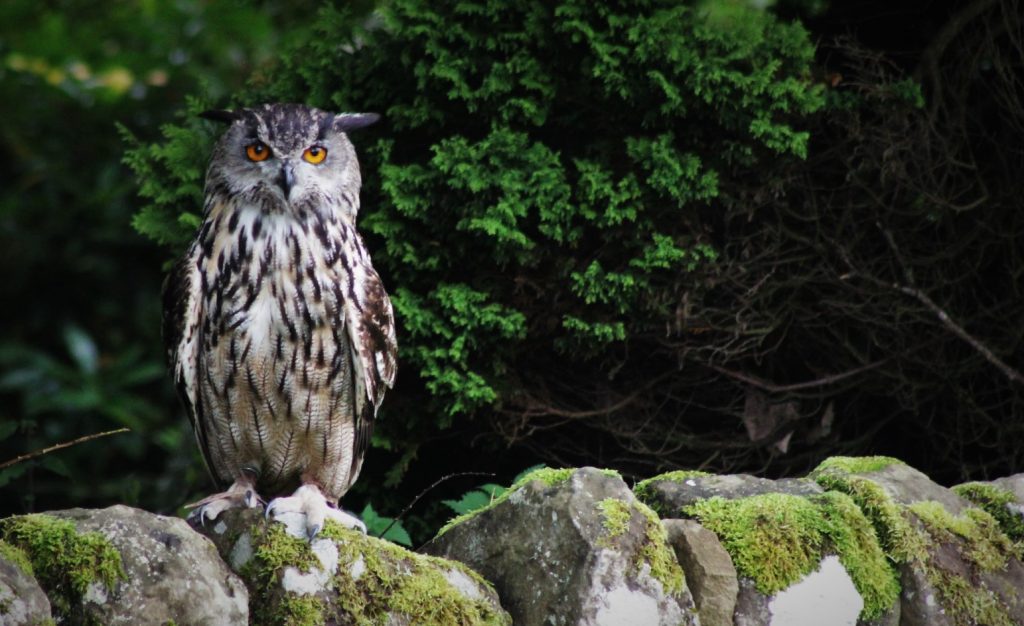
Eurasian Eagle-Owl (Bubo bubo)
Distribution: Very rare, scattered around the north of the UK, including Lancashire, Greater Manchester, Galloway, and Inverness-shire.
What to look for: The Eurasian eagle-owl has tufts similar to the long-eared owl. It is a large bird, weighing up to 4.6kg compared to the barn owl at 500g. This species is mottled, but there is a high variation in plumage colouration for this species, from browny-black to a pale grey. There is often a dark band running from the eye to the ends of the ‘ear’ tufts. It may have pale sections around the eyes and beak, with a darker, splotched forehead.
Did you know? There is serious debate surrounding this owl species and its place in the UK countryside. While there is fossil evidence that suggests this species inhabited the UK before becoming extinct, many don’t believe it is a native species. Therefore, the conservation of this species and the safety of the individuals present in the UK is under threat.