Persecuted mercilessly in Britain, the magnificent Osprey became extinct in the 1890s. However, the return of the species to Scotland in the 1950s was the catalyst for reintroduction programmes elsewhere, and this remarkable raptor is now an increasingly common sight in our skies. This Poyser monograph includes over 150 photographs and details the distribution, migration, foraging ecology, breeding behaviour and population dynamics of this spectacular bird. It also places emphasis on the conservation efforts across the species British and African haunts, the latter of which has only recently been discovered thanks to satellite tagging technology.
Persecuted mercilessly in Britain, the magnificent Osprey became extinct in the 1890s. However, the return of the species to Scotland in the 1950s was the catalyst for reintroduction programmes elsewhere, and this remarkable raptor is now an increasingly common sight in our skies. This Poyser monograph includes over 150 photographs and details the distribution, migration, foraging ecology, breeding behaviour and population dynamics of this spectacular bird. It also places emphasis on the conservation efforts across the species British and African haunts, the latter of which has only recently been discovered thanks to satellite tagging technology.
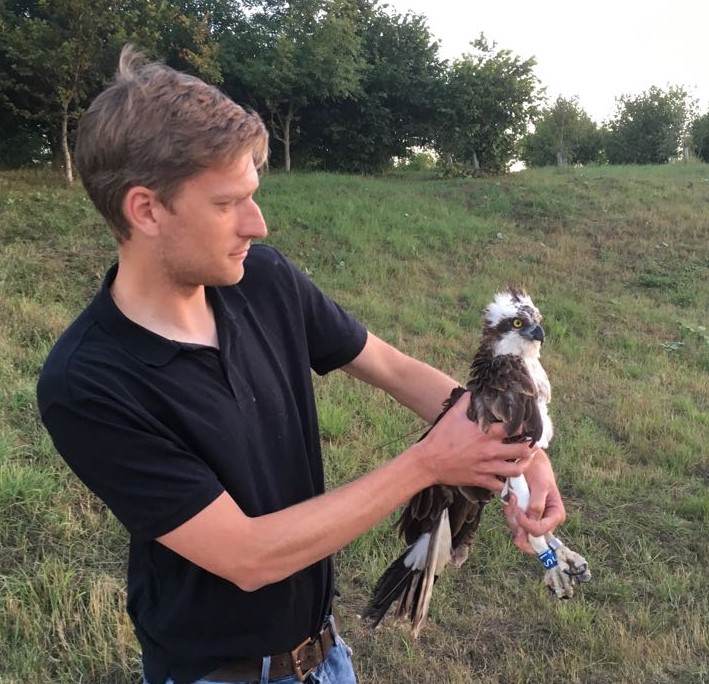

Nature conservationist Dr Tim Mackrill completed a PhD on Osprey migration at the University of Leicester and has since worked with the Roy Dennis Wildlife Foundation on various reintroduction projects, including the return of Osprey’s and White-tailed Eagles to England. He managed the Rutland Osprey Project for over ten years and is the founder of the Osprey Leadership Foundation, which aims to inspire the next generation of conservation leaders by working with young people who live along the Osprey’s migratory route.
We recently had the opportunity to speak to Tim about The Osprey, including why he is so captivated by this species, the technological advances that have helped increase our knowledge of them and more.
Your entire adult life, and indeed much of your childhood, appears to have been spent observing and studying Ospreys. What is it about this species that so captivates you?
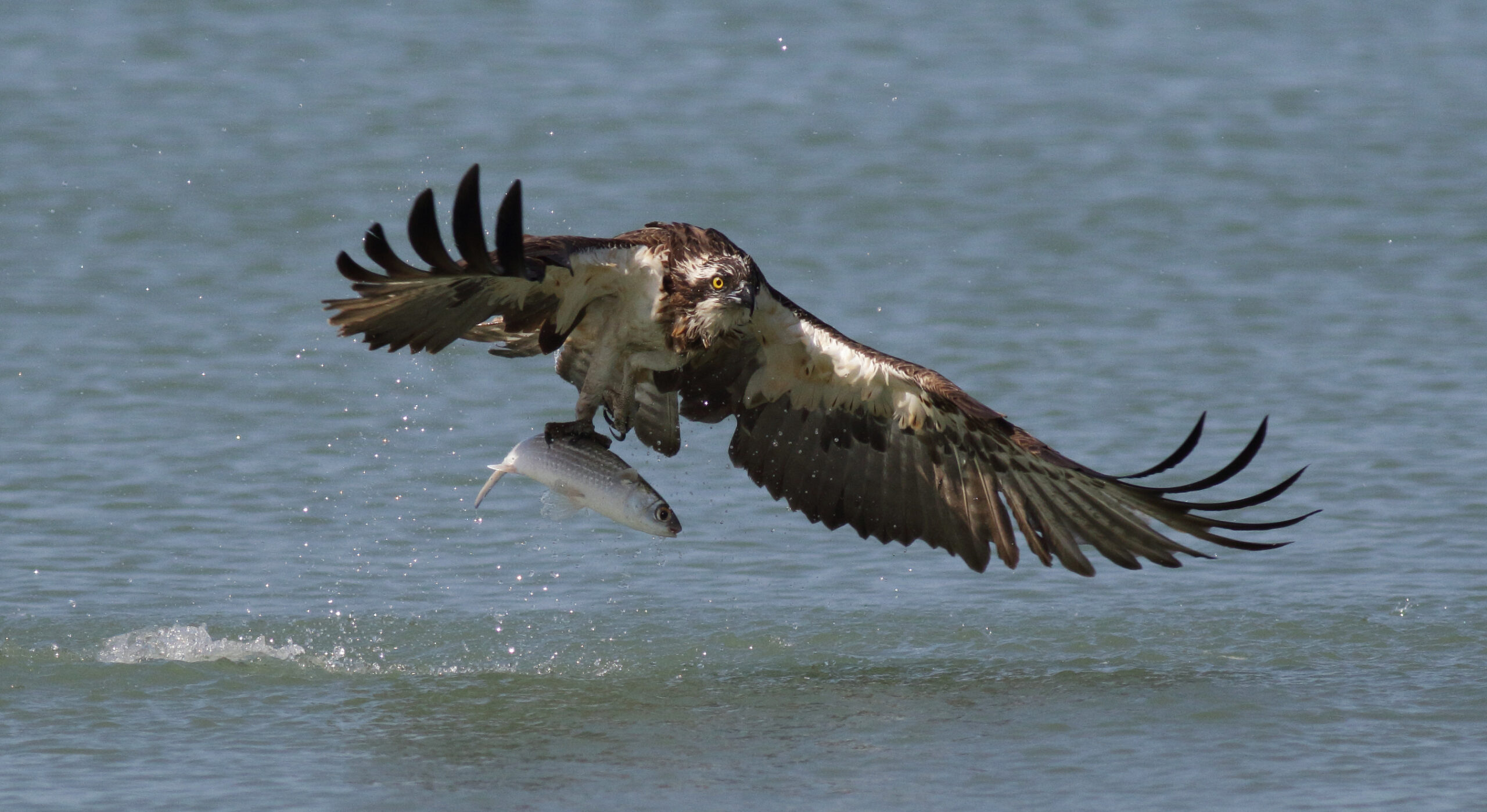
Anyone who has seen an Osprey will vouch for the fact that they are a spectacular bird, particularly if you have been fortunate enough to see one plunge into water to catch a fish. However, it is the species’ migration that I find so captivating. As I write in chapter 6 of The Osprey, whenever I see a newly arrived Osprey perched beside its nest in the spring, I always think it is rather humbling to consider what the bird might have experienced since leaving its wintering site a few weeks earlier: traversing the Sahara, negotiating imposing mountain ranges, crossing areas of open sea. It could even have flown through the night – its path illuminated only by stars and moonlight – with the urge to reclaim its nest– a source of great motivation to power its way north. The fact that Ospreys are faithful to the same nest site each year, and that we know them as individuals, makes it even more special to see a familiar bird back home in the spring.

In the introduction of your book, you mention that there can be few bird species that are as well studied as the Osprey. What technological advancements over the past few decades do you think have been most influential in increasing our knowledge of this species?
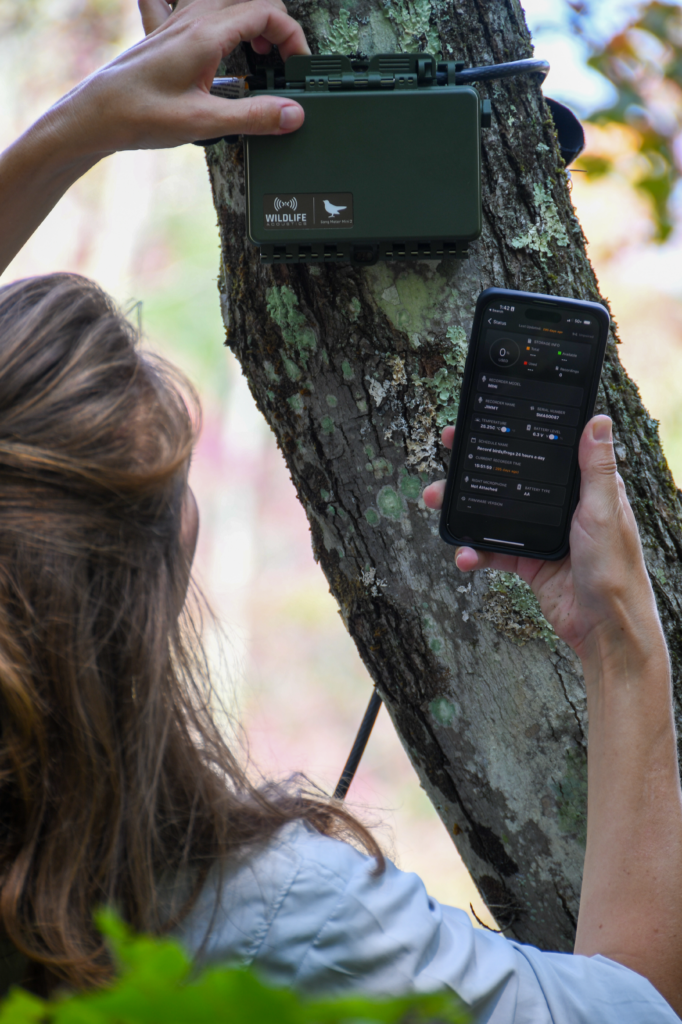
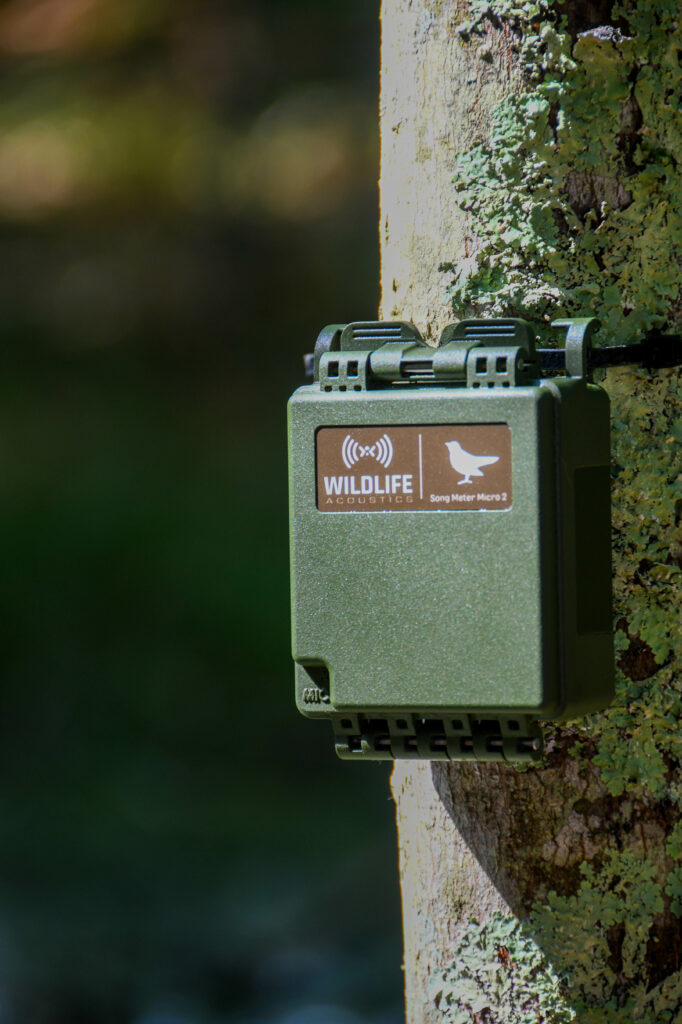
The advances in satellite tracking technology since the 1990s have added greatly to our knowledge of Ospreys. The most recent transmitters are able to log data at very high temporal resolution – as often as once per second in some cases – and this gives some amazing insights into the migratory journeys of individual Ospreys. It has shown how Ospreys are able to adapt their flight according to environmental conditions, and to make very long sea crossings – something that most raptors avoid. It has also demonstrated how experiences on the first migration shape the subsequent migratory habits of individuals, and also how young birds enter the breeding population for the first time.
Historically, the persecution of Ospreys has been a large problem within Britain. Is this something that is still an issue?
Fortunately, this is much less of an issue now. Egg collecting was a major threat during the early years of the Osprey recovery in Scotland, but has declined since the introduction of custodial sentences. Historically, persecution at fishing ponds was a major cause of the population decline of Ospreys in the British Isles, and although the occasional Osprey is still shot, the sight of an Osprey plunging into the water at great speed, and then lifting off a few seconds later with a fish grasped in its talons, is much more likely to excite and inspire people than to create animosity. The success of an Osprey photographic hide at a working trout farm, Horn Mill, in Rutland is testament to that.
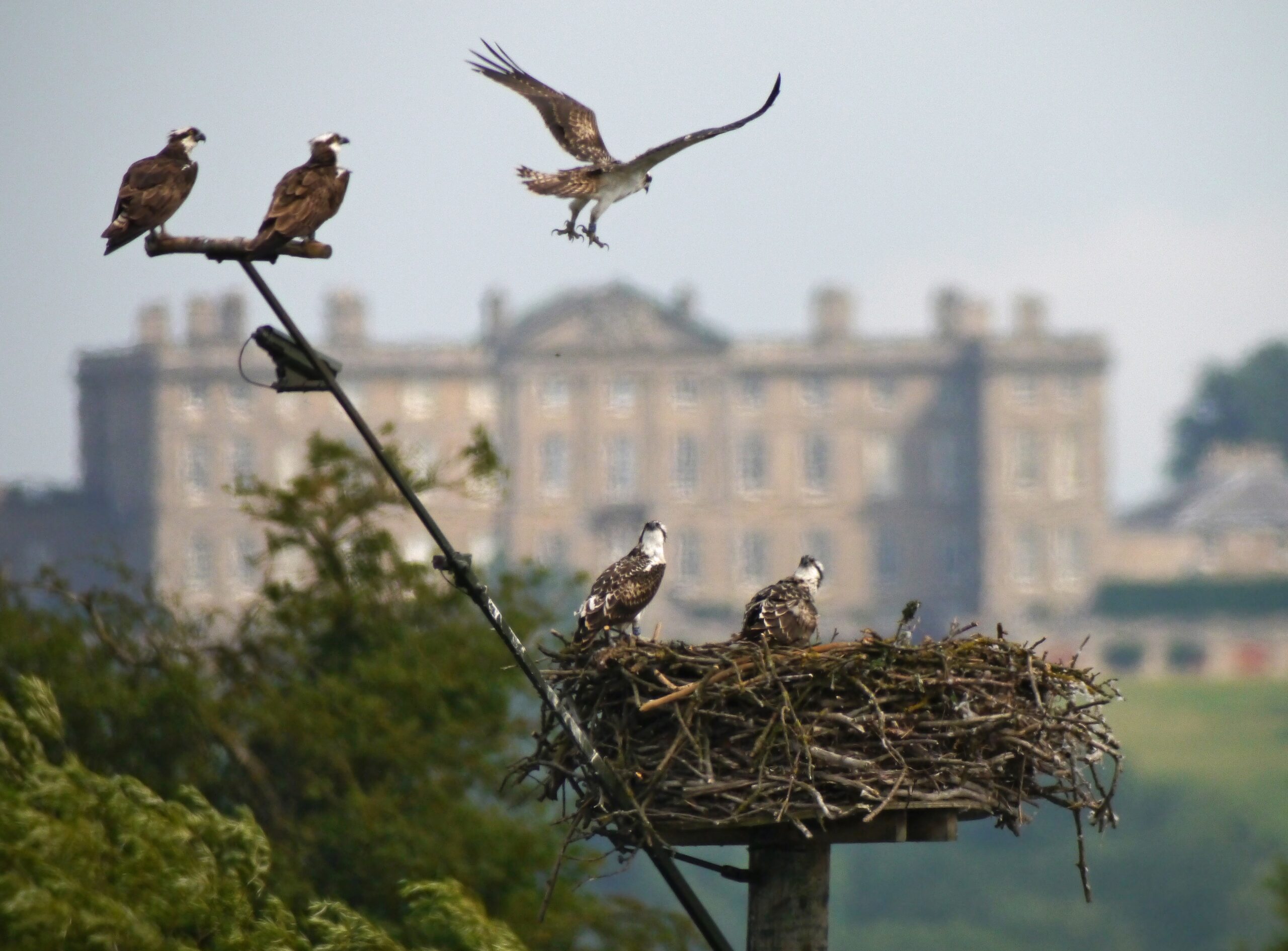

Ospreys appear to respond well to translocation projects. Is this down to the characteristics of their species, or because we have good quality research and evidence to indicate how best to undertake such projects?
Translocation has been a key tool in helping the Osprey recover from the negative impacts of historical persecution and DDT. The first Ospreys to be translocated were in the United States in the late 1970s and in Europe, at Rutland Water, in the mid-1990s. As such, a wealth of information on all aspects of the translocation process has been developed and refined over the years, which means that more recent projects are much better informed than earlier ones. However, it is the species’ own breeding biology that is key. Young Ospreys, particularly males, are highly site faithful and usually return to breed close to their natal site. The imprinting process seems to occur after fledging and prior to migration and so, by moving young birds at around five to six weeks, when they are a fortnight from making their first flight, they regard the release site as home, rather than their natal nest. All young Ospreys undertake their first migration alone, and so as long as translocated Ospreys are provided fish after fledging in the way that wild-fledged birds are provisioned by their parents, they migrate as normal. Then, all being well, they return to the release site for the first time at two years of age.
As a fully piscivorous species, do Ospreys suffer from ingesting water-borne pollutants or plastic waste?
The Osprey is regarded as something of a sentinel species for environmental contaminant exposure and effects in aquatic ecosystems. It was badly affected by DDT in the United States and some parts of Europe. More recently, research in the United States has identified Polybrominated biphenyl ether (PBDE), flame retardants used in thermoplastics, textiles, polyurethane foams and electronic circuitry, as a potential emerging threat to Ospreys.
PBDEs have been shown to bioaccumulate and biomagnify up the food chain, but unlike organochlorine pesticides which have declined in aquatic ecosystems in recent decades, PBDEs have increased since the 1970s. Plastic waste is also an issue, particularly in some of the coastal areas where Ospreys overwinter. It is a sad sight to see a wintering Osprey perched on a beach surrounded by ubiquitous plastic pollution.
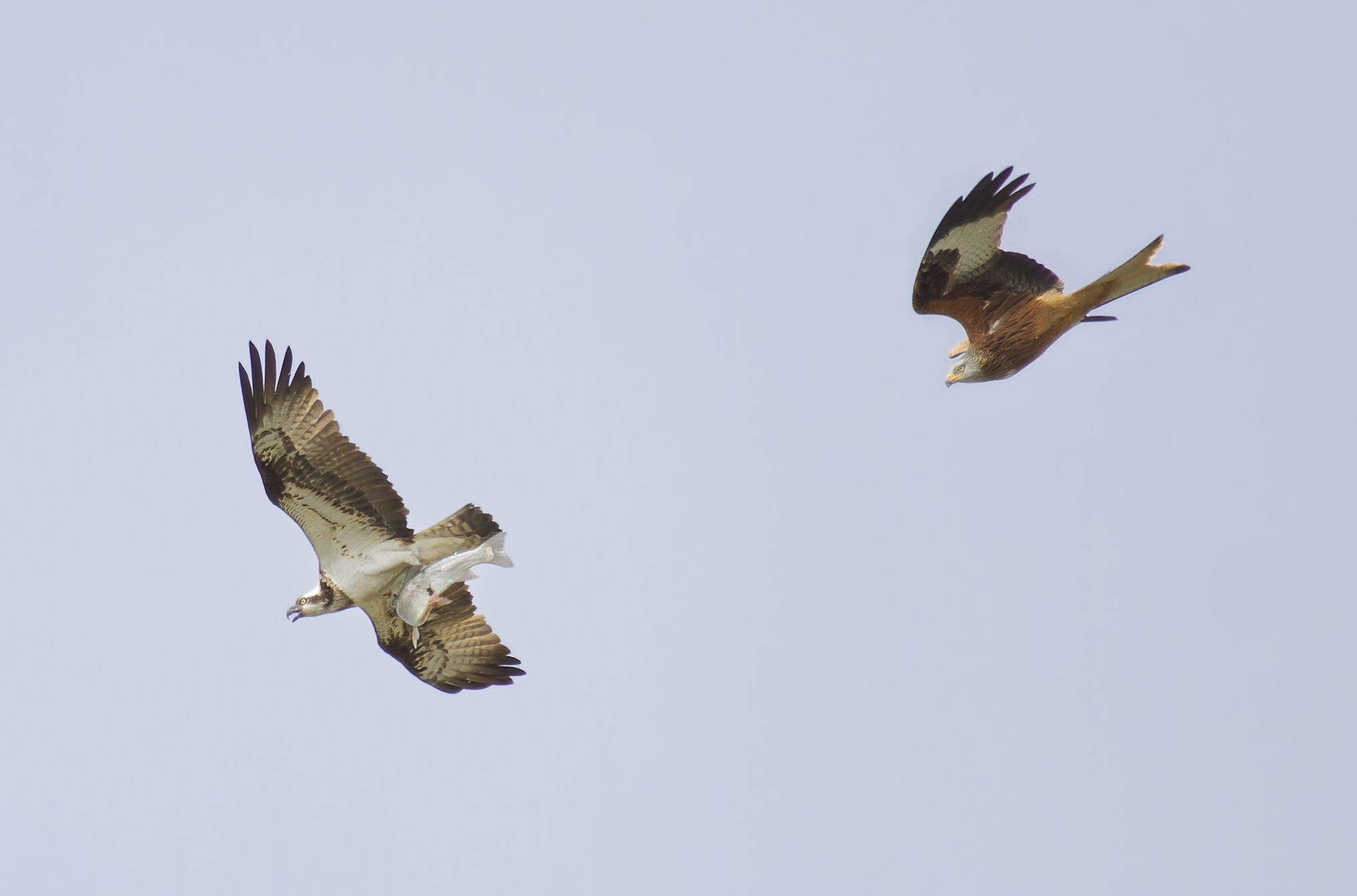

When it comes to the Osprey, where are the gaps in the knowledge? What are the things that you’re still excited to find out about them?
There are still elements of migration that we do not fully understand. We know that young birds use a process known as vector summation (an inherited programme of distance and direction) on their migration, and that adults become expert navigators as they become more experienced, but we do not know the exact mechanisms for this, though factors such as landscape features may be important. Personally, I like the fact that there is still this mystery around certain aspects of bird migration – it adds to the sense of awe that is created by the remarkable journeys of Ospreys and other species.
Finally, what’s keeping you occupied day-to-day at the moment? And do you have plans for further books?
One of the most exciting projects I am involved with at present, through my work with the Roy Dennis Wildlife Foundation, is the reintroduction of White-tailed Eagles to southern England. The first pair bred successfully last year and it has been exciting and encouraging to see how the birds are fitting into southern England. Like Ospreys, they take fish from the South Coast estuaries and so there is a wealth of suitable habitat for them. The fact that there are now breeding Ospreys and White-tailed Eagles back on the South Coast of England is very exciting and testament to what a positive, proactive approach to conservation can achieve. I love writing and so I definitely have plans for future books.
A few years ago I also set-up a charity, the Osprey Leadership Foundation (OLF), which works to inspire and enable young conservation leaders. I feel very privileged to have had Roy Dennis, who wrote the foreword for The Osprey, as a friend and mentor for many years, and I hope the work of OLF will help the next generation of conservationists to follow the lead of people like Roy to undertake bold and ambitious projects for nature recovery – we certainly need it.
The Osprey is available to order from our online bookstore.


 Mike Langman has been a full-time illustrator specialising in birds since 1992 and has published a total of 85 books
Mike Langman has been a full-time illustrator specialising in birds since 1992 and has published a total of 85 books




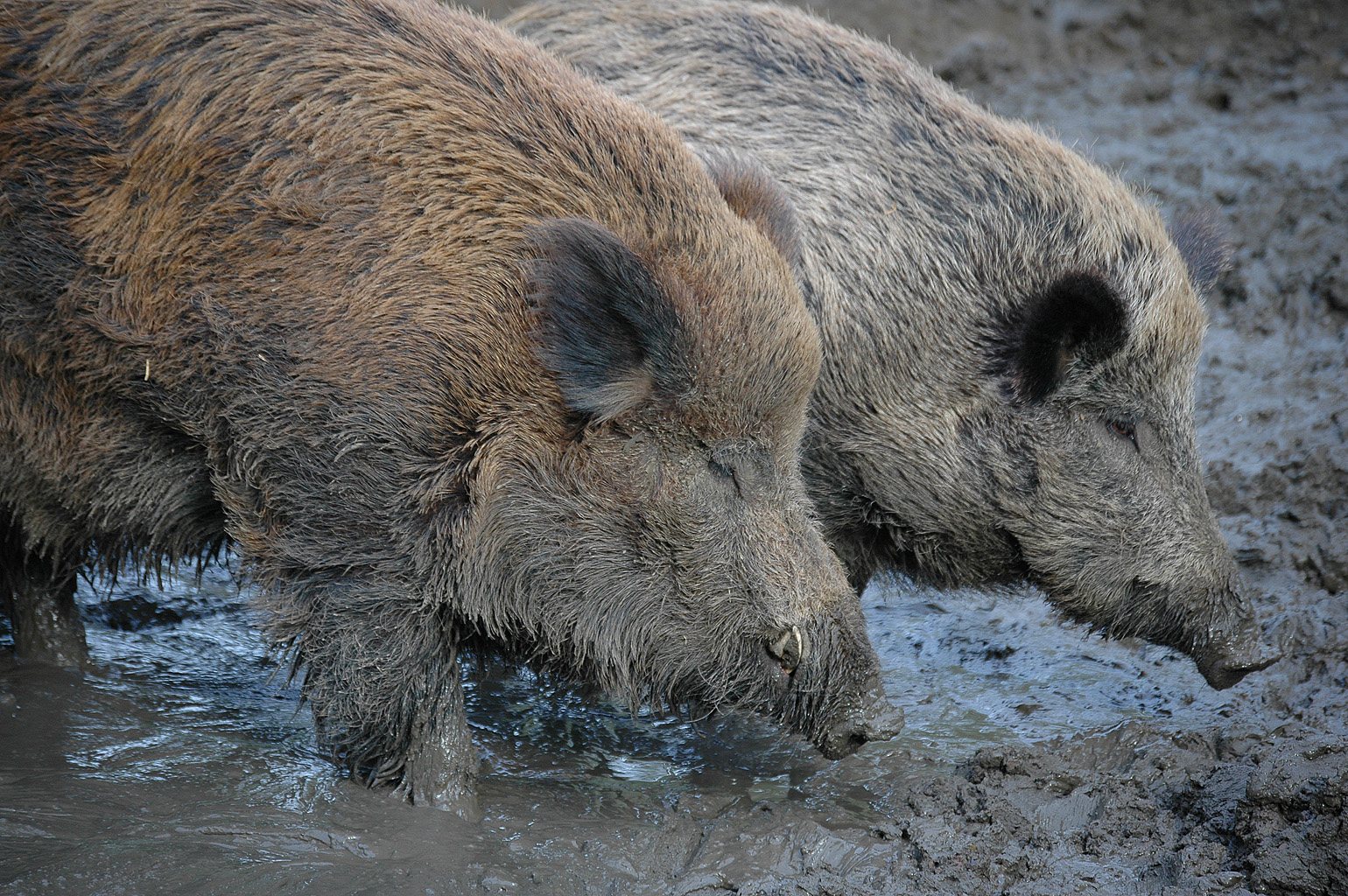
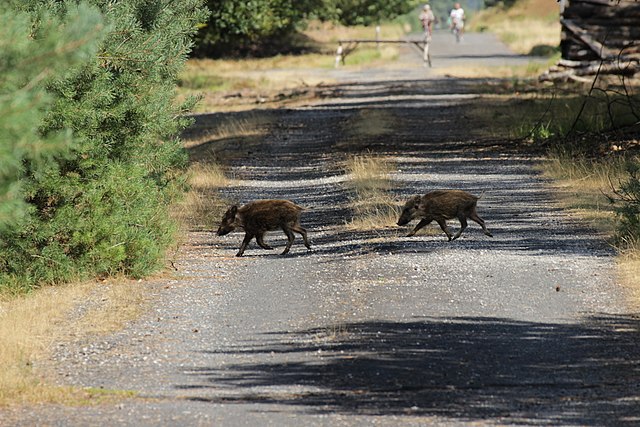
 Chantal Lyons is a naturalist, writer and science communicator. Having grown up in the tidy countryside of Kent, her encounters with the growing rewilding movement opened her eyes to the potential for restoring nature in Britain, and inspired her to study the relations between people and Wild Boar in the Forest of Dean. She currently lives in Cheltenham, never too far from the boar.
Chantal Lyons is a naturalist, writer and science communicator. Having grown up in the tidy countryside of Kent, her encounters with the growing rewilding movement opened her eyes to the potential for restoring nature in Britain, and inspired her to study the relations between people and Wild Boar in the Forest of Dean. She currently lives in Cheltenham, never too far from the boar.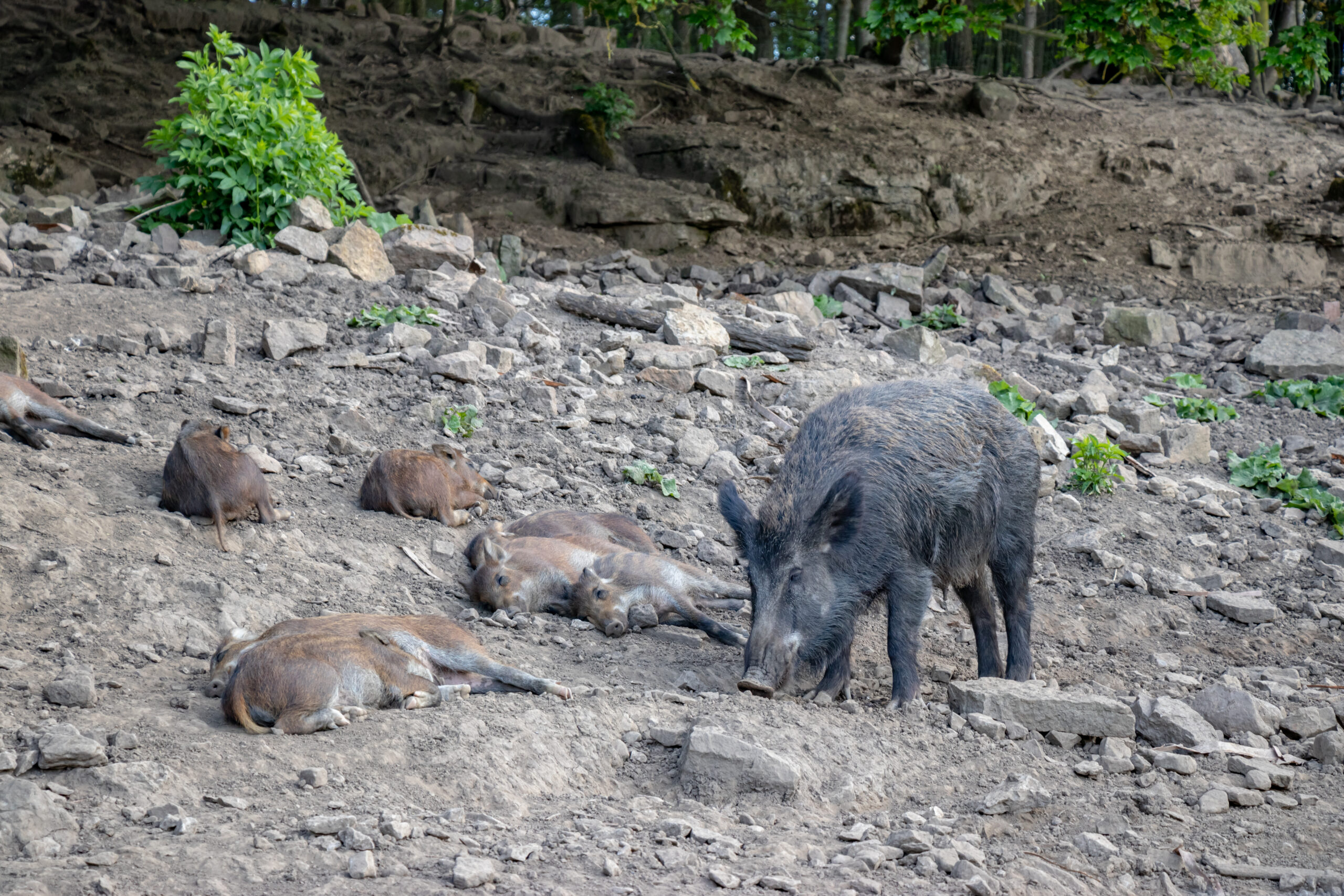




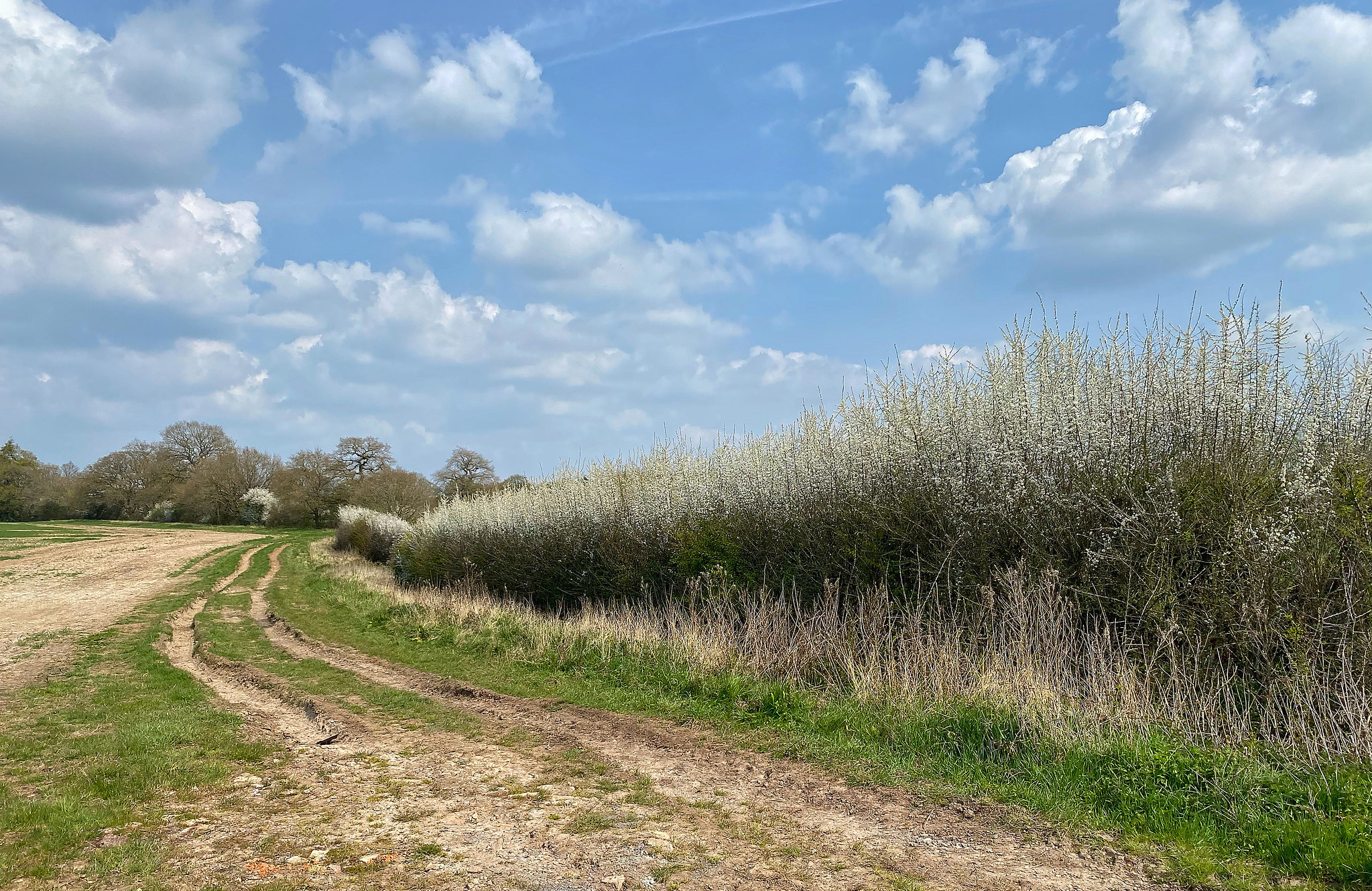
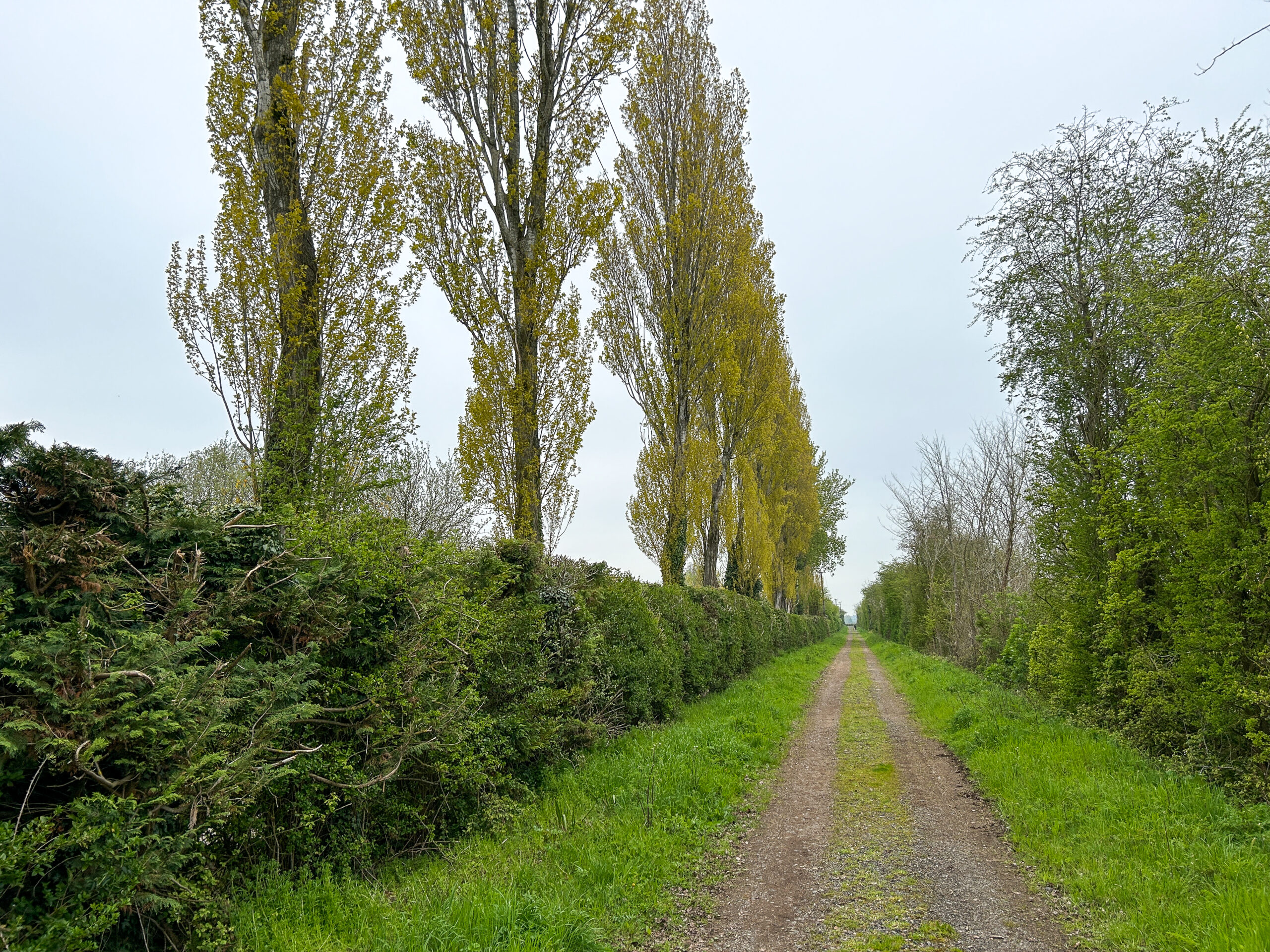
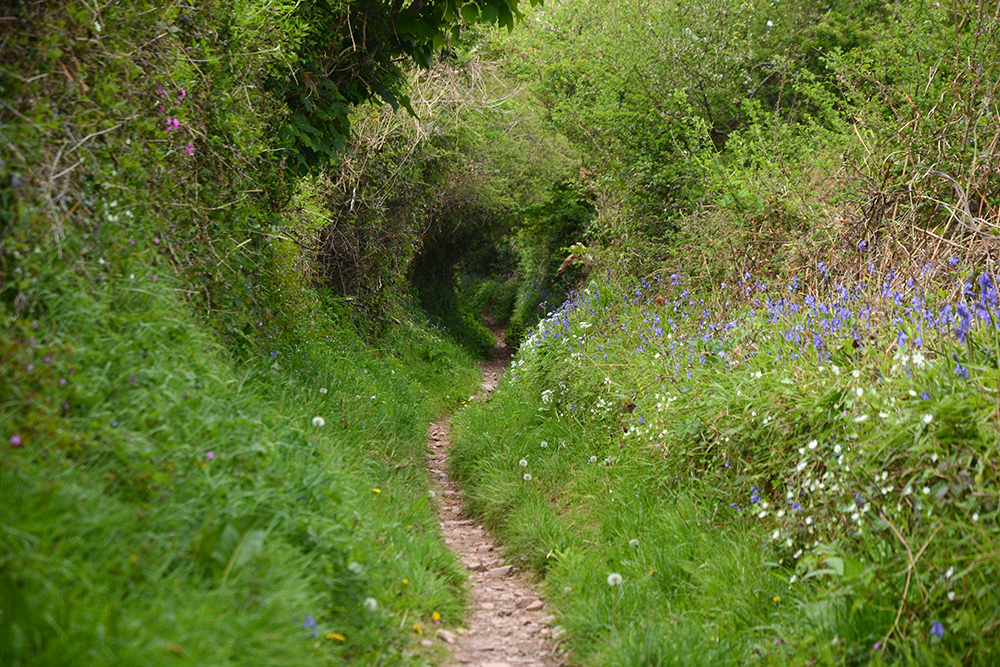
 In Hedges, Robert Wolton brings together decades of research and personal experiences from his farm in Devon to explore the ecology, biology, nature conservation and wider environmental values of the hedges in the British Isles. Containing over 300 photographs and figures, this latest addition to the British Wildlife Collection offers a detailed commentary on hedges and their importance in our landscape.
In Hedges, Robert Wolton brings together decades of research and personal experiences from his farm in Devon to explore the ecology, biology, nature conservation and wider environmental values of the hedges in the British Isles. Containing over 300 photographs and figures, this latest addition to the British Wildlife Collection offers a detailed commentary on hedges and their importance in our landscape. Robert is an ecological consultant and writer specialising in the management of farmland and associated habitats for wildlife. He is a former hedgerow specialist for Natural England, the founder, chair, editor and lead author of the Devon Hedge Group, has been involved in Hedgelink since it began, and has written a number of reports and articles specialising in hedges.
Robert is an ecological consultant and writer specialising in the management of farmland and associated habitats for wildlife. He is a former hedgerow specialist for Natural England, the founder, chair, editor and lead author of the Devon Hedge Group, has been involved in Hedgelink since it began, and has written a number of reports and articles specialising in hedges.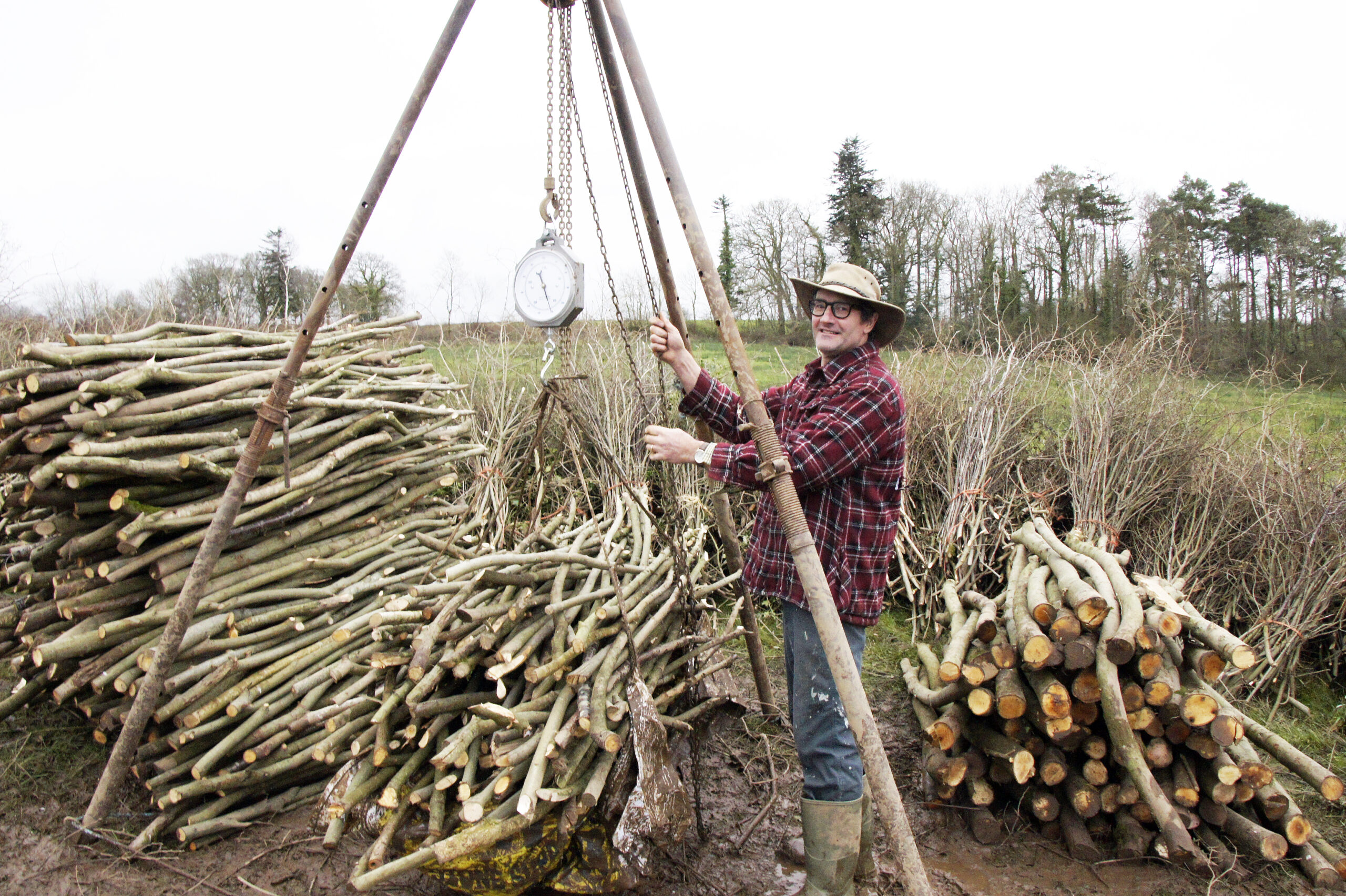










 What has stayed the same?
What has stayed the same?
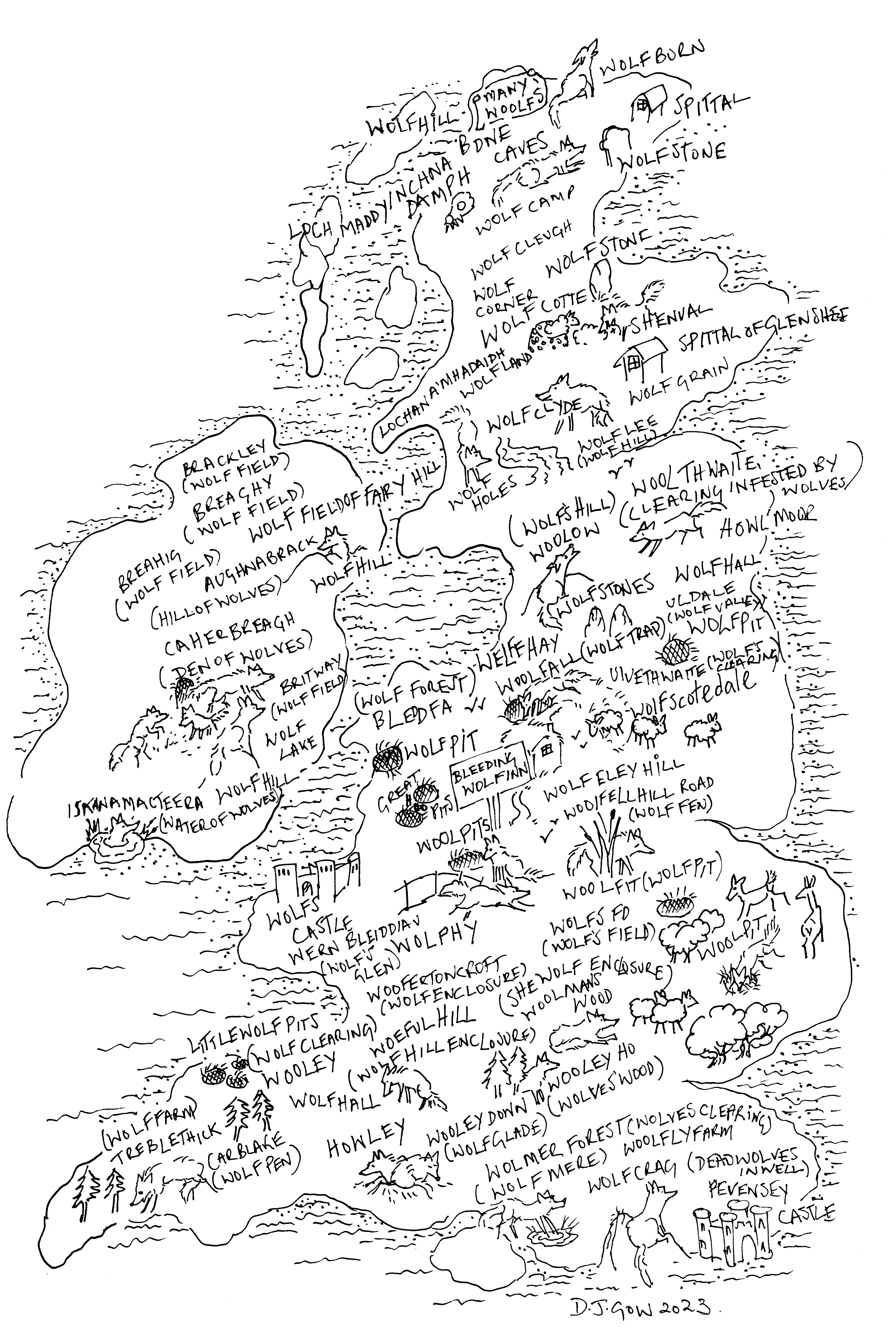
 Renowned rewilder Derek Gow has a dream: that one day we will see the return of the wolf to Britain. As Derek worked to reintroduce the beaver, he began to hear stories of the wolf. With increasing curiosity, Derek started to piece together fragments of information, stories and artefacts to reveal a shadowy creature that first walked proud through these lands and then was hunted to extinction as coexistence turned to fear, hatred and domination.
Renowned rewilder Derek Gow has a dream: that one day we will see the return of the wolf to Britain. As Derek worked to reintroduce the beaver, he began to hear stories of the wolf. With increasing curiosity, Derek started to piece together fragments of information, stories and artefacts to reveal a shadowy creature that first walked proud through these lands and then was hunted to extinction as coexistence turned to fear, hatred and domination.
 Even in children’s tales, the wolf invariably represents a character of fear, violence and threat. Do you think these types of stories have a significant role to play in the development of our feelings towards wolves as adults?
Even in children’s tales, the wolf invariably represents a character of fear, violence and threat. Do you think these types of stories have a significant role to play in the development of our feelings towards wolves as adults? 
 Finally, what is occupying your time this winter? Do you have plans for more books?
Finally, what is occupying your time this winter? Do you have plans for more books?