 Featuring 130 of the most common and readily available spider species, Pocket Guide to British Spiders is the ideal companion for both beginners and more experienced enthusiasts alike. Detailing identifying features, webs, egg cocoons and behaviour, these accounts are interspersed with beautifully illustrated spreads showing similarities and differences at a glance, making this introductory guide the perfect companion for use in the field.
Featuring 130 of the most common and readily available spider species, Pocket Guide to British Spiders is the ideal companion for both beginners and more experienced enthusiasts alike. Detailing identifying features, webs, egg cocoons and behaviour, these accounts are interspersed with beautifully illustrated spreads showing similarities and differences at a glance, making this introductory guide the perfect companion for use in the field.
 Richard Lewington is a renowned wildlife illustrator, whose beautifully detailed drawings feature in a wide array of identification guides including The Butterflies of Britain and Ireland, Field Guide to the Moths of Great Britain and Ireland, and Field Guide to the Bees of Great Britain and Ireland. In 1999, he was awarded Butterfly Conservation’s Marsh Award for the promotion of Lepidoptera conservation, as well as the Zoological Society of London’s Stamford Raffles Award for contribution to zoology in 2010.
Richard Lewington is a renowned wildlife illustrator, whose beautifully detailed drawings feature in a wide array of identification guides including The Butterflies of Britain and Ireland, Field Guide to the Moths of Great Britain and Ireland, and Field Guide to the Bees of Great Britain and Ireland. In 1999, he was awarded Butterfly Conservation’s Marsh Award for the promotion of Lepidoptera conservation, as well as the Zoological Society of London’s Stamford Raffles Award for contribution to zoology in 2010.
We recently had the opportunity to speak to Richard about his latest book, including how he first became an author, why he chose to focus on arachnids and which techniques he uses to create these stunning illustrations.
Firstly, can you tell us a little bit about yourself, and how you first became an author and illustrator?
I became a freelance wildlife illustrator soon after leaving art college in the 1970s. I’ve always had an interest in the natural world, particularly butterflies and moths, so invertebrates were the subjects I concentrated on right from the start. I’ve always worked in collaboration with various experts, until about 25 years ago, when I wrote and illustrated my first book How to Identify Butterflies. Since then, I’ve written and illustrated five books, though most of the books I work on are collaborations with authors with specialist knowledge of the subjects.
Pocket Guide to British Spiders is your 29th identification guide published since 1979. What inspired you to focus on arachnids for this book, and how did you choose which of the 680 British species to include?
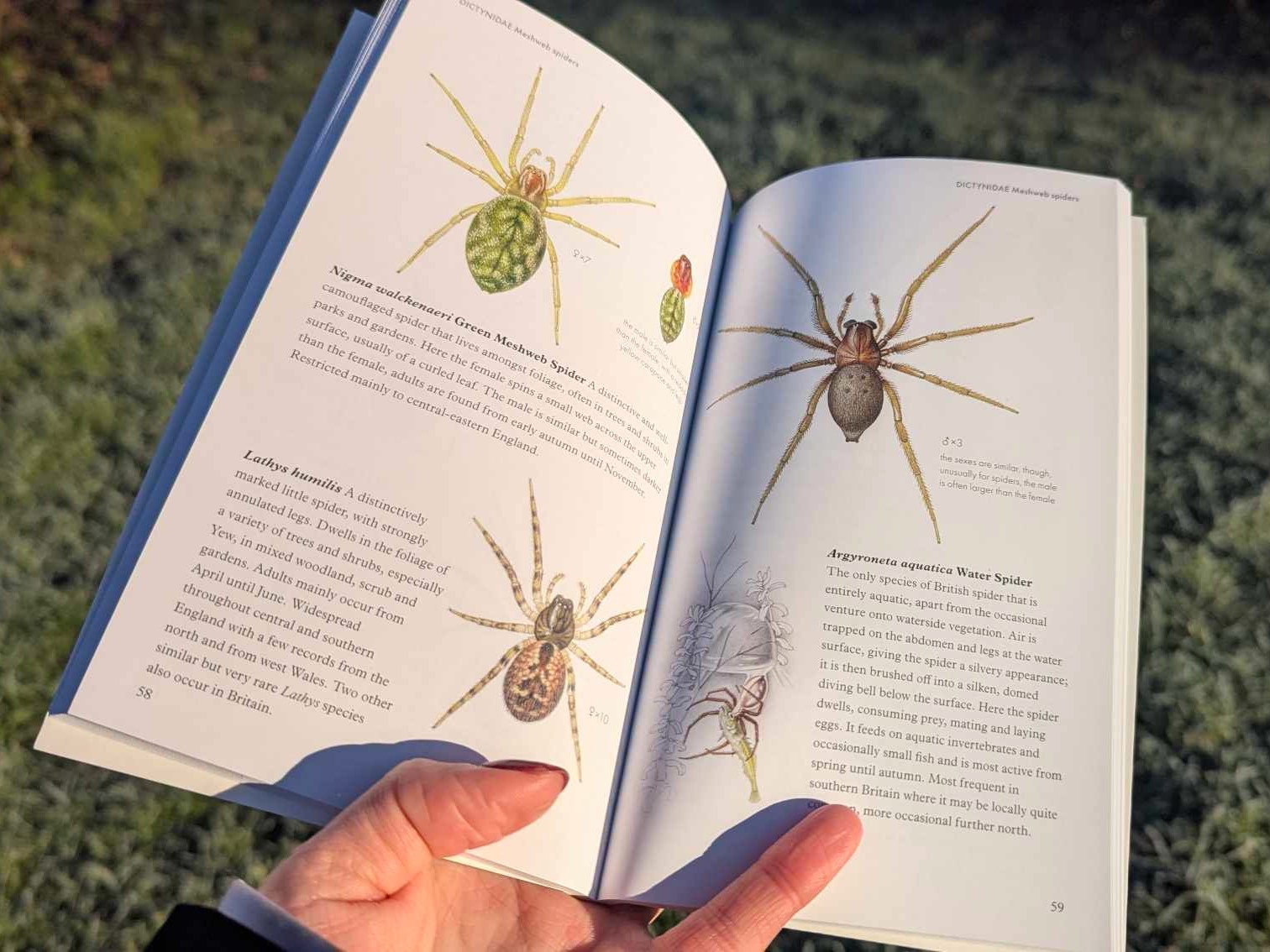
I’ve had an interest in spiders for many years and have a collection of paintings, some of which I did about 50 years ago. I thought they would form the basis of a pocket guide, and I added more illustrations in the last few years to go with those I already had. The aim was to include common, well-known and easily identifiable species – about 130 in total. As many spiders are very small and similar to each other, it is necessary to examine them through a microscope to identify many of them, which is the next step up for those who want to study them in greater detail.

I was surprised to learn about the somewhat limited conservation efforts being undertaken to protect endangered spider species across Britain. What are the largest threats to spiders, and how can we protect these vital invertebrates in the future?
As with much of the natural world, spiders are under threat from habitat loss and pollution, but because they don’t have the same appeal as some other groups, they receive less attention. However, they are just as important, helping to keep the balance in ecological systems by eating and being eaten by a vast number of other creatures. Gardens are becoming more important, and we can all help spider well-being by not being too tidy in the garden to encourage a good variety of mini habitats in which they can live.
Pocket Guide to British Spiders includes a vast amount of detail on nomenclature, structure, anatomy, mythology, identifying features and more. What was the most interesting thing you learned while researching this book?
Probably their diversity. They vary hugely in size, shape and colouring, and can be found in every habitat from mountain tops to beneath the surface of water. Many also occur throughout the year when many other invertebrates are dormant.
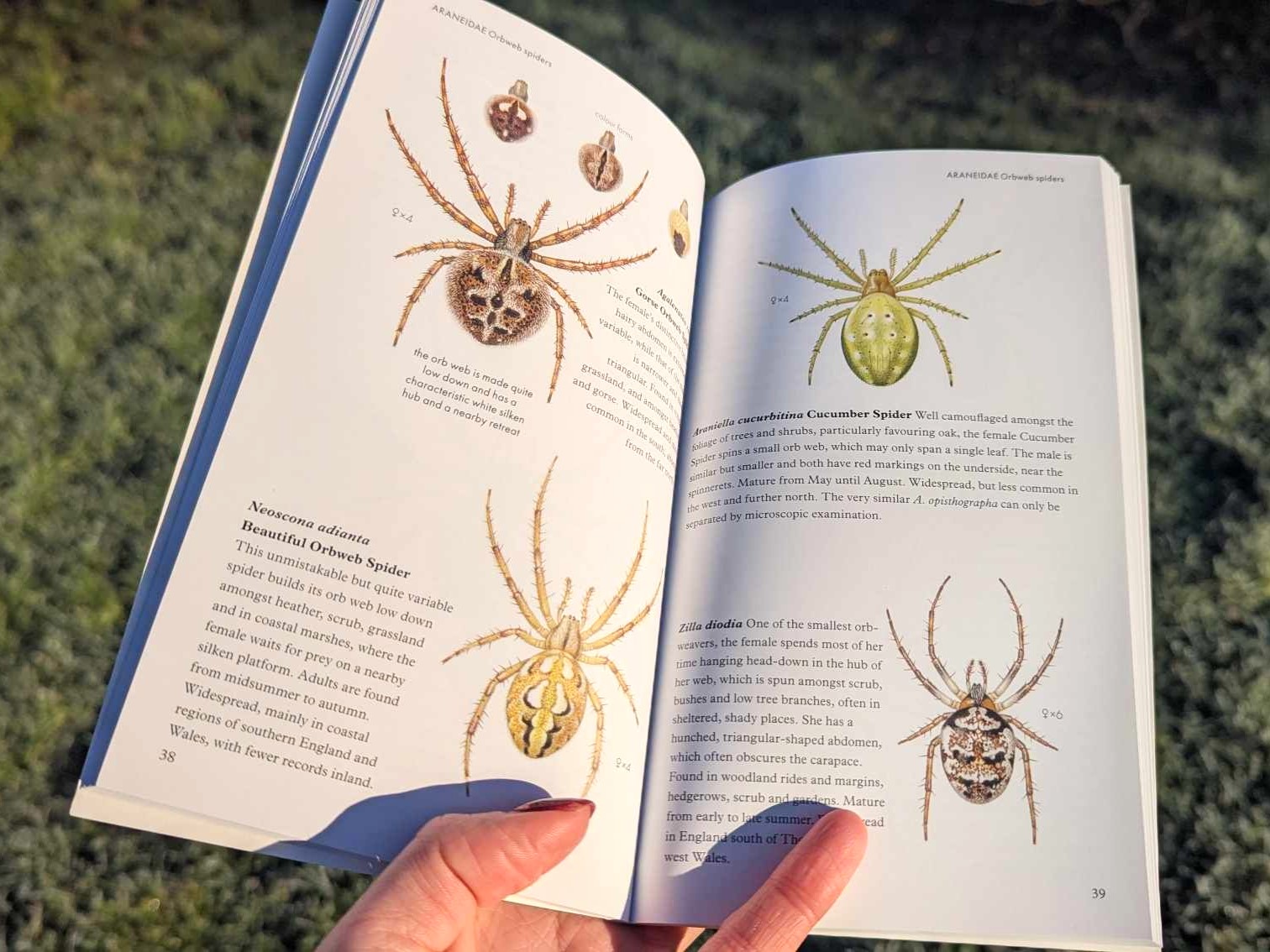
Having illustrated many guides throughout your career, can you give us an overview of the techniques you use to create such detailed works of art, and explain how your painting style has evolved over time?
I start by doing a detailed, measured drawing on layout paper. This is transferred to watercolour paper and, using Designers’ Gouache paints, I apply washes, gradually building the colour intensity and the effect of light and shadow. Details such as textures and highlights are added to give a three-dimensional appearance. More recently, I’ve been scanning the artwork before sending it to the publishers, so that I can adjust, enhance and touch-up the images using a tablet and image enhancing software.
What were the most difficult aspects of illustrating spiders, given their intricate and often microscopic features?
Spiders can’t be preserved in museum collections like butterflies and beetles, as they have soft bodies which shrivel after death, so working from live specimens or from detailed photographs are the best options. This means going into the countryside to find specimens and asking other spider enthusiasts to help. I like to take my own macro photographs from the exact angle to avoid any distortion, I can then work using the photos and the live specimen, observing it under my microscope. It’s also necessary to have a good knowledge, so that the subjects can be correctly identified, as some are very similar.
Finally, what’s taking up your time at the moment? Are you planning to write or illustrate any more books over the coming years?
My next book will be a field guide to Orthoptera, which I completed several years ago but has been long delayed. After that I shall be working on a project about my work as a wildlife illustrator, concentrating mainly on British moths, butterflies and their caterpillars.
Pocket Guide to British Spiders is available from our online bookstore.
