 The Atlas of Early Modern Wildlife is a ground-breaking volume compiling the observations of early modern amateur naturalists, travellers and local historians for the first time. Drawing on over 10,000 records, this book looks at the early modern state of wildlife in Britain and Ireland, the era before climate change, before the intensification of agriculture, before even the Industrial Revolution. The book presents maps and notes on the former distribution of 153 species, providing a new baseline against which to discuss subsequent declines and extinctions, expansions and introductions. This remarkable resource will be of great value to conservationists, archaeologists, historians and anyone with an interest in the natural heritage of Britain and Ireland.
The Atlas of Early Modern Wildlife is a ground-breaking volume compiling the observations of early modern amateur naturalists, travellers and local historians for the first time. Drawing on over 10,000 records, this book looks at the early modern state of wildlife in Britain and Ireland, the era before climate change, before the intensification of agriculture, before even the Industrial Revolution. The book presents maps and notes on the former distribution of 153 species, providing a new baseline against which to discuss subsequent declines and extinctions, expansions and introductions. This remarkable resource will be of great value to conservationists, archaeologists, historians and anyone with an interest in the natural heritage of Britain and Ireland.

Lee Raye is an associate lecturer at the Open University and a Fellow of the Linnaean Society, specialising in the history of wild animals and plants in pre-industrial Britan and Ireland. We were lucky enough to have the opportunity to speak with them about what inspired them to write this atlas, what the most difficult aspect of creating this book was, what their future plans were and much more.
What inspired you to write this atlas?
Several years ago I worked for the RSPB. I went on a weekend induction to The Lodge in Sandy, Bedfordshire, and had a walk around with the reserve archaeologist. He explained that, although it was simple enough to know which animals had declined and gone extinct in the historical period, there was a lack of clarity about how and when this happened. I realised that I already had some of the answers he needed. Around that same time, as a research project, I was translating and analysing the records of wild animals and plants from a single 17th-century natural history book, Robert Sibbald’s Scotia Illustrata (1684). That source is really valuable because it was contributed to by so many people and contains so many important records. For example, there are records of the Great Auk, the Bustard and the Angel Shark amongst the animals and Darnel, Shepherd’s Needle, and Greater Water-parsnip amongst the plants. While doing this project, I started making a list of other comparable texts from the same time period, and to my surprise I realised there was a whole understudied genre of them! I realised that if I combined all of these sources together I could give a decent estimate of the distribution of species in the 16th-18th centuries.

Do you think it’s possible for us to restore our wildlife to the condition it was in early modern Britain or has our landscape changed too drastically?
When we are doing conservation work it’s really important that we have a strong baseline to work against, otherwise we don’t know when we are restoring biodiversity and when we are just adding species to an environment. I think the early modern period is a good choice of baseline for two reasons. First, it comes before some of the most alarming declines in biodiversity which followed trends like the industrial revolution, the 20th century agricultural revolution, and the gamekeeper culls of raptors and mammalian predators of the nineteenth and early 20th century. But it was still a period when all of Britain and Ireland was managed for human needs, including some big cities. Secondly, there are a lot of sources available from the time period, so the Atlas of Early Modern Wildlife could reconstruct the fauna found at the time. But we are never going to be able to perfectly return to that baseline. The islands of Britain and Ireland are even more intensively managed and exploited now, and we need to keep that up to provide for the human population. The early modern period was also a time when there was a temporary climate change, the Little Ice Age, which meant that the so-called ‘northern species’ were doing really well, and the ‘southern species’ had a more restricted range. Modern global heating is going to become much more severe than the Little Ice Age was, and is likely to magnify the differences so that Britain and Ireland in the 21st century is going to have significant differences in its flora and fauna to the 17th century, no matter what we do.
The distribution trend for the majority of species mentioned in this book was either uncertain or unchanged, compared to 24 increases and 26 decreases. Did this surprise you?
I knew that there would be lots of uncertainty in the data from the time period, but I was a bit surprised that so few species showed a decline in distribution. We know that we are in a biodiversity crisis now, but the declines in abundance we are currently facing are going to take some time to result in declines in distribution at a regional level, which is the rather crude metric I was able to track in the Atlas of Early Modern Wildlife. It’s also true that there have been official and unofficial reintroductions in the modern period, which have restored species like Beaver, Otter and Greylag Goose across much of their early modern range, meaning that comparing early modern and present distribution hides what happened to these species in between.

You mention that there was a bias towards recording exploitable species in the early modern period and a bias towards recording birds now. Did this affect which species you were able to include in this book?
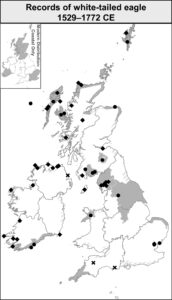
Yes, with the exception of a few species of conservation concern, I included only the best-recorded species in my Atlas of Early Modern Wildlife. That means that there is a bias towards certain groups of species. For example, I was able to map the past distribution of 18 freshwater fishes but only five small songbirds. Don’t ask me about the distribution of the Sparrow or the Great Tit in the early modern period, because my sources don’t offer much data about them!
What was the most difficult aspect of creating this book?
The most complicated part of the Atlas of Early Modern Wildlife has been trying to solve the recorder-effort problem. I needed to be able to tell when species were not recorded because they were absent (like the Wolf, which seems to have been extinct in England and Wales already by this time period), and when animals were not recorded simply because not enough effort had been put into recording them (like those Sparrows and Great Tits which no-one really cared about). My solution was to statistically compare how many records I had for each species from different regions of Britain and Ireland with a figure of how well-recorded each different region was in the early modern period. I also used some habitat suitability modelling to try and establish patterns behind absences, but this has been complicated, speculative work!
Do you have any future plans that you can tell us about?
I think I could take this project further in the future. It should be possible to map the distribution of wild plants 250-500 years ago, or to join up the distribution of Britain and Ireland’s wildlife with the distribution of wildlife in other parts of Europe from the same time period. But I also want to work a bit more on poetry from the early modern period. There are a few very strange poems written c.1580-1650 that protest environmental destruction and are told from the perspective of animals which I think deserve to be much more widely known.

The Atlas of Early Modern Wildlife by Lee Raye is due to be published by Pelagic Publishing in July 2023 and is available for pre-order from nhbs.com.

