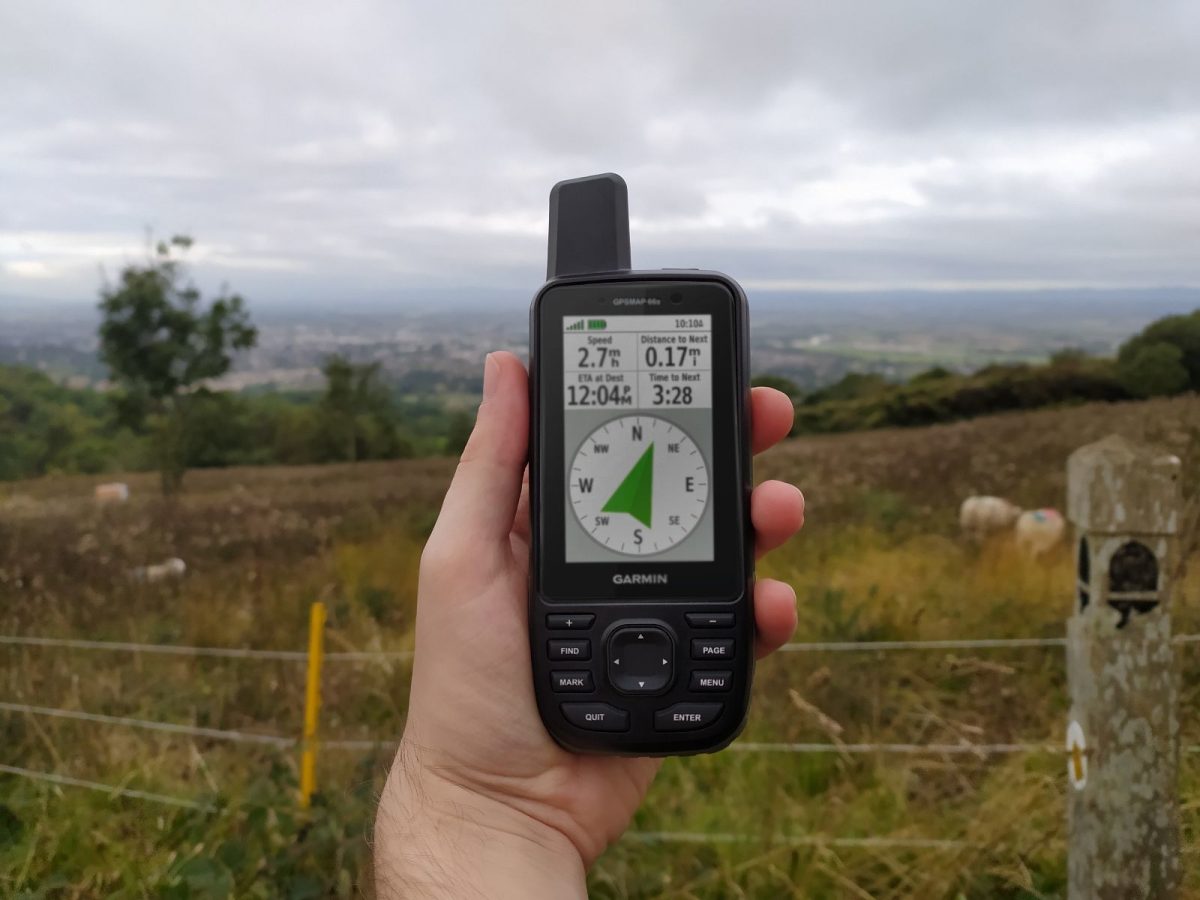
The GPSMAP 66s is one of Garmin’s most advanced handheld GPSs. Originally released in 2018, the 66s builds on the success of earlier models to provide the best tracking possible, along with a plethora of other features and improvements.
Handheld GPS devices are used by researchers and ecologists in situations where there is a need to create or follow a particular route (e.g. a transect survey) or where there is an area of interest (e.g. a bat roost) that may need to be marked for later analysis or to allow the surveyor to return to that spot in the future.
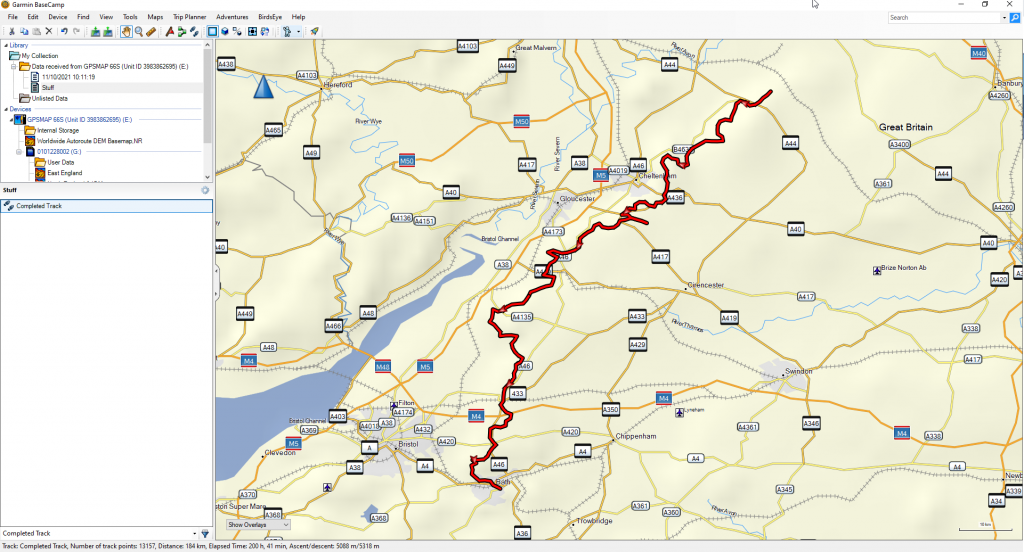
Outside of environmental monitoring and research, handheld GPSs are primarily used by walkers, hikers and cyclists looking to plot and record their routes. In late September, I tested the usability of a Garmin GPSMAP 66s by taking one with me on an eight-day walk along the Cotswolds Way – a national trail covering around 100 miles from Chipping Campden to Bath.
How we tested
Setting up the path on the GPS
One of the most important things to understand with all Garmin GPS units is the difference between a “track” and a “route”. The published literature from Garmin does not do a great job of distinguishing this, but thankfully there are a few superb YouTube videos that helped clarify the distinction between these terms and allowed me to choose the most suitable option for my purposes.
Routes: Designed to help guide you along a strict path, similar to a Satnav in your car. A route is made up of a number of waypoints (coordinates) placed typically at places where the user would have to change course or direction – this means that more complex routes require more waypoints to provide accurate navigation (hiking trails in remote areas, for instance, would most likely need more waypoints than driving in the city). When following a route, the GPS gives you on-screen advice about the direction you should be heading to reach the next waypoint and can alert you when you need to be aware of an upcoming change in direction. The two major drawbacks I found when using routes for my purpose were that the dense number of waypoints required made the screen almost unreadable and I did not need or particularly want the device directing me exactly where to go the entire time.
Tracks: Designed to show you on a map where you or someone else has been previously, like drawing a line on a map. A track is in principle far simpler than a route. The GPS inherently has a running log of your current activity, including your location which is displayed on-screen as a cyan trail across the map you have loaded. When you are done with that period of activity, you can save this data as a track if desired. When needed, you can load this track and it will display your previous path on screen as a red line, which you can then use to navigate. Tracks, however, do not provide active navigational assistance; when you have a track loaded, the GPS will not direct you to go one way or the other and it will not alert you if you deviate at all. In my case, I did not want instructive navigation and the visual clarity offered by a track when compared to an equivalent route meant this was far more appealing to use for my walk.
Once I had decided the system I was going to use, I was able to easily find a track of the Cotswolds Way online. Tracks and routes can be exported from or imported onto your GPS as GPX files. A handy tool when checking a route or track is Garmin’s BaseCamp program. This free software can be used on your computer to view routes/tracks, add in waypoints and transfer files to and from your GPS. I used BaseCamp to make sure the track I found looked suitable and I also added in a few waypoints to mark specific points along the walk, such as our accommodation and a few shops. You can customise the icon and name of these waypoints to provide the best denotation, and additionally, you can add notes to each waypoint (particularly handy for noting down the contact details of accommodation).
Using the GPS
The GPS was able to operate for approximately 25 hours on the walk before needing to replace the batteries, so for my purposes, I only had to carry one additional set of batteries to power the GPS for the whole 8 days. The GPSMAP 66s comes with a carabiner clip piece, which is easily slotted onto the device. This was very convenient as it allowed me to attach the device to the outside of my backpack, meaning I could easily check the device without having to worry about it falling out of a side pouch. I ran the GPS for the duration of each day’s walking and saved these as individual tracks, which I later combined in BaseCamp for the purposes of this article.
What we found
I found that using the GPSMAP 66s was slightly intimidating at first as there are a lot of settings and it can be easy to push the wrong button and end up on a different sub-menu. However, I put a bit of time aside before we started to allow myself to test using the device, and this was enough to help me resolve a few small issues I was having.
On the walk, I found the GPS was easy to use and very handy. Turning on in the morning and saving the track at the end of the day’s activity is fast and simple, and having the on-screen route was an incredibly handy reference in areas where the written directions were unclear, or the route signage was lacking. My unit came with the TOPO Great Britain PRO Bundle, which includes Ordnance Survey maps of all Great Britain, and this was very helpful in getting a quick detailed picture of the surrounding area. This was of great help in one instance where we needed to find a safer alternative route to our accommodation to avoid a rather unpleasant walk along the A436.
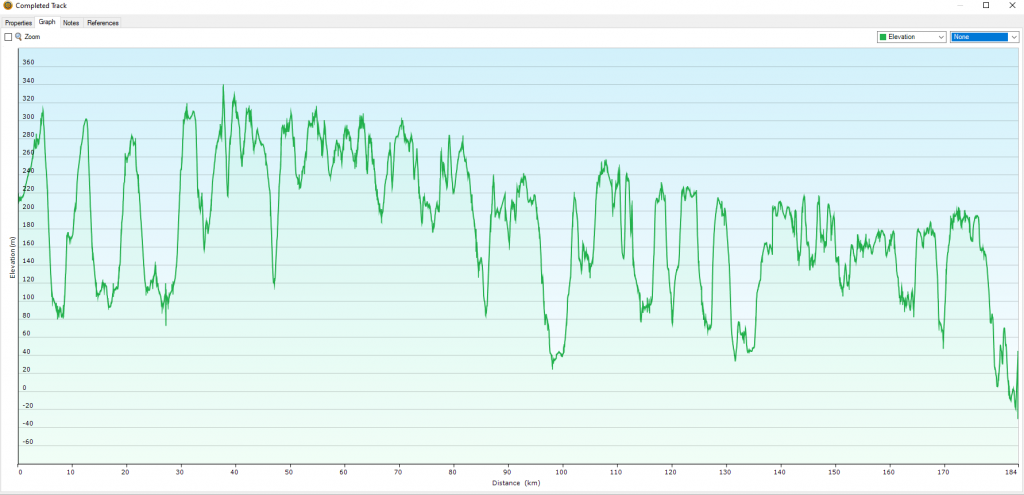
One unexpected benefit of the GPSMAP 66s was the reward of reviewing your activity at the end of the day on the GPS. The device will give you a summary of your walk including interesting data such as your average movement speed, total elapsed movement time and, thanks to its built-in barometric altimeter, your total ascent and descent (also visible as an elevation graph). Being able to see these data after a particularly exhausting day was a fantastic morale boost!
The saved individual tracks were easy to import back into BaseCamp and, once imported, I was then able to merge these to form an overall track of the entire route. This is a very nice feature as you are then able to view your entire route and you are provided summary data along with this. One slight issue was that the summary data did not initially update properly, showing just a single day’s activity rather than the complete walk. However, deleting a single point of data was sufficient to kickstart the program into correcting this issue.
Our opinion
Overall, I was pleasantly surprised by the Garmin GPSMAP 66s. It exceeded my expectations in terms of usability and usefulness. While there is certainly a slight intimidation factor involved when first using the device, it does not take long for those fears to dissipate and in a short space of time, it can become an incredibly helpful tool for navigating and recording.
Based on my experiences, I would suggest that the GPSMAP 66s would be suitable for ecological work in open spaces where there is a need to recording transect routes or coordinates. However, care should be taken when using the GPS to mark precise coordinates as the unit is only accurate to around 2 to 5 meters in good conditions and features such as tall buildings, steep valleys, harsh weather and dense tree cover can reduce this accuracy.
I would recommend the TOPO Pro Bundle option as the more detailed OS maps are a massive step up from the basic maps that come with all Garmin GPS devices.
The GPSMAP 66s can be found here. Our full range of handheld GPS devices can be found here.
If you have any questions about our range or would like some advice on the right product for you then please contact us via email at customer.services@nhbs.com or phone on 01803 865913.


