 Standing a metre tall, with a wingspan approaching three metres, the Steller’s Sea Eagle is a magnificent and impressive bird.
Standing a metre tall, with a wingspan approaching three metres, the Steller’s Sea Eagle is a magnificent and impressive bird.
Published in November, Richard Sale’s new book is the first English-language study of this bird of prey. A translation of an earlier Russian book written by Masterov and Romanov, the English version benefits from significant updates and a wealth of new photographs.
We recently chatted with Richard about the Steller’s Sea Eagle, his passion for birds and his love of the Arctic.
![]()
In your author biography you are described as a physicist with a PhD in astrophysics. Is physics still a part of your life or do you now devote all of your time to your writing and natural history studies?
Physics will always be a part of my life. I started out as a working physicist, at first as a glaciologist in Switzerland because they paid me to stay in the mountains where I could climb on my days off. Then I moved back to the UK to work. After a few years I left full-time employment and started a consultancy which allowed me to share physics with my love of birds and of snow and ice.
 You obviously have a huge passion for birds, and you also spend much of your time studying Arctic ecology. Where did these twin passions come from?
You obviously have a huge passion for birds, and you also spend much of your time studying Arctic ecology. Where did these twin passions come from?
The love of birds started with my father who was a birdwatcher. Our holidays were geared around the breeding season and we went to the moors rather than the beach. He taught me to really watch birds, not just to be able to name them but to able to understand their habits. My other love as a kid was climbing; at first rock faces, then mountains. The love of snow and ice and birds led naturally to wanting to visit the Arctic. After the first trip I really didn’t want to go anywhere else, especially as I am no lover of hot weather.
 How did the collaboration for Steller’s Sea Eagle come about? Were you approached to work on the English version of the book or is it something that you yourself instigated?
How did the collaboration for Steller’s Sea Eagle come about? Were you approached to work on the English version of the book or is it something that you yourself instigated?
I had visited Kamchatka in summer and winter and been in the field with Yevgeni Lobkov, one the experts on Kamchatka’s Steller’s. I subsequently went to Hokkaido several times to see the eagles on the sea ice. Then I found the Russian book and corresponded with Michael Romanov. That led to the idea of translating it into English, so I obtained the English rights from the Russian publisher. At first the idea was just to translate the Russian book, but by questioning Michael and Vladimir about sections of text, and then suggesting that we include my work on flight characteristics, the two of them suggested I should be co-author as the book was now looking substantially different from the original.
 Can you describe your first sighting of a Steller’s Sea Eagle? How did it make you feel?
Can you describe your first sighting of a Steller’s Sea Eagle? How did it make you feel?
I mentioned Yevgeni Lobkov above. He and I took a trip along the Zupanova River in a Zodiac and I remember the first time a Steller’s came over us. It was low down and seemed to blot out the light because of its size. No one who sees a Steller’s can avoid being impressed and I was immediately enraptured.
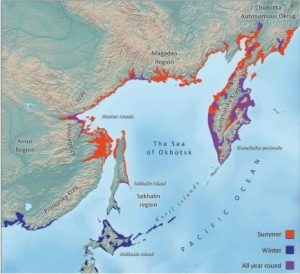 I was intrigued to read that you have worked with a captive Steller’s Sea Eagle here in the UK. Can you tell us more about this experience?
I was intrigued to read that you have worked with a captive Steller’s Sea Eagle here in the UK. Can you tell us more about this experience?
Once in the Arctic, on Bylot Island, I was watching a Gyrfalcon hunting Arctic Ground Squirrels and because of the terrain, a narrow valley, I could see the falcon was not stooping in a straight line. That led to investigating the physiology of falcon eyes, and to designing a small unit with gps, tri-axial accelerometers, magnetometers and gyros (and other bits) to fly on falconry birds to study how they fly. I managed to get the weight down to a few grams – though that hardly mattered when I found someone flying a captive Steller’s in England as it weighed 5kg. It was flying the units on that bird that is in the new book. Atlas, the eagle, was flown in demonstrations for the public and allowed me to investigate wing beat frequencies, speed etc. It was great fun as he was such a docile bird, a real gentle giant, and being allowed to get so close to him was marvellous.
 It seems that two of the main pressures on the Steller’s Sea Eagle are fossil fuel exploration from humans and predation from brown bears. Are there currently any population estimates for the species, and are you hopeful for their future survival?
It seems that two of the main pressures on the Steller’s Sea Eagle are fossil fuel exploration from humans and predation from brown bears. Are there currently any population estimates for the species, and are you hopeful for their future survival?
The situation is not good. The company drilling for oil and gas have been helpful in taking enormous care over onshore works near breeding sites and are to be commended for that. But the fact is that, as human activities of all sorts have expanded close to Steller’s habitats (most of which are well away from the oil/gas exploration sites), the population has gone into decline. We can overcome bear predation by fitting anti-bear devices to trees. We can erect artificial nest and roost sites. But despite all of this, at the moment the population numbers are slowly coming down, probably as a result of global warming, though we are not yet definite about that. Hopefully the population will stabilise but only time will tell if our efforts have been sufficient.
 Within a given year, how much time do you spend travelling and how much writing? Do you enjoy each part of the process equally?
Within a given year, how much time do you spend travelling and how much writing? Do you enjoy each part of the process equally?
Age is catching up with me now and so I spend less time in the Arctic than I did (when I could be there for many weeks during the breeding season). But I still get into the field regularly – particularly at the moment with my units flying on falconry birds and with studies on Merlins in Iceland, Scotland and Hobbies in England and Wales. But I also spend a lot of time in the library reading about birds and, sadly, the damage we are causing them through industrialisation and climate change. As everyone knows, there is hardly any money to be made nowadays as a writer of books on natural history and related topics, but I also enjoy the process of writing and preparing books for publication.
 Another of your books, The Arctic, is due for publication in December. What’s next for you? Do you have another project in the pipeline?
Another of your books, The Arctic, is due for publication in December. What’s next for you? Do you have another project in the pipeline?
That book is an updated, but shortened, version of one I produced some years ago with new photographs by myself and a Norwegian photographer I bumped into one winter out on the sea ice of Svalbard. We have made several journeys together since and stay in close touch as we share a love of the Arctic. The next will likely be an updated and expanded version of the one I produced on the Merlin. Merlins are my favourite raptor. Falcons are, in general, warm-weather birds. The exceptions are the Gyrfalcons, which are the largest falcons, the Peregrine (which lives more or less everywhere) and is also large, and the tiny Merlin. I am as entranced by these little birds making a living in the harshest climates as I am by the huge Steller’s.
![]()

Richard Sale is a physicist with a PhD in astrophysics, who now devotes his time to studying Arctic ecology and the flight dynamics of raptors. With Eugene Potapov he co-authored The Gyrfalcon monograph which won the US Wildlife Society Book of the Year in 2006. His other books include The Snowy Owl, Wildlife of the Arctic and the New Naturalist title Falcons.
Browse all ornithology and Arctic ecology books by Richard Sale.
 Steller’s Sea Eagle: The first English-language study of this bird of prey, is published in November.
Steller’s Sea Eagle: The first English-language study of this bird of prey, is published in November.
Hardback | Nov 2018 | ISBN-13: 9780957173231
£39.99
 The Arctic: A condensed and updated edition of an earlier work with new photographs, is published in December.
The Arctic: A condensed and updated edition of an earlier work with new photographs, is published in December.
Paperback | Dec 2018 | ISBN-13: 9781849953429
£24.99
Please note that all prices are correct at the time of posting and are subject to change at any time.





