Many of us delight at butterflies visiting the flowers in our gardens, be it the drunken admirals of autumn or the spritely orange-tips in spring, yet some of us still seem to shudder at the thought of dingy moths bothering our windows at night or worse still munching our clothes to dust in our cupboards. In the middle of June, armed with two moth traps and a couple of trusted field guides, I attended an open garden in Somerset ready to join the #Mothsmatter conversation initiated by Butterfly Conservation to dispel the moth myths and encourage a fascination for these insects.

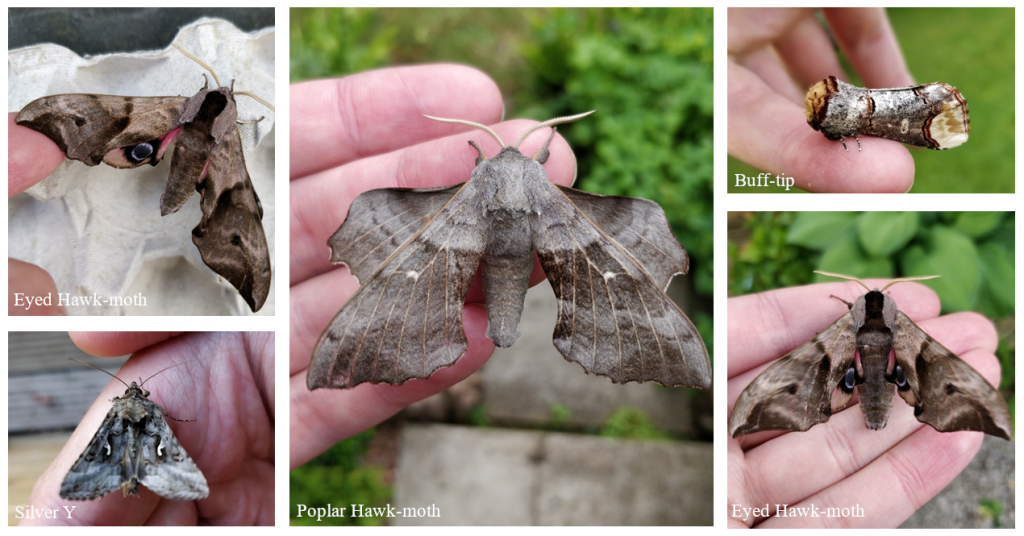
Setting up a Skinner moth trap in a covered porch over a couple of cold nights, I wasn’t entirely sure what species would be flying, but sure enough in the morning as I lifted the lid and slid the egg boxes out, there were some delightful species to see. Visitors in the garden were suffice to say, in awe of the moths the light brought in; the Poplar Hawk-moth and the Eyed Hawk- moth, the Fox Moth with his rabbit ear antennae and the remarkable Buff-tip.

We are becoming well aware that UK moths are in decline with an overall decrease in numbers by 28% since 1968, and over 60 species becoming extinct in the 20th century. Moths are a key indicator of environmental health and, as vital as they are to other creatures as a food source (their declines are impacting on breeding birds and bats) they are also vital for the pollination of native flora, an essential element to the tapestry of wild life. There is also evidence to suggest that climate change is shifting the habitable ranges of many of the moths that call the UK home, and while this can produce some spectacular species visiting from continental Europe, many of the species that have relied on the temperate climate in the UK are being forced out northward.
With a recent trend in wildlife gardening and more strict rules on chemicals used in agriculture, there is hope however that we can retain and rebuild some of the moth populations that are so vital in our countryside. Butterfly Conservation have a wealth of information available on their website about the trends of moth populations and, very importantly, what you can do to take action, join the conversation and promote moths at https://butterfly-conservation.org/moths/why-moths-matter
If you are interested in learning about which moth species are visiting your garden or local wild places, light trapping is simple and loads of fun. At NHBS we supply a range of moth traps suited for a number of habitats and a wide selection of amazing field guides to aid in identifying the moths you find. Below we have listed some of our favourite traps and provided a little more information on the differences between them, however if you wish to see our full selection of moth traps please visit our website.
Robinson Moth Traps
These large traps are renowned among lepidopterists because they offer the highest attraction and retention rates available. These traps are fitted with either mercury vapour or actinic electrics. Mercury vapour bulbs offer greater brightness than actinic bulbs and consequently they will often attract more moths. However actinic electrics may be favourable in areas where the brighter bulbs may cause disturbance; they also run cold and do not need to be shielded from rain, unlike mercury bulbs which are likely to shatter when used without a rain guard.
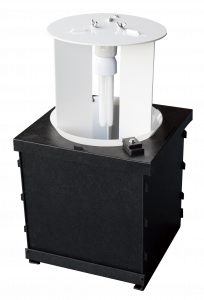
Skinner Moth Traps
These traps are precursors to the Robinson, and as well as being a more economic choice, they allow the catch to be accessed while the trap is running. They feature a plastic or wooden box with a light fitted to a cross member above a long slit through which moths fall and become trapped. A highlight of this box are the transparent panels that make up the trap lid. These can be removed to access the catch while the trap is running, which is great for real-time surveys and demonstrations. These traps can be easily collapsed down for easy storage and transport.
Compact 20W Skinner Moth Trap (240V)
* Price: £179.00 inc VAT
* Dimensions: 32 (h) x 35 (w) x 35 (d) cm
* Weight: 3kg
* Electrics: 240V mains electric
* Alternative battery-operated units also available.
Heath Moth Traps
These traps are favoured for their lower cost and compact design which makes them highly portable (excellent for use in remote areas) and easy to store; some are even small enough to fit into a rucksack. They are usually battery powered and feature a low wattage light source of between 6 and 20 Watts (however some mains operated traps can reach 40 Watts), and consequently these traps have lower catch sizes and retention rates than Skinner or Robinson models.
Compact 20W Actinic Heath Moth Trap (240V)
* Price: £149.00 inc VAT
* Dimensions: 47 (h) x 25 (w) x 25 (d) cm
* Weight: 3kg
* Electrics: 240V mains electric
* Also available as a battery-operated unit.
Suggested books on Moths
Field Guide to the Moths of Great Britain and Ireland
Paperback | Nov 2018| £27.99 £34.99
A comprehensive guide with full colour illustrations and up-to-date information on the taxonomy, ecology and distributions of the UK’s macro-moths.

Concise Guide to the Moths of Great Britain and Ireland
Paperback | Oct 2018| £13.99 £16.99
This compact guide features full colour illustrations and concise descriptions for almost all British and Irish species of macro-moths
 Emperors, Admirals & Chimney Sweepers | The Weird and Wonderful Names of Butterflies and Moths
Emperors, Admirals & Chimney Sweepers | The Weird and Wonderful Names of Butterflies and Moths
Hardback | May 2019| £24.99 £29.99
A beautifully written book that seeks to explore the origins and meanings of the names of our butterflies and moths.
 The Moth Snowstorm | Nature and Joy
The Moth Snowstorm | Nature and Joy
Paperback | Apr 2016| £9.99
Drawing on a wealth of memorable experiences from a lifetime of watching and thinking about wildlife and natural landscapes Michael McCarthy presents a new way of looking at the world around us.
Please note that prices stated in this blog post are correct at the time of publishing and are subject to change at any time.